Media Extrapolating a Trend From A Single Data Point: 2018 Heat Wave Edition
This article in something called Inside Climate News seems to be typical of many I have seen this year: Because we have had much attention in the media on heat waves this year, there must be an upward trend in heat waves and that is a warning signal that man-made global warming is destroying the planet. Typical of these articles are a couple of features
- Declaration of a trend without any actual trend data, but just a single data point of events this year
- Unstated implication that there must be a trend because the author can't remember another year when heat wave stories were so prevalent in the media
- Unproven link to man-made global warming, because I guess both involve warmth.
I have no idea if well-publicized heat waves this year are a harbinger of an accelerating global warming trend. But since we are discussing "trends" it struck me as useful to actually liven up the discussion with some actual trend data, ie data for more than one summer. There is a real danger to extrapolating trends from volume of media coverage, as I discussed here. If you don't want to click through, I have a funny story in the postscript.
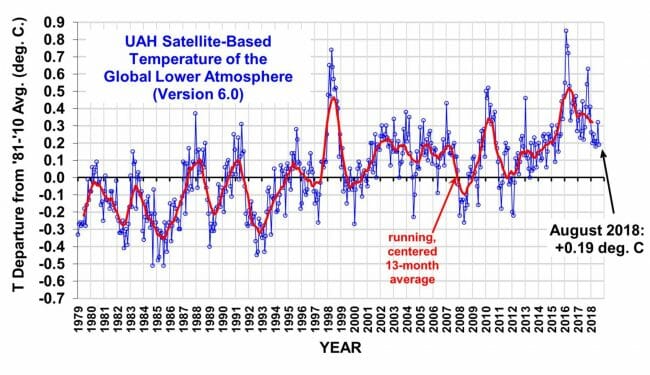
First, our most reliable temperature trend data does not really show a spike in temperatures this summer. Remember, a heat wave that covered the entire US would only affect 6% of the world's landmass and <2% of the world's total area (source). You can easily see the trend upwards several tenths of a degree over the last 40 years, but it is impossible to see much unique about the last 3 months of summer.
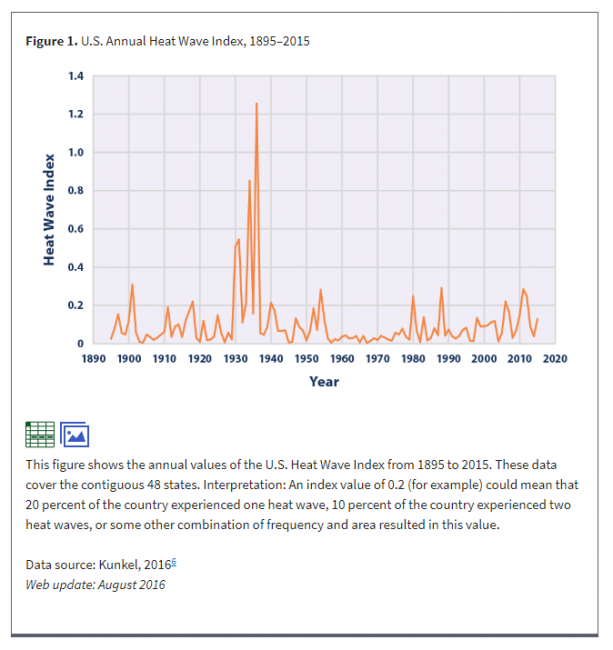
Second, there really is no substantial upward trend in US heat wave index (from right off the EPA's web site, as are all of the following charts. Look at the source for yourself to make sure I am not playing games). Note that all of the following charts are through 2016 and do NOT include the recent summer but are pretty meaningful none-the-less.
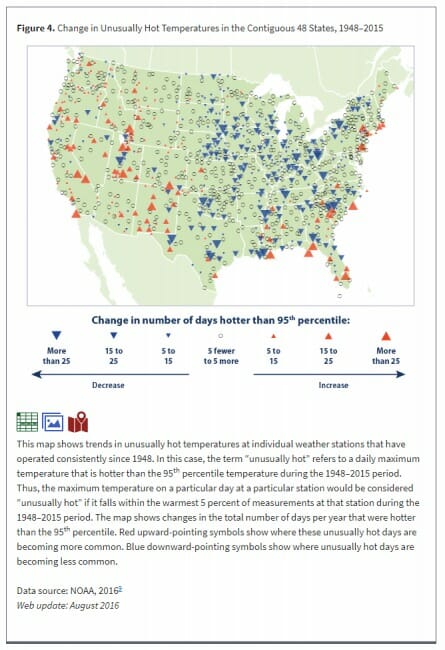
Third, in most of the country, there is actually a downward trend rather than upward trend in extreme heat days.
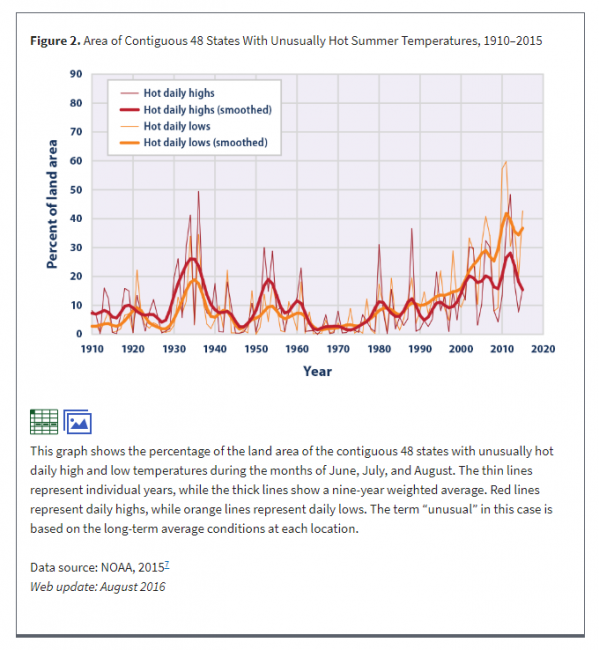
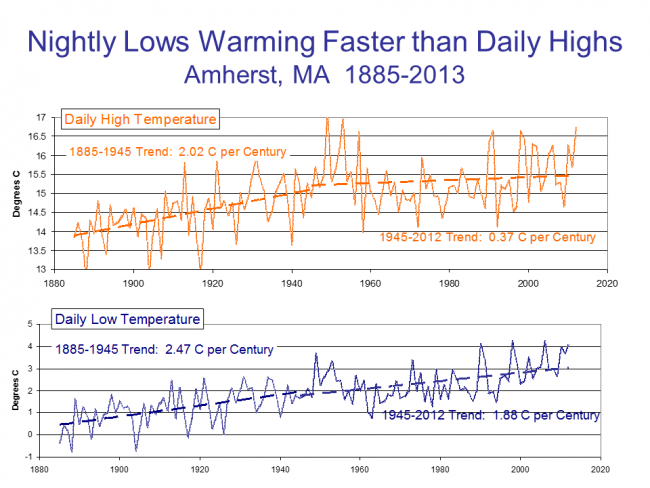
Pretty much everyone agrees, skeptics included, that the world and the US has warmed. So why are extreme heat days down in many locations, and certain down from the 1930's? This defies our intuition. The explanation is in part due to a feature of global warming that is seldom explained well by the media, that much of the warming we see and as predicted in climate models is in the night. We are seeing some increase in hot daytime highs, but really not at an unprecedented level over the last century. BUT, we see MUCH more of a trend in hot daily lows, which basically means warming evenings.
I spoke at Amherst College a while back and here was their temperature trends, broken up between daily highs and nighttime lows. All of Amherst's temperature trend since 1950 has not been in increased daytime highs but higher nighttime lows. This is a pattern you see repeated over and over at nearly every temperature station.
This is why I consider media reports of heat waves, at least of the scope we have seen to date, absolutely irrelevant to "proving" the world is warming.
Postscript: Here is the story everyone should keep in mind when extrapolating from media coverage volume to underlying trends:
let's take a step back to 2001 and the "Summer of the Shark." The media hysteria began in early July, when a young boy was bitten by a shark on a beach in Florida. Subsequent attacks received breathless media coverage, up to and including near-nightly footage from TV helicopters of swimming sharks. Until the 9/11 attacks, sharks were the third biggest story of the year as measured by the time dedicated to it on the three major broadcast networks' news shows.
Through this coverage, Americans were left with a strong impression that something unusual was happening -- that an unprecedented number of shark attacks were occurring in that year, and the media dedicated endless coverage to speculation by various "experts" as to the cause of this sharp increase in attacks.
Except there was one problem -- there was no sharp increase in attacks. In the year 2001, five people died in 76 shark attacks. However, just a year earlier, 12 people had died in 85 attacks. The data showed that 2001 actually was a down year for shark attacks.
Update: I am not really an active participant in the climate scene any more, particularly when positions hardened and it was impossible to really have an interesting discussion any more. The implicit plea in this post goes beyond climate -- if you are claiming a trend, show me the trend data. I can be convinced. There is clear trend data that temperatures are increasing so I believe there is an upward trend in temperatures. Show me the same for droughts or heat waves or hurricanes and I will believe the trend about those as well, but so often the actual data never matches the arm-waving in these media sources.