Another Plea to Global Warming Alarmists on the Phrase "Climate Denier"
Stop calling me and other skeptics "climate deniers". No one denies that there is a climate. It is a stupid phrase.
I am willing, even at the risk of the obvious parallel that is being drawn to the Holocaust deniers, to accept the "denier" label, but it has to be attached to a proposition I actually deny, or that can even be denied.
As help in doing so, here are a few reminders (these would also apply to many mainstream skeptics -- I am not an outlier)
- I don't deny that climate changes over time -- who could? So I am not a climate change denier
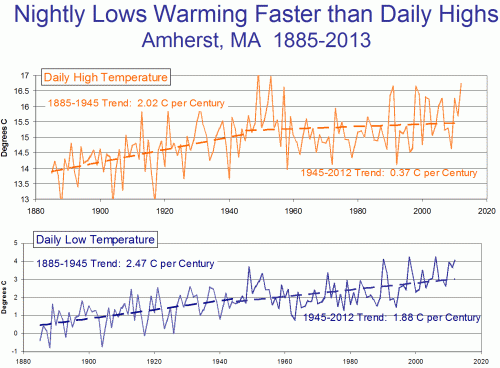
- I don't deny that the Earth has warmed over the last century (something like 0.7C). So I am not a global warming denier
- I don't deny that man's CO2 has some incremental effect on warming, and perhaps climate change (in fact, man effects climate with many more of his activities other than just CO2 -- land use, with cities on the one hand and irrigated agriculture on the other, has measurable effects on the climate). So I am not a man-made climate change or man-made global warming denier.
What I deny is the catastrophe -- the proposition that man-made global warming** will cause catastrophic climate changes whose adverse affects will outweigh both the benefits of warming as well as the costs of mitigation. I believe that warming forecasts have been substantially exaggerated (in part due to positive feedback assumptions) and that tales of current climate change trends are greatly exaggerated and based more on noting individual outlier events and not through real data on trends (see hurricanes, for example).
Though it loses some of this nuance, I would probably accept "man-made climate catastrophe denier" as a title.
** Postscript -- as a reminder, there is absolutely no science that CO2 can change the climate except through the intermediate step of warming. If you believe it is possible for CO2 to change the climate without there being warming (in the air, in the oceans, somewhere), then you have no right to call anyone else anti-science and you should go review your subject before you continue to embarrass yourself and your allies.