The Failure of Technocratic Government Economic and Energy Policy
The news came out the other day that Porsche will stop making diesel-engine cars. This is the beginning of the end of significant diesel car production in Europe, and is the ultimate proof that the diesel engine is a dead-end technology choice for Europeans concerned with the environment.
The story is a long one and I will leave you with some links in a moment, but the basic story flow is:
- European governments are concerned about CO2 production, want to "do something"
- European car-makers have a lead over the rest of the world in diesel technology, urge governments to choose diesel as the technology of the future, since at the time it was more efficient than gasoline engines.
- European governments, hot to "do something" and also keen to do it in a way that seems to advantage domestic producers in the high profile automobile trade, promote diesel in a number of ways (including lowering taxes on diesel fuel and diesel car purchases).
- As Europeans adopt diesel, problems emerge as air quality degrades -- diesels may be more efficient, but have a number of harmful emissions that are far worse than with gasoline engines. There are tests and standards for these emissions but it is discovered that most manufacturers are cheating on emissions tests.
- Too late, it is realized that other technologies (electric hybrids, all electric) are pushing well past diesel in terms of efficiency. Diesel is a dead-end in terms of CO2 reduction, and increases harmful emissions.
- Emissions tests are tightened, but it is clear manufacturers cheated because they do not have the technology to produce cars people will buy that meet the standards. Companies like Porsche start to exit the business.
One of the best articles I have found about this history is actually at Vox, that bastion of free market economics and government non-interventionism.
The failure here is entirely predictable and is subsumed in the general criticism of "government picking winners." As with many such failures, they boil down to information and incentives. In terms of information, folks in government have no idea of the range of technology choices now and in the future, and how these technology choices might or might not make sense in a broad range of applications. In terms of incentives, government officials usually have very different true incentives from their publicly stated ones (in this case CO2 reduction). In the US, the Feds continue to support insanely stupid ethanol subsidies and mandates in part because the first Presidential primary is in corn state Iowa. In Europe, it may well have been that officials were more ready to support diesel, which Europeans were good at, over hybrids, which Asian companies were good at, no matter what the relative merits were.
If you think that is cynical, even the folks at Vox noticed:
At the time, there were lots of different paths Europe's automakers could have taken to green itself. They could've pursued direct injection technology for gasoline vehicles, making those engines more fuel-efficient. They could've ramped up development of hybrid-electric cars, as Toyota was doing in Japan. But European companies like Peugeot and Volkswagen and BMW had already been making big investments in diesel, and they wanted a climate policy that would help those bets to pay off.
Europe's policymakers obliged. The EU agreed to a voluntary CO2 target for vehicles that was largely in line with what diesel technology could meet. As researcher Sarah Keay-Bright later noted, these standards were crafted so as not to force Europe's automakers to develop hybrids, electric vehicles, or other advanced powertrains.
The result?
Although overall pollution in Europe has gone down over time, diesel vehicle emissions remain stubbornly high. Today, Paris sometimes has smoggy days comparable to those in Beijing. London is struggling with unhealthy levels of nitrogen dioxide. Germany, Austria, and Ireland have NOx pollution well above the legal limits, with vehicles accounting for roughly 40 percent of that output.
The health toll is likely considerable. One recent study estimated that diesel pollution from cars, buses, and trucks in Britain caused 9,400 premature deaths in 2010 alone. It's difficult to pinpoint what fraction of those deaths might have been avoided if emission rules on cars had been strictly enforced all along, but that gives a sense of the stakes.
Even Vox is willing to call for some technocratic humility:
Which brings us to the third takeaway. The future is hard to predict. Diesel cars seemed like a reasonable idea in the 1990s and a disaster today. That suggests that policymakers should have a lot more humility when crafting energy policy. Maybe battery-electric cars will win out, or maybe it'll be hydrogen, or maybe it'll be something else entirely. (Heck, perhaps diesel cars that are genuinely clean could play a role in reducing CO2 emissions.) No one knows for sure.
So one approach here might be to pursue technology-neutral policies focused on preferred outcomes — say, tightly enforced standards that require lower emissions — rather than favoring specific industries and technologies just because they happen to seem promising at that moment in time.
This conundrum is likely to come up again and again. For years, governments have been laying down big bets on emerging clean energy technologies. France did it with nuclear power in the 1970s and '80s. Germany did it with wind and solar power in the 2000s, through feed-in tariffs. The United States has done it with corn ethanol in the past decade.
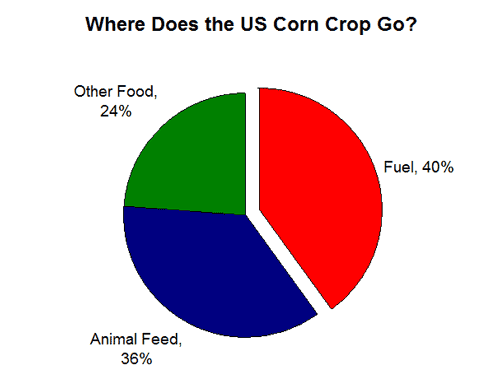
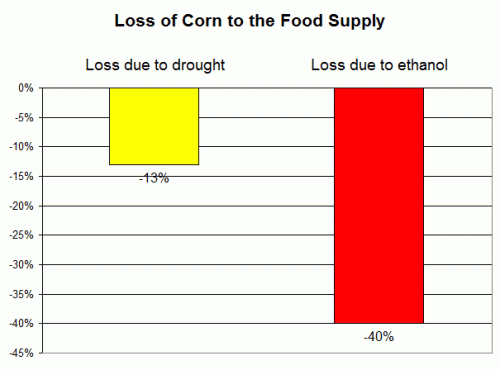
Done right, this sort of government support can be valuable, helping useful new energy options break into the mainstream against entrenched competition. But there's also a huge risk that governments will end up gambling on badly flawed technologies that then becomethe entrenched competition — and prove impossible to get rid of. The US arguably made that mistake with ethanol, which has had unintended ripple effects on the food supply and deforestation that are proving politically difficult to untangle. The drive for diesel looks like it belongs in that category, too. It's not a story we'd like to keep repeating.