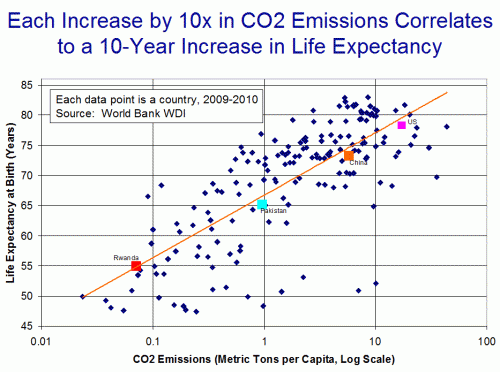
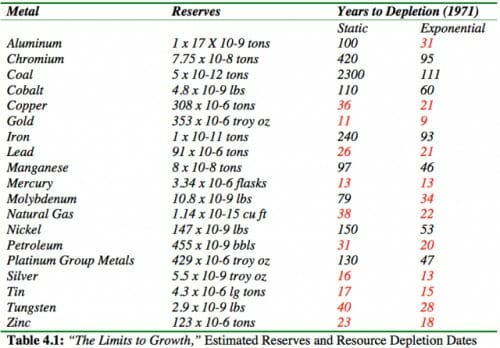
I am always amazed that the media will credulously run stories against "corporate welfare" for oil companies (which usually mostly includes things like LIFO accounting and investment tax credits that are not oil industry specific) but then beg and plead for us taxpayers to subsidize movie producers.
I wish I understood the reason for the proliferation of government subsidies for film production. Is it as simple as politicians wanting to hobnob with Hollywood types? Our local papers often go into full sales mode for sports team subsidies, but that is understandable from a bottom-line perspective -- sports are about the only thing that sells dead-tree papers any more, and so more local sports has a direct benefit on local newspapers. Is it the same reasoning for proposed subsidies for Hollywood moguls?
Whatever the reason, our local paper made yet another pitch for throwing tax dollars at movie producers
Notwithstanding a recent flurry of Super Bowl-related documentaries and commercials that got 2015 off to a good start, Arizona appears to be falling behind in a competitive and lucrative business. The entertainment industry pays well, supports considerable indirect employment and offers the chance for cities and states to shine on a global stage.
Seriously? I am sure setting up the craft table pays better than catering a party at my home, but it is a job that lasts 2 months and is then gone. Ditto everything else on the production. And I am sick of the "shines on the world stage thing." Who cares? And is this really even true? The movie Chicago was filmed in Toronto -- did everyone who watched Chicago suddenly want to go to Toronto? The TV animated series Archer gets a big subsidy from the state of Georgia. Have they even mentioned Georgia in the series? Given the tone of the show, would they even want to be mentioned?
When government subsidizes an industry, it is explicitly saying that resources are better and more productively invested in the subsidized industry than in other industries in which the money would have been spent in a free market. Does the author really have evidence that the money I would have spent to improve the campgrounds we operate in Arizona is better taken from me and spent to get a Hollywood movie shot here instead? Which investment will still be here 6 months from now?
Arizona is one of 11 states that don't offer tax incentives, primarily in the form of income-tax credits, and that's the core of the problem. There's also no state film office to help out-of-state crews obtain filming permits, locate vendors, hire temporary staff and so on.
Arizona's tax incentives expired after 2010 and the film office closed in the wake of a recession that hit the state especially hard and necessitated tough spending choices. Although bills to revive those programs have been introduced, they're not given high odds of success in the current session as the governor and lawmakers struggle to close $1.5 billion in deficits over this year and next.
"Right now, there's nobody to call, the phone isn't being answered and nobody responds to e-mails," said Mike Kucharo, a local producer and director who serves as the state-government liaison for the Arizona Production Association, an entertainment trade and networking group. "We need a film office."
Yeah for us! While all the lemmings in other states bid up the price of a few politicians being able to get their picture with Hollywood types on a production set, we have chosen not to play. Good for us. Only an industry insider clown with a straight face could say that we need a taxpayer-funded film office. Really? Do we need a taxpayer-funded florist office to attract flower sales?
Years ago I wrote an article calling sports team subsidies a prisoners dilemma game, where the only winning move was not to play. The NFL has 32 teams, mostly in the largest cities. Without subsidies the NFL would have ... 32 teams, mostly in the largest cities, and taxpayers would have saved billions of dollars. The same is true for film:
Indeed, the number and size of incentives escalated from just two states offering $2 million in combined incentives in 2003 to 40 states offering $1.2 billion just six years later, according to the Tax Foundation.
So subsidies have gone up by over a billion dollars a year, and yet roughly the same films are being made. This is one of the best examples I can think of where politicians are using taxpayer money to increase their personal prestige. The AZ Republic should be embarrassed they are out front actively encouraging this behavior.
Postscript: For all of its flaws in teaching real-world relevant business topics, the Harvard Business School was very good, at least when I was attending it, at teaching business strategy. My memory may be fuzzy here, but I am pretty sure that "40 other groups have all jumped into this activity and have ramped up their spending by a factor of 50 in just six years and all 40 competitors are really focused on winning almost irregardless of the price they pay" is not a very good pitch for investing money in a new field.
Postscript #2: All of this is a wonton violation of the AZ state Constitution, though of course big government advocates are really good at totally ignoring Constitutional limits on government power. Here is what our Constitution says:
Section 7. Neither the state, nor any county, city, town, municipality, or other subdivision of the state shall ever give or loan its credit in the aid of, or make any donation or grant, by subsidy or otherwise, to any individual, association, or corporation, or become a subscriber to, or a shareholder in, any company or corporation, or become a joint owner with any person, company, or corporation, except as to such ownerships as may accrue to the state by operation or provision of law or as authorized by law solely for investment of the monies in the various funds of the state.
Update: From the Manhattan Institute, film tax breaks return 30 cents for every dollar spent
Similar to most targeted tax breaks, movie production incentives routinely fail to deliver on the economic promises made by their proponents. Supporters frequently claim movie incentives create jobs and lead to net gains in tax revenue. However, data from several states find movie production incentives generate less than 30 cents for every lost dollar in tax revenue.
Providing tax breaks specifically to the film industry is an example of government working to choose winners and losers in the marketplace. States could attract almost any industry if they paid for a quarter to a third of its expenditures, but such a policy would be fiscally unsustainable. A better system would be to lower state tax rates for everyone, encouraging economic growth.
Film is a particularly poor industry to subsidize because it does not create long-term employment and other lasting economic benefits for states. Even though a well-made film might boost tourism, productions only offer short-term employment and the workers are highly specialized. Production and workers can easily move from one location to wherever better deals are offered.
Update #2: The AZ Free Enterprise Club was on this last month
 working to slip a biofuel mandate that would add $150 million to New Yorkers’ heat expenses into the state budget just as a company he owns completes construction of the largest biofuel plant in the region.
working to slip a biofuel mandate that would add $150 million to New Yorkers’ heat expenses into the state budget just as a company he owns completes construction of the largest biofuel plant in the region.