Archive for September 2008
Lenders Have to Lend
I know this may be pointing out the obvious, but I think it needs to be said: Lenders have to lend, just as much as borrowers have to borrow. I know most people understand the "borrower" part of this phrase, but they seem to act as if lenders are somehow only putting their money on the street as some sort of charitable activity, and if we don't sufficiently kow-tow to all their needs, they will run away and never help us all again.
The fact is that people with large pools of money -- banks, pension funds, insurance companies -- HAVE to lend. And in a time where stocks are dicey, they probably have more, not less, cash than normal they want to lend, much of it short-term. Now, they may be temporarily scared off from doing so for a few days or weeks as they try to assess what is safe and what is not, but they can't stick their money in a mattress or buy tons of gold or invest in ammunition and run for the hills. Banks have to pay off depositors; insurance companies often aim to break
even on premiums and payouts and make their money on investing the cash
in between; pension funds can't make their long-term obligations
without making steady returns.Their very survival, in many cases, depends on making continuous returns off their free cash.
Wisdom from Schoolhouse Rock:
You got a couple hundred bucks saved up in your birthday stash.Why not deposit them dollars in the bank instead?
Then at the end of the year you'll come out way ahead,
Because the bank'll pay you money in exchange for the use of your cash!
And that's called interest; you're makin' money that way,
And you can buy that gear about a year from today.
In Praise of Price Gouging
As I have pointed out any number of times, when supplies of something are short, you can allocate them either by price or by rationing. Robert Rapier, via Michael Giberson made the point that combining shortages with tough state price-gouging laws inevitably led to rationing and long lines:
Someone asked during a panel discussion at ASPO whether we were going
to have rationing by price. I answered that we are having that now. But
prices aren't going up nearly as much as you would expect during these
sorts of severe shortages. Why? I think it's a fear that dealers have
of being prosecuted for gouging. So, they keep prices where they are,
and they simply run out of fuel when the deliveries don't arrive on
time. If they were allowed to raise prices sharply, people would cut
back on their driving and supplies would be stretched further.
Neal Boortz made the same point yesterday, as the gas shortages in the southeast dragged out (unsurprisingly) for a second week:
nearly 200 gas stations in Atlanta are being investigated for price gouging. Don't investigate them! Reward them! Price gouging is exactly what we need! It should be encouraged, not investigated....
The real problem now is panic buying. People will run their tanks
down by about one-third and then rush off to a gas station. Lines of
cars are following gas tanker trucks around Atlanta. The supplies are
coming back up, but as long as people insist on keeping every car they
own filled to the top and then filling a few gas cans to boot, we're
going to have these outages and these absurd lines.So, how do you stop the panic buying? Easy. You let the market do
what the market does best, control demand and supply through the price
structure. The demand for gas outstrips the supply right now, so allow
gas stations respond by raising the price of gas .. raise it as much as
they want. I'm serious here so stop your screaming. The governor
should hold a press conference and announce that effective immediately
there is no limit on what gas stations can charge for gas. I heard
that there was some gas station in the suburbs charging $8.00 a
gallon. Great! That's what they all should be doing. Right now the
price of gasoline in Atlanta is artificially low and being held down by
government. That's exacerbating the problem, not helping it. Demand
is not being squelched by price.As the prices rise, the point will be reached where people will say
"I'm fed up with this. I'll ride with a friend, take the bus or just
sit home before I'll pay this for a gallon of gas." Once the price of
a gallon starts to evoke that kind of reaction, we're on our way to
solving the problem. When gas costs, say, $8.00 people aren't going to
fill their tanks. They also aren't going to rush home to get their
second car and make sure it is filled up either ... and you can forget
them filling those portable gas cans they have in the trunk. Some
people will only be able to afford maybe five gallons! Fine! That
leaves gas in the tanks for other motorists. Bottom line here is that
people aren't going to rush out to fill up their half-empty tanks with
$8.00 gas.
Here is something else to think of about lines and shortages. What is the marginal value of your time? I think most people underestimate this in their day to day transactions. Some will say it is whatever they make an hour at work, and that is OK, but I will bet you that is low for most folks. Most folks would not choose to work one more hour a week for their average hourly rate. Start eating into my free time and family time, and my cost goes up. That's why overtime rates are higher.
So let's say an individual values his/her time at the margin for $25. This means that an hour spent waiting in line or driving around town searching to fill up with 10 gallons raises the cost by $2.50 a gallon. And this does not include the fuel or other wear on the car used in the search. Or the cost of that sales meeting you missed because you did not have the gas to get there. So an anti-gouging law that keeps prices temporarily down by a $1 or so a gallon may actually cost people much more from the shortages it creates.
The Alternate View
Several people I know have argued with my "do nothing" approach to the current mortgage and liquidity mess. Their argument is that the current crisis has frozen the short term money market, with banks refusing to lend to each other, and only doing so via central banks. The problem, they claim, is that this could lead to an extended drying up of business to business credit. For example, two people both used the fuel retailing example, arguing that inventory purchases are made on credit, and paid off as the inventory is sold. The logic, I assume, is that businesses have all reduced their working capital, and so a drying up of short term business credit will cause the economy to lock up, with producers and retailers unable to buy components and inventory. One such argument here.
I guess the questions are 1) for how long and 2) how best to fix it. To the first question, this is by no means the first time in my lifetime that short-term credit has dried up. Liquidity eventually returns, mainly because lenders need to lend as much as borrowers need to borrow. As to the second question, central banks are currently handling this by increasing the amount of money they will lend short term. Rather than lend to each other directly, bank A deposits with the Fed and then the Fed lends to bank B. The cycle ends NOT when every bank is healthy but when banks and other institutions are confident they know which banks are healthy. All the bailout is doing is delaying this reckoning. I don't think it matters that banks and certain financial institutions survive, I think it matters that the ones who are not going to survive are identified quickly so the rest can start lending again to each other.
Given these concerns, I reiterate my position that if the government is going to inject liquidity and create new financial asset insurance programs, it makes more sense to me to do it at the point of concern, i.e. in the credit market to main street businesses, rather than dumping the money into the toxic sludge of credit default swaps.
Two MILLION Visitors


Thanks, folks. I still remember the first month I blogged about four years ago, when I wrote and wrote and was fairly sure not a single person was reading. Like performing to an empty room.
Where is the Credit Crisis?
Mark Perry observes that if we are in for a credit crunch, its not showing up in the numbers yet, as bank loans and leases hit an all-time high and most other types of lending are still near their peaks.
Shadegg on the Bailout
I missed this excellent interview with my local Congressman, John Shadegg, whom I don't always agree with but is still way better than 99% of Congress:
David Freddeso: Is a bailout necessary to save the economy at
this point from complete collapse "” from a major failure of multiple
institutions at the same time?Shadegg: I think that's the most difficult question that
could be posed under these circumstances, and it's the question that I
have struggled all week to find the answer to. I have talked to a lot
of smart people who know Wall Street, know banking, know the economy
quite well, and you hear different opinions. Some will tell you that it
is absolutely essential. Quite frankly, I'm skeptical about that.But I think that in some ways the question doesn't matter any more.
Because Secretary Paulson chose to raise the matter in the way he did "”
that is, to go public in a very high-profile way, not just with his
concern, but with a kind of Chicken-Little, the-sky-is-falling kind of
demand "” it became a self-fulfilling prophecy.That is to say, once the secretary of the Treasury announces to the
world that there is a pending financial collapse, perhaps as great as
the Great Depression, and Congress must act "” he has sent a signal that
essentially tells world markets that Congress must act. I will tell you
that has been one of the most frustrating things about this since the
very beginning...I can't tell you how many members of Congress were stunned at that
news, and were stunned that none of their local bankers were calling
them. And then they called their local bankers, as I called my local
bankers, and my local bankers said, "I think things are just fine." I
talked to one banker who said, "Gosh, we've got money, and we're
liquid, and we're making a profit. And we're in the market selling
loans, and we've got competitors trying to sell loans against us."So, at that point, there's a disconnect. Secretary Paulson is
claiming that this is a catastrophe of generational proportions that
could go worldwide. And none of what we were hearing back home matches
that. And I'm not speaking just for myself, but also for many of my
colleagues who were making similar calls. They weren't being called by
their bankers, or by any of the businesses back home saying, "I can't
borrow any money".... If, in fact, Paulson had struck a chord with the
American banking community, wouldn't you think that after he announced
on Friday that there was a crisis of liquidity that threatens the
entire nation's financial solvency and Americans' jobs from coast to
coast, that my community bankers in Arizona wouldn't have been picking
up the phone by Monday morning, if not over the weekend, to say that "I
share the Secretary's concerns"?
Dale Franks on the Bailout
I thought Dale Franks has a really good post on why the bailout is a crock. Its quite long, but here is one excerpt:
Banks that made bad mortgage choices get a buttload of money for their
bad MBS paper. Banks that charted a more reasonable course"”and yes,
there are quite a few"”get no reward.In a real free market, of
course, the banks that made bad decision would have to take the hit.
They'd auction them off at whatever price the market would bear, and
they'd have to suck up the losses on the difference between face value
and sale value, even if that meant driving them out of business.
Meanwhile, the more rational banks would be able to pick up the MBS
paper at a discount, and make some cash off of the distress sale from
the incompetent banks.And, of course, the incompetent banks would probably be driven out of business. Which, after all, is how it is supposed
to work. But, the government seems entirely uninterested in letting the
market work this out, which brings me to my next point....I keep hearing over and over again"”and I've even said it"”that no one
knows what these mortgage backed securities are worth. But let's be
clear here: the reason we don't isn't because the price is mystifyingly
unknowable. It's because they haven't even tried to sell them off yet.
We already know it's possible to find out what the price is, simply by
offering them up for sale. Indeed, we did it in July when Merril Lynch sold off its entire MBS portfolio.The reason we're not doing it now is because the holders of MBS paper expect a government bailout, and they expect to
receive through it a price significantly higher than they would in the
secondary market. If it were otherwise, they'd already be auctioning
them off.After all, we're talking about securities based on the
value of mortgage repayments. We already know that the default rate on
most of the MBS paper will be around 5%, with a maximum of probably no
more than 10%. Everybody already knows this. Now, just to turn the
screw, a buyer might want a discount of over"”perhaps well over"”50%.
after all, it's a fire sale, and everybody wants a bargain, right.But there is a market-clearing price for these securities, and everybody on the street knows it.
What they also know is that they have an excellent chance of receiving
a much better price from the Feds, and that waiting for the bailout
gives them a better chance to stay in business, even if the Treasury is
a large shareholder in the company. And, after all, if the Treasury is
a shareholder, how likely is it that the government will let them fail, losing all that equity?The
bailout doesn't solve the problem. It keeps the bad banks in business,
lets them escape the worst consequences of their malfeasance, and
prevents the better run banks from taking up the reins that would be
otherwise dropped when the bad banks went out of business.
Exactly
Sometimes I snap at someone for their criticism of a particular politician. Typically, they assume I am doing so because I support that politician. But in reality, I am using just sick of the implication that somehow other politicians would have been much better. I absolutely agree with Don Boudreaux's comment:
Fareed Zakaria (author of a truly fine book and columnist for the
Washington Post) rightly argues that Sarah Palin is unqualified to be
president of the United States (and, hence, by extension, unqualified
to be V-P). Mr. Zakaria is correct that Gov. Palin's recent answer to a
question about the economy "is nonsense - a vapid emptying out of every
catchphrase about economics that came into her head." He's correct also
that she's unfit to be entrusted with the power of the modern
presidency.But Mr. Zakaria is incorrect to suppose that these traits separate
Gov. Palin from other candidates for high political office. Calls by
Senators McCain and Obama for cracking down on "speculators" are full
of classic and wrongheaded catchphrases, as is Sen. Obama's vocal
skepticism about free trade. Gov. Palin is merely less skilled in
passing off inanities and claptrap as profundities.
My Alternative to the Bailout
This is taken from and expanded from the end of this post.
Everyone involved in the bailout plan says, at least publicly, that they are not trying to bail out a bunch of Wall Street folks who lived high off the risk premium of these investments but now want to avoid the costs when the actual risks become clear. They claim to be bailing out Wall Street and various large banks because they fear that a financial meltdown and liquidity crisis will starve main street businesses of cash, and create a deep economic slowdown.
OK, if this is the real policy goal -- to maintain the ability of main street businesses to borrow -- then here is my alternative proposal:
- Immediately increase the SBA loan gaurantee authority by $100 billion dollars. That is enough for a million new small business loans of $100,000 each.
- Authorize treasury to spend up to X hundred billion to buy rated new issues of bonds and commercial paper of US non-financial companies. Some limits should be applied - such as the feds cannot buy any more than 30% of a single issue and/or more than 10% of the entire outstanding debt of one company.
That's the plan. Here are the advantages:
- The government is addressing the actual policy goal of keeping liquidity in main street business directly
- The government is investing in success, in main street companies trying to grow, and not in failed banks and financial institutions
- Moral hazard issues are avoided with financial institutions.
- The SBA loan guarantees cost nothing today. In fact, they are cash positive in the short term due to loan guarantee payments by borrowers. Of course, they risk future losses, but such losses in the future are in part covered by the guarantee payments, and a future loss is cheaper than a loss today.
- Investments in corporate bond issues are much easier to value, and are far less risky, than investments in illiquid mortgage securities. The taxpayer is far less likely to take a beating on these purchases.
- Banks may still fail, but the FDIC has an infrastructure and experience for handling this. If necessary to calm people, the FDIC could make a public commitment to assisted mergers to maintain all depositors.
- If there is some big financial meltdown, which I still doubt, there might be a need to inject some mortgage liquidity, but since the Feds now own Fannie and Freddie, the vehicle for doing so is easily available.
Update: I was not clear -- this is actually an alternative to by alternative. My first, preferred alternative plan is "do nothing."
Final Thoughts on the Bailout (I Still Don't Like It)
I sat this weekend and pondered the pending financial bailout. A number of fairly smart people who know more about Wall Street than I seem to think it a necessary evil, and this includes several folks who are nearly as libertarian as I. Is a sort of knee-jerk libertarianism preventing me from accepting a necessary step to avert economic Armageddon?
I don't think so. By the light of day on Monday morning, I still think it a bad idea.
Here is some of my thinking (to some extent my last point is the one that is most important to me -- if we want liquidity, let's put it in the right place).
- I am tired of businesses heading to the government bailout trough and arguing that the continued functioning not only of their industry, but of all the existing players in their industry, is critical to the health of the US economy and thus requires some sort of government subsidy/bailout/protection. Coyote's first law of rent-seeking is that companies will always claim that failure of their business will have a disproportionately negative effect on the economy. Coyote's first corollary to this law is that Congress usually accepts this argument at the exact point in time when it is no longer true.
- This bailout is even more grotesque than a normal industrial bailout. GM can be said to have honestly tried to make the right cars, and just failed. I don't like bailing them out, because I don't particularly like diverting capital into the hands of organizations that are proven failures at using capital well. But the financial investors that we are bailing out today knew they were taking a lot of risk by purchasing risky securities and then leveraging them up on their balance sheets. They lived high for years off of the fat returns for taking this risk, arrogantly explaining that they made lots of money because they were smarter than everyone else and because they were being rewarded for taking on risk. But then they come running to the government when the returns on their risky securities turned south, which just makes me sick. They were paid for taking this risk, so take it. I am sorry that you have no cushion because all those earlier returns are already spent on Maserati's for your mistresses, but that is what chapter 7 is for.
- As many as 300,000 small businesses go bankrupt every year (this number is very, very hard to pin down, as it is hard to separate personal from business bankruptcy with small business). Something like 299,998 of them do not get bailed out by the feds. Why do the other 2 get special treatment vs. other US taxpayers? Because they are better at lobbying Washington that they are essential?
- Yes, the government created the Alt-A and sub-prime mortgage markets,and caused them to flourish via Fannie and Freddie aggressively asking for and buying these loans. And the feds, via tax policy, and local governments, via zoning, helped pump up the housing bubble. But nothing forced private companies, particularly highly leveraged institutions like banks, to load up their balance sheets with these things, or, crazily, to write insurance policies on their value. Libertarians want to use these government interventions as an excuse for the bailout, but it doesn't wash. I do think many banks reasonably have lawsuit material against ratings agencies Moodys and S&P, which is fine. I think new blood in that business would be a very good thing.
- The total market capitalization of traded equities of public corporations on NYSE and NASDAQ is between $15 and $20 trillion. That means that the first $150 billion of the bailout is equivalent to about a 1% price move on the exchanges, something that occurs almost every day. Have we really close-coupled everything so tightly that a cumulative balance sheet hole on the order of magnitude of a 1% move on the stock market can bring down the whole financial system? If so, we should just let the whole thing come down and rebuild itself in a more robust form.
- Wall Streeters pat themselves on the back all the time for how creative they are financially. So get creative here. Create some sort of new entity and have banks contribute toxic mortgages into the entity in exchange for equity. Find some pension funds to invest in the new entity at a deep discount.
- These banks, who are experts in this stuff, claim they cannot value these failing, complex, illiquid mortgage packages. OK, that may be true. But how is the government possibly going to do any better? Such a situation cannot possibly end well for the taxpayers.
- I saw folks writing in fear last week that the commercial paper market might dry up. The commercial paper market dries up all the time. It comes back eventually. People treat lending markets like they are charities or something, and they fear that lenders will give up and never come back. But they are not charities. They serve just as much of a purpose for lenders and for borrowers. Businesses and folks with capital need to make money on short term cash. They are not going to stop lending forever. Even capital markets dry up from time to time. The IPO market has disappeared several times, including several years in the post-Internet-bubble period. The junk bond market comes and goes.
- What is the government really worried about? I presume that they are worried that liquidity will dry up and the ability of main street businesses to borrow will be impaired. OK, then save the freaking $700 billion and if main street starts to have trouble borrowing, have the government participate somehow in that lending market. Buy corporate bond issues, and/or increase the limit on SBA loan guarantees by a $100 billion (this latter would allow a million new $100,000 SBA loans, and would actually generate money now in guarantee fees and only potentially cost money much later if the loans fail). This way, we are investing liquidity in successful companies trying to grow rather than in failing banks that got us all into this. Let's invest in success rather than in failure.
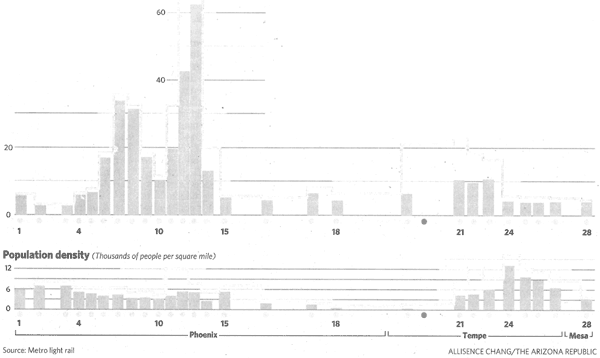
Why Phoenix Light Rail is Doomed in One Chart
The Arizona Republic had another of its cheerleading articles on light rail this morning. In it was a chart that, contrary to the intent of the article, summarized exactly why Phoenix light rail is doomed. Below is a chart of the employment density (top chart) and population density (bottom chart) at each stop along the first rail route. Note that this line goes through what passes for the central business district of Phoenix and the oldest parts of town, so it was chosen to run through the highest density areas - all future extensions will likely have lower numbers. Unfortunately, they do not reproduce this chart online so here is a scan:
Take the population density chart. As a benchmark, lets take Boston. The average density for all of the city of Boston is 12,199 people per square mile. Phoenix's light rail line cut through the highest density areas of town has only one stop where density reaches this level, and most stops are less than half this density. And this is against Boston's average, not against the density along its rail routes which are likely much higher than the average.
Rail makes zero sense in a city like Phoenix. All this will do is create a financial black hole into which we shift all of our bus money, so the city will inevitably end up with a worse transportation system, not a better one. Cities that build light rail almost always experience a reduction in total transit use (even the great God of planners Portland) for just this reason - budgets are limited, so since rail costs so much more per passenger, other transit is cut back. But the pictures of the train will look pretty in the visitor's guide.
Postscript: Phoenix's overall average density is around 2,500 per square mile. Assuming that the 12,000 in the chart above is one of the densest areas of Phoenix, this gives a ratio of about 5:1 between peak and average density. This same ratio in Boston would imply peak density areas of 60,000 per square mile. This may be high, but indicates how much higher route densities on Boston rail should be. Oh, and by the way, Boston rail is losing a ton of money.
Other city densities here from 1990. People think of LA as spread out, but LA has a density over three times higher than Phoenix!
So We Can't Have Even One Candidate Who Truly Understands Free Speech
I stand by my no-McCain vow I made years ago after his role in campaign speech limitation. But Obama does not look like a very promising alternative:
The Obama campaign disputes the accuracy of the advertisement, which is
fine. It has also threatened regulatory retaliation against outlets
that show it, which isn't fine. Instead of, say, crafting a response
ad, Obama's team had general counsel Robert F. Bauer send stations a
letter [pdf]
arguing that "Failure to prevent the airing of 'false and misleading
advertising may be 'probative of an underlying abdication of licensee
responsibility.'" And, more directly: "For the sake of both FCC
licensing requirements and the public interest, your station should
refuse to continue to air this advertisement."
In particular, I would love to see Obama actually say what positions that are ascribed to him on gun control are false, and what his actual, specific positions are. A vague, gauzy support for the second amendment does not necessarily mean he has walked away from his earlier positions. In fact, I am sure that McCain would say he supported the First Amendment but I would certainly feel comfortable pointing out how he fails to do so in the details.
How Much Authority Are We Proposing to Give the Treasury?
Much has been made of the bailout legislation provision that the administration would be immune to any scrutiny of any sort for any decision made vis a vis the $700 billion in bailout funds and the resulting spending decisions. But I thought this was equally telling of the over-broad power grab that is going on at Treasury:
The SHR [senior House Republican] calls this an insurance program and the original Paulson plan a
purchase program. He says Treasury Department people have told him that
they considered an insurance program but decided that a purchase
program would be better. But he also added that in the draft
legislation Paulson has advanced, the Treasury would have the authority
to set up such an insurance plan without congressional authorization.
From what he said, it struck me that both courses could be followed.
After all, neither purchases nor insurance is contemplated to take
place unless and until a financial institution comes forward and
requests one or the other.
Jeez, how much latitude are they asking for? Is the bill really so broad that the secretary of the treasury could set up an entirely new government insurance program for financial assets without further Congressional approval?
While I think Cantor is being overly-optimistic about the near-term cash flow of his insurance proposal, it does seem to be at least an incremental improvement over Paulson's plan.
Couldn't The Taxpayer Make Money From the Bailout?
So, apparently the US government is going to authorize up to $700 billion taxpayer dollars to purchase distressed financial assets. I had an email today that said, to paraphrase, couldn't the government make money off these assets if they buy them for the right price?
My first thought was that this was theoretically possible, though my internal cynic found it unlikely in a pricing game run by elected officials between the taxpayer and powerful Wall Street interests that taxpayers would get the upper hand.
But then I realized there was no possible way this will end well for taxpayers. Because the government cannot exercise discretion in day to day financial decisions. It establishes rules and benchmarks and the typical bureaucrat is punished far worse for violating these processes and rules than he/she ever is for reaching a bad result. So the government will establish rules and benchmarks for what price at which they will buy assets (this will be all the more true given the great rush everyone seems to be in). And having set this in place, do you know what assets will be put to them? All the ones that the current holders think are worth less than the benchmark. This is the winners curse on steroids.
Update from Megan McArdle:
there's a gigantic asymmetrical information problem: the owners of
these securities know much more about them than the Fed. And there
isn't (obviously) a large liquid market for the Fed to check against.
So the Fed is likely to overpay, because there won't be a lot of
bidders in any one auction.
Megan, of course, reluctantly supports the bailout where I do not. But she has her eyes open about what she is buying into.
Can We Go Back to Ignoring Naomi Klein Now?
In her wild and somewhat bizarre polemic aimed at Milton Friedman, Naomi Klein argues that major historic crises have always been manufactured by capitalists to slip free market principles into action against the wishes of the socialist-leaning masses.
Really? In what crisis, ever, did the government end up smaller? What about the current crisis and the government response to it carries any good news for free marketeers? History is a series of problems created by government intervention but blamed on the free market, which can supposedly only be solved via more government intervention.
Update: Critique of Klein here. Seriously, it is amazing that this rings true with anyone:
Klein's basic argument is that economic liberalization is so unpopular
that it can only win through deception or coercion. In particular, it
relies on crises. During a natural disaster, a war, or a military coup,
people are disoriented, confused, and preoccupied with their own
immediate survival, allowing regimes to liberal-ize trade, to
privatize, and to reduce public spending with little opposition.
According to Klein, "neoliberal" economists have welcomed Hurricane
Katrina, the Southeast Asian tsunami, the Iraq war, and the South
American military coups of the 1970s as opportunities to introduce
radical free market policies. The chief villain in her story is Milton
Friedman, the economist who did more than anyone in the 20th century to
popularize free market ideas.
As is typical, Klein confuses support for capitalism with government support of individual capitalists.
Michael Lewis on the Bailout
I liked this bit in particular:
Think of Wall Street as a poker game and Goldman as the
smartest player. It's sad when you think about it this way that
so much of the dumb money on Wall Street has been forced out of
the game. There's no one left to play with. Just as Goldman was
about to rake in its winnings and head home, the U.S. government
stumbles in, fat and happy and looking for some action. I imagine
the best and the brightest inside Goldman are right this moment
trying to figure out how it uses the Treasury not only to sell
their own crappy assets dear but also to buy other people's
crappy assets cheap
Update: LOL, via Q&O:
In fact, some of the most basic details, including the $700 billion figure Treasury would use to buy up bad debt, are fuzzy.
"It's not based on any particular data point," a Treasury spokeswoman told Forbes.com Tuesday. "We just wanted to choose a really large number."
Could these be the dumbest guys in the room?
I Think I am Voting for Obama
I am tired of watching the free markets trashed by people who claim to champion capitalism and free enterprise. Better, I am starting to think, to have free markets trashed by someone who does not pretend to support them. Besides, the Republicans in Congress tend to be much stronger supporters of small government, low taxes, and light regulation when they are in opposition. Except possibly for Jeff Flake, who always seems to have his head in the right place.
Update:
"When
it comes to this I should prefer emigrating to some other country where
they make no pretense of loving liberty - to Russia, for instance,
where despotism can be taken pure, without the base alloy of hypocrisy."-- Abraham Lincoln
Think Again
Been smugly thinking that you were smart enough not to take out an interest only mortgage to finance a house at the peak of the market? Or savvy enough not to invest your savings in a mortgage portfolio or some sort of interest rate swap?
Sorry, think again. Because GWB and the US Congress have decided to force you to be an investor in crappy, devalued investments. To the tune of at least $700 billion.
Four years ago, privatization of Social Security was scuttled in large part because Congress thought it unfair to toss the average taxpayer into the volatile marketplace with his/her retirement savings. Now, the government is forcing us all to participate in the financial markets, but only allowing us to invest in the worst assets. Just great.
Climate Presentation
One of the reason my posting has been light of late is that I was working on a climate presentation for the California Regional Council of Rural Counties. That's behind me now, but you can read a brief report on the meeting and download my presentation here.
Save Our Industry, The Economy Depends on It
I have been on a Civil War reading binge lately, which began when I read "Time on the Cross", which is a really interesting economic analysis of American slavery. Since I have read a number of other Civil War and Ante-Bellum history books, including James McPherson's excellent one volume Civil War history.
I was struck in several of these books by the reaction of British textile manufacturers to the war and, more specifically, the informal southern embargo of cotton exports in 1860-61. These textile producers screamed bloody murder to the British government, demanding that they recognize the Confederacy and intervene on their behalf, claiming that the lack of cotton would doom their industry and thereby doom the whole country. On its face, this was a credible argument, as textiles probably made up more of the British GDP at the time than any three or four industries account for in the US today.
Fortunately, the British chose not to intervene, and risked the economic consequences of not supporting the textile industry by jumping into the American Civil War. As it turned out, the British economy was fine, and in fact even the textile industry was fine as well, as demand was still high and other sources around the world stepped up (because of the higher prices that resulted from the Southern boycott) with increased cotton supplies.
This Seems Kind of Obvious in Hindsight
Saul Hansell at the NY Times has an interesting article about why risk assessment programs in investment banks were not sounding the alarm coming into the recent turmoil. The article contains this gem:
Ms. Rahl said that it was now clear that the computers needed to
assume extra risk in owning a newfangled security that had never been
seen before."New products, by definition, carry more risk," she said. The models
should penalize investments that are complex, hard to understand and
infrequently traded, she said. They didn't.
I continue to see parallels between recent problems and the meltdown at Enron. In fact, in many ways events in the natural gas trading market were a dry run for events in the mortgage market. One filmmaker coined the phrase "Smartest Guys in the Room" to describe the hubris of the guys who ran Enron. To some extent the phrase was absolutely true - I knew Jeff Skilling at McKinsey and he was indeed the smartest guy in the room. But everyone can be wrong, and sometimes the smartest guys can be spectacularly wrong as they overestimate their ability to predict and control complex events. I think this is a fair description of what went on in Wall Street over the past several years.
Best Take Yet on the Bailout
The foundation of the U.S. economy could crumble, President George
Bush said today, if Congress fails to approve a U.S. Treasury plan to take over
foundering financial firms, a proposal which the president called "a
much-needed 21st-century civil rights act for stupid people.""To sustain this shining city on a hill," Mr. Bush said, "we need to rescue
the ignorant, irresponsible folks "” from Wall Street to Capitol Hill to
Main Street "” who got us to where we are today. We must guarantee that no American suffers the soft bigotry of being forced to live with the consequences of his bad decisions."The president, in remarks to the news media clearly aimed at
reluctant Republicans in Congress, said, "Our financial system rests on
a foundation of huge banks, brokerage houses and quasi-governmental
agencies that followed Washington's lead by gambling on long-shot,
poorly-collateralized investments. Now this glorious way of life is
threatened, and we must act to preserve it.""We need to guarantee that the structures, systems, people and
products that got us to this point won't be tossed on the ash heap of
history," said Mr. Bush. "If these giant companies fail, then America
will be left with nothing but thousands of small to mid-sized financial
firms that made prudent investment decisions during the past 15 years."
I'm Sure This Is Not In Any Way Relevant To Recent Events
Via Carpe Diem, comes this September 30, 1999 NY Times story:
In a move that could help increase home ownership rates among
minorities and low-income consumers, the Fannie Mae Corporation is
easing the credit requirements on loans that it will purchase from
banks and other lenders.The action, which will begin as a
pilot program involving 24 banks in 15 markets -- including the New
York metropolitan region -- will encourage those banks to extend home
mortgages to individuals whose credit is generally not good enough to
qualify for conventional loans. Fannie Mae officials say they hope to
make it a nationwide program by next spring.Fannie Mae, the
nation's biggest underwriter of home mortgages, has been under
increasing pressure from the Clinton Administration to expand mortgage
loans among low and moderate income people and felt pressure from stock
holders to maintain its phenomenal growth in profits.In
addition, banks, thrift institutions and mortgage companies have been
pressing Fannie Mae to help them make more loans to so-called subprime
borrowers. These borrowers whose incomes, credit ratings and savings
are not good enough to qualify for conventional loans, can only get
loans from finance companies that charge much higher interest rates --
anywhere from three to four percentage points higher than conventional
loans.''Fannie Mae has expanded home ownership for millions of
families in the 1990's by reducing down payment requirements,'' said
Franklin D. Raines, Fannie Mae's chairman and chief executive officer.
''Yet there remain too many borrowers whose credit is just a notch
below what our underwriting has required who have been relegated to
paying significantly higher mortgage rates in the so-called subprime
market.''Demographic information on these borrowers is
sketchy. But at least one study indicates that 18 percent of the loans
in the subprime market went to black borrowers, compared to 5 per cent
of loans in the conventional loan market.In moving, even
tentatively, into this new area of lending, Fannie Mae is taking on
significantly more risk, which may not pose any difficulties during
flush economic times. But the government-subsidized corporation may run
into trouble in an economic downturn, prompting a government rescue
similar to that of the savings and loan industry in the 1980's.''From
the perspective of many people, including me, this is another thrift
industry growing up around us,'' said Peter Wallison a resident fellow
at the American Enterprise Institute. ''If they fail, the government
will have to step up and bail them out the way it stepped up and bailed
out the thrift industry.''
Those heartless free marketing guys at the AEI -- always predicting doom every time we open our hearts to poor people. Bailout? What ridiculous scare-mongering.