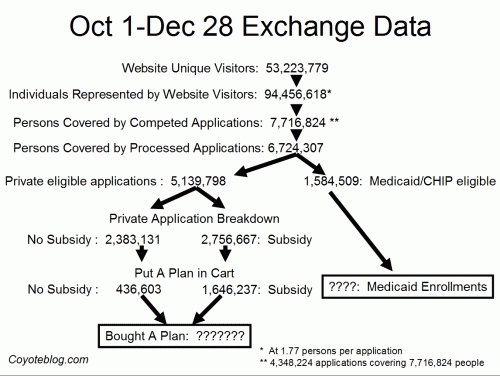
So I guess the Left has hit on its favored meme in response to the millions of insurance cancellations. From Obama to Valerie Jarrett to any number of bloggers, the explanation is that the cancelled policies were "sub-standard". We may have thought we liked them, but it turns out we were wrong. Deluded in fact.
These folks -- despite not knowing my income, my net worth, my health situation, my age, my family size, my number and age of kids, my risk adversity, my degree of hypochondria, my preventative care habits, my diet, my lifestyle, my personal preferences and priorities, or any details about my insurance policy that I spend many hours analyzing and cross-comparing -- have decided they know better than I what health insurance I should want.
My plan was not substandard. I graduated magna cum laude in engineering from Princeton and was first in my class at Harvard Business School. I spent hours shopping for my coverage and was fully satisfied with my resulting policy. Many of the aspects of my policy that cause Obama to call it "sub-standard" -- lack of mental health care, lack of pediatric dental care, lack of maternity care, lack of free contraception, a higher than average deductible -- were my preferences. I got what I wanted.
More expensive, more highly featured products are not necessarily "better". A Mercedes is not necessarily the best car choice for a middle class buyer just because it has more features than his Taurus. Would Obama tell that person his Taurus is "sub-standard" and force him to pay for a Mercedes? If not, why the hell is doing the exact same thing but with health insurance OK?
From his speech today, via Bryan Preston
When Obama came to that section of his speech when the line usually falls, he went with a new spin. If you’ve lost your healthcare thanks to his law, he wants you to know that you were just “under-insured.” Because he says so.
“One of the things health reform was designed to do was to help not only the uninsured but also the under-insured,” he said.
“If you had one of these substandard plans before the Affordable Care Act became law, and our really liked that plan, you are able to keep it. That’s what I said when I was running for office.”
“But ever since the law was passed, if insurers decided to cancel or downgrade these substandard plans, what we said, under the law, is you have got to replace them with quality, comprehensive coverage,” he said, “because, that, too, was a central premise of the Affordable Care Act from the very beginning.”
Update: ugh

Update #2: Yesterday I said the time seemed right for the Left to pick a meme to explain the insurance cancellations and then give the media its marching orders. David Firestone of the NYT has gotten the memo
The so-called cancellation letters waved around at yesterday’s hearing were simply notices that policies would have to be upgraded or changed. Some of those old policies were so full of holes that they didn’t include hospitalization, or maternity care, or coverage of other serious conditions.
Republicans were apparently furious that government would dare intrude on an insurance company’s freedom to offer a terrible product to desperate people.
“Some people like to drive a Ford, not a Ferrari,” said Marsha Blackburn of Tennessee. “And some people like to drink out of a red Solo cup, not a crystal stem. You’re taking away their choice.”
Luckily, a comprehensive and affordable insurance policy is no longer a Ferrari; it is now a basic right. In the face of absurd comments and analogies like this one, Ms. Sebelius never lost her cool in three-and-a-half hours of testimony, perhaps because she knows that once the computer problems and the bellowing die down, the country will be far better off.
So you see the talking points as the media gets their orders. 1. All policies that were cancelled were sub-standard. 2. People will be better off with more expensive policies, even if they are too dumb to konw it.
My policy was perfectly fine. I was not tricked. I am willing to bet I am at least as smart as David Firestone. I am positive I am smarter than Barrack Obama. And yet my policy was cancelled.