People Who Express Opinions Outside of their Domain Seldom Have Really Looked into it Much
My family often jokes about my obsessive behavior vis a vis Tesla and Elon Musk (on the off chance you are unaware of my thoughts, the most recent are here). My daughter texted me last night that "Wealthy millennials seem to love Elon." And that is true. My answer to her is the title of this post, "People who express opinions outside of their domain seldom have really looked into it much."
Of course, I am not in any way arguing for some sort of strong credentialism wherein people should not express opinions outside of their domain. God forbid, I would have to shut down this blog. But I am saying that just because someone is really smart and successful at A does not necessarily mean their opinion on B is worth squat. As always, as a consumer of opinions, caveat emptor should always be the watchwords.
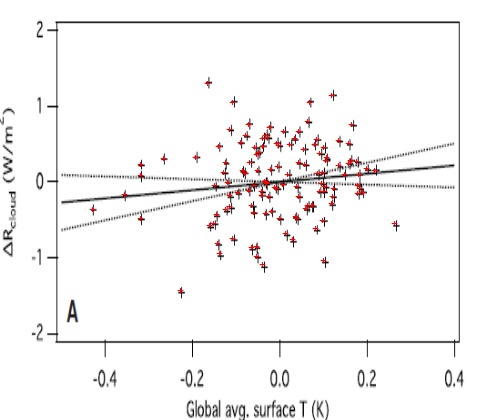
The first time I really encountered this phenomenon (outside of obvious examples such as the political and economic opinions of Hollywood celebrities) was related to climate change. I don't see them as often today, but for a while it used to be very common for letters to circulate in support of climate change science signed by hundreds or thousands of scientists.
The list of signatures was always impressive, but when you looked into it, there was a problem: few if any of the folks who signed had spent any time really looking at the details of climate science -- they were busy happily studying subatomic particles or looking for dark energy in space. It turned out most of them had fallen for the climate alarmist marketing ploy that opposition to catastrophic man-made global warming theory was by people who were anti-science. And thus by signing the letter they weren't saying they had looked into it all and confirmed the science looked good to them, they were merely saying they supported science.
When some of them looked into the details of climate science later, they were appalled. Many have reached the same general conclusions that I have, that CO2 is certainly causing some warming but the magnitude of that warming or in particular the magnitude and direction of its knock on effects like floods or droughts or tornadoes, is far from settled science.
So it is often the case that people who show strong support for ideas or people outside of their domain do so for reasons other than having made use of their expertise and experience to take a deep dive into the issues. Theranos is a great example from the business world. Elizabeth Holmes convinced a bunch of men (and they were mostly all men -- women seemed to have more immunity to her BS) who were extraordinarily successful in their own domains (George Schultz, the Murdochs, Henry Kissinger, Larry Ellison) to become passionate believers in her vision. Which is fine, it was a lovely vision. But they spent zero time testing whether she could really do it, and worse, refused to countenance any reality checks about problems Theranos was facing because Holmes convinced them that critics were just bad-intentioned people representing nefarious interests who wanted her vision to fail.
Which now brings us to Tesla and Elon Musk. I used to love Elon like everyone else. I still think that having four or five billionaires in a space race against each other is finally the world I thought I was going to get growing up reading Heinlein. The Tesla Model S was probably one of the most revolutionary cars of the last 50 years. But he lost me when he committed outright fraud in the Solar City - Tesla deal and since then have only become more skeptical about he and Tesla.
I sort of laugh when folks tell me that really smart successful rich people believe in Tesla. You mean like James Murdoch, on the board of Tesla and who also was lost his entire investment in Theranos? Or like Larry Ellison, an adviser and fan of Elizabeth Holmes who invested $1 billion in Tesla just 6 months ago and has already lost 40% of it? The window on this is probably closing, but over the last 10 years if you wanted to get Silicon Valley investors to throw a lot of money at you, find a traditional bricks and mortar business and devise a story in which you take that industry and convert its economics to that of the networked software world (see: Uber, WeWork, Tesla, and even Theranos is some of its strategic pivots).
Or how about true millennials and Elon Musk? Name a wealthy millennial supporter of Elon Musk and Tesla and I can bet you any amount of money they have not looked at Tesla's balance sheet or cash flow or the details of its global demand trends. They have not thought about its dealership strategy or manufacturing strategy and the cash flow implications of these. They just like what Elon says. It sounds big and visionary. They buy into Elon's formulation that he is saving the environment and everyone opposed to him is in a cabal with big oil (ignoring the fact that Elon routinely uses his Gulfstream VI to commute distances less than 60 miles). So saying that rich millenials adore Elon is effectively saying that they want to be associated with the same things Elon says he is for -- the environment and space travel et al.
Elon Musk is Ferdinand DeLesseps. He is PT Barnum. He is Elizabeth Holmes. He is the pied piper. He is fabulous at spinning visions and making them sound science-y. But he is not Tony Stark. There is a phenomenon with Elon Musk that everyone thinks he is brilliant until they hear him speak about something about which they have domain knowledge, and then they realize he is full of sh*t. For example, no one who knows anything about transportation or physics or basic engineering has thought his Boring Company and Hyperloop make any sense at all. His ideas would have been great cover stories for Popular Mechanics in the 1970's, wowing 13-year-old boys like me with pictures of mile-long cargo blimps and flying RV's. He is like a Marvel movie that spouts science that is just believable-enough sounding that it moves the plot along but does not stand up to any scrutiny.
All of this would be harmless if he was not running a public company. I don't really care about the rich folks who were duped by Elizabeth Holmes, but hundreds of thousands of small millenial investors who have totally bought into the Elon hype are literally putting their last dollar into Tesla, and sometimes borrowing more. Tesla shorts often laugh at these folks on Twitter, calling them "bagholders," but it is a tragedy. Unless Tesla finds a sugar daddy sucker, and the odds of that are getting longer, I think it is going to end badly for many of these investors
As a disclosure, I have been short Tesla via puts for a while now. It you really want to understand Elon, the best book I can recommend is The Path Between The Seas about the building of the Panama Canal. First, it is a great book you should read no matter what. And second, Ferdinand DeLesseps is the best analog I can find for Musk.