A Skeptics Primer for "An Inconvenient Truth"
Update: Please enjoy this post; however, I have published a (free) more comprehensive guide to the skeptics arguments concerning man-made global warming. You can find the HTML version here and a free pdf download here.
A few days ago, my wife announced to me that she wanted me to take her to
"An Inconvenient Truth", the recent movie vehicle for communicating
Al Gore's views on climate change. I told my wife that I found the
climate issue incredibly interesting -- I have always had a passion for
inter-disciplinary science and climate requires integration of bits not just
from climate science but from economics, statistics, biology, and more. I
told her I would love to see a true documentary on climate change, but I was as
interested in seeing a "science" film from the group that put this movie
together as I presume she was in seeing a "even-handed" movie on
abortion produced by the Catholic Church.
Never-the-less, she has insisted, so I put together a skeptic's primer for
her, which I will also share with you. Note that I am not actively involved in climate research myself, so the following is my admittedly incomplete understanding of all the issues. It is meant to raise issues that you may not find discussed in most global warming accounts.
Overview: The earth has warmed by 2/3 of a degree to as much as a degree (all temperatures in Celsius)
over the last 100 years, of which man may be responsible for no more than half
through CO2 emissions. The poles, which are important to all the global
deluge scare scenarios, have warmed less than the average. Man's CO2
emissions will warm the earth another degree or so over the next 100
years. There is a possibility the warming will be greater than this, but
scary-large warming numbers that are typical of most climate reports today
depend on positive feedback loops in the climate that are theoretical and whose
effect has not yet been observed. The effects of warming will be a mix of
positive and negative outcomes, recognizing that the former never seem to get
discussed in various media scare stories. If the effects of warming are a
net negative on mankind, it is not clear that this negative outweighs the costs
in terms of lost economic growth (and the poverty, disease, and misery that
comes with lower growth) of avoiding the warming. In other words, I
suspect a warmer but richer world may be better than a cooler but poorer world.
The Hockey Stick: The Hockey Stick graph as become the emblem,
the sort of coat-of-arms, for the climate change intelligentsia. Until
recently, the climate consensus for the last 1000 years, taken from reams of
historical records (things like the history of X river freezing in winter or Y
region having droughts) was this:
This chart is from the 1990 IPCC climate report, and in it you can see
features that both historians and scientists have discussed for years -- the
warm period during the Middle Ages and the "little ice age" of the
late 17th century. Of course, this chart is barely better than a guess,
as are most all historical climate surveys. For example, 3/4 of the earth
is water (where few consistent observations were taken) and only a small percentage of the rest was "civilized" to
the extent of having any historical records. In addition to historical
records, scientists try to use things like ice cores and tree rings to get a
sense of long-term global climate patterns.
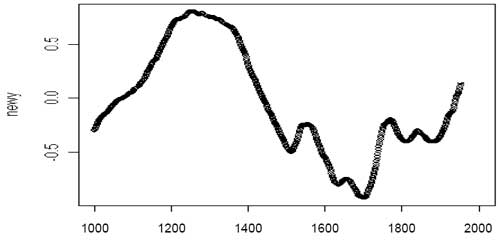
This long-held consensus changed with Mann, et. al., a study that created a new climate
picture for the last millennia that has immediately caught the fancy of nearly
every advocate of climate Armageddon.
For obvious reasons, this graph is called "the hockey stick" and
it is beloved by the global warming crowd because it hammers home the following
message: Climate has been incredibly steady over the past 900 years with a flat to declining temperature trend until
man came along and caused a dramatic shift. Based on this analysis, Mann
famously declared that the 1990's were the warmest decade in a millennia and
that 1998 was the hottest year in the last 1000 years. (For real hubris, check
out this recent USAToday
graphic, which purports to know the world's temperature within .001 degree
for every year going back two thousand years)
In fact, what Mann's chart shows for the last 100 years is about what I said in my overview - that
the world has warmed a degree and that man maybe has contributed up to half of
this. Notice that tacked onto the end of the previous consensus view, the
last 100 years seem like it might just be the start of another natural cyclical
climate variation. Not necesarily a reason for panic. Ah,
but Mann's chart! That's a chart that anyone eager to have the government
intervene massively in the economy is bound to love. It says that we are currently entering an unprecedented anomoly, and that the chief suspect for creating this change must be human civilization.
So is Mann right? Well, a couple of things to note. First, its
instructive to observe how eagerly the climate community threw out its old
consensus based on years of research in favor of Mann's study. It's
unusual for a healthy
scientific community to throw out their old consensus on the basis of one
study, especially when no one had replicated its findings independently.
Which no one has ever been able to do, since Mann has refused to share his
models or methodology details. In fact, it took a US Congressional subpoena
to get any of his underlying models into the public domain. This behavior
by a scientist would normally engender ENORMOUS skepticism in the community --
normally, I mean, except for in climate science, where mountaintop revelation without 3rd party repeatability
is OK as long as it supports a dire man-made climate catastrophe model.
In short, climate change advocates wanted the study to be true, because it was such a
powerful image to show the public.
Despite Mann's reticence to allow anyone to check his work, skeptics still
began to emerge. Take that big temperature bulge in the Middle
Ages shown in the previous concensus view. This bulge was annoying to climate
interventionists, because it showed that large variations in temperature on a
global scale can be natural and not necessarily the fault of modern man.
But Mann made this whole medieval bulge go away. How? Well, one of
the early revelations about Mann's work is that all the data before 1450 or so
comes from studying the tree rings of one single tree. Yes, that's one tree
(1). Using the evidence of this one tree, Mann flattened the temperature
over the 500 year period from 1000-1500 and made the Medieval warm period just go poof. Wow!
The bigger criticism of Mann has come from statisticians. Two Canadian
statisticians began questioning Mann's methodology, arguing that his
statistical approach was incorrect. They demonstrated that Mann's
statistical approach was biased towards creating hockey sticks, and they showed
how the Mann model could be applied to random noise and produce a hockey
stick. The climate change establishment did not take this criticism
well, and tried their hardest to rip these two guys up. In fact, you might have believed that the two had been molesting little boys or declaring the world is flat rather than just questioning another scientist's statistical methodology.
Recently, a US Congressional Committee asked a group of independent statisticians led by
Dr. Edward Wegman, Chair of the National Science Foundation's Statistical
Sciences Committee, to evaluate the Mann methodology. Wegman
et. al. savaged the Mann methodology as well as the peer review process
within the climate community:
It is important to note the isolation of the paleoclimate community; even
though they rely heavily on statistical methods they do not seem to be
interacting with the statistical community. Additionally, we judge that the
sharing of research materials, data and results was haphazardly and grudgingly
done. In this case we judge that there was too much reliance on peer review,
which was not necessarily independent. Moreover, the work has been sufficiently
politicized that this community can hardly reassess their public positions
without losing credibility. Overall, our committee believes that Dr. Mann's
assessments that the decade of the 1990s was the hottest decade of the
millennium and that 1998 was the hottest year of the millennium cannot be
supported by his analysis.
Further, Wegman concurred on almost every point with the Canadians, coming to the conclusion that the hockey stick was deepfly flawed. In most other scientific communities, the Mann analysis would have been sent
to the dustbin along with cold fusion and Archbishop James Ussher's dating of
the earth to October 23, 4004 BC.
The problem is that the Mann chart has become too politically important. Prominent men
like Al Gore have waved it around for years and put it in his books. No
one in the core of the climate community can back away from the hockey stick
now without the rest of the world asking, rightly, what else is wrong with your
analyses? If I seem too hard on the climate science community, then
consider this
quote from National Center for Atmospheric Research (NOAA) climate researcher and global warming action promoter,
Steven Schneider:
We have to offer up scary scenarios, make simplified, dramatic statements,
and make little mention of any doubts we have. Each of us has to decide what
the right balance is between being effective and being honest.
Now you know why, for all its flaws, you will continue to see the hockey
stick in the press. Because it is not about the facts, but about "scary scenarios" and "dramatic statements".
Has Man Been Causing the Warming?
Yes, some of it. But its a little more complicated than the global
warming community lets on. First, note the last 100 years of the
hockey stick. The big upwards spike begins in 1900, long before any large
man-made concentrations of CO2 were put into the atmosphere. In fact,
even those most fanatical about assigning maximum blame for climate change to
man don't blame man-made effects for most of the first half of the 20th century
temperature spike.
Which begs the question, what caused the 1900-1940 spike of about 1/2 a
degree? Answer: Nobody really knows. Which begs the follow-on
question: If we don't know what caused the 1900-1940 run-up, how do we
know that this same force is not responsible for some of the run-up since
1950? Answer: We don't. As I will explain below, climate
scientists trying to validate their models have reasons for wanting the
post-1950 temperature rise to be all man-made. But just because they
assume it to be due to man-made rises in atmospheric CO2 concentrations does
not make it so -- correlation does not equal causation.
Well, what else could be causing this increase? It could at least partially be
natural cyclical variations in climate that we don't really understand.
Or it could be something more obvious, like, say, the sun was brighter. I
can imagine your reaction -- no way it could be just a brighter sun,
Coyote. I mean, that's the first thing the climate scientists would check
if earth temperatures were rising, right?
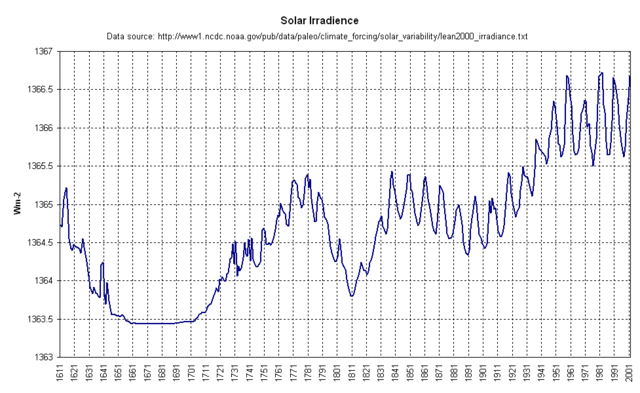
This chart compiled from data by Judith Lean of the Naval Research Library
and charted from her data at NOAA by Junkscience.com
shows that interestingly, the sun's output does appear to be higher today than they have been in many, perhaps hundreds of years. Would such increased activity be
expected to result in higher earth temperatures? I don't know, but if you
think it odd that scientists talk about global warming without mentioning how
hot the sun is, well, welcome to the world of climate science. Its kind of like scrambling to find out why your room is too hot without first checking to see where the thermostat on the furnace is set. More
on the sun's variance
and climate change here.
Future Warming: The key question, of course, is about future warming - i.e.,
based on man's economic growth and projected output of CO2, how much can the
world be expected to warm, say over the next 50-100 years. I don't know
what the movie "An Inconvenient Truth" will claim until I see it, but
most recent studies have shown warming from 2-8 degrees (consistent with what is depicted by the
USAToday graphic linked above).
There are lots of issues with these forecasts that occasionally might even get
mentioned in the popular press. Some issues are unavoidable, like the
inherent complexity and unpredictability of climate. Some issues probably
could be avoided, like the egregiously bad economic forecasting that drives CO2
output forecasts in many of these models. I won't delve into these issues
much, except to say that we are dealing with massively complex systems.
If an economist came up with a computer model that he claimed could predict the
market value of every house in the world in the year 2106 within $10,000, would
you believe him? No, you would say he was nuts -- there is way to
much uncertainty. Climate, of course, is not the same as housing
prices. It is in fact, much, much more complex and more difficult to
predict.
All these forecasts are created by a pretty insular and incestuous climate
science community that seems to compete to see who can come up with the most
dire forecast. Certainly there are financial incentives to be as aggressive
as possible in forecasting climate change, since funding dollars tend to get
channeled to the most pessimistic. The global warming community spends
a lot of time with ad hominem attacks on skeptics, usually accusing them of
being in the pay of oil and power companies, but they all know that their own
funding in turn would dry up rapidly if they were to show any bit of skepticism
in their own work.
Leaving aside all the other modeling problems and focus on one fact:
Most climate scientists would agree that if you focus narrowly just on the
effects of CO2 on warming, that even under the most extravagant assumptions of
CO2 production, the world will not warm more than a degree or two in total,
some of which we have already seen. The reason is that the effect of CO2
concentration on global temperature is logarithmic. This means that
increasing concentrations of CO2 have diminishing returns on temperature.
For example, if the first doubling of CO2 concentration raises temperatures by
a degree, then the next doubling may only raise it by a tenths of a
degree. This is because CO2 only absorbs sunlight and energy in certain
frequency bands and this ability to absorb energy gets saturated, much like a
pot of water can only dissolve so much salt before it is saturated.
There is fair amount of argument over just how saturated the CO2 layers are
in terms of energy absorption, but most scientists will agree that at some
point, in isolation, additional CO2 added to the atmosphere by man stops having
any significant effect on global temperature.
So how do we get these dire forecasts of 6, 7, 8 degrees of warming?
Well, I was careful to say the effect of CO2 in isolation maxes
out. To get to higher levels of warming, scientists posit "positive
feedback loops" that augment the warming effect. Positive feedback generally means that once a process gets going in a direction, there is some force that will accelerate the process
faster or farther in the same direction. Negative feedback means that
once a process is moving there is some force that tends to try to slow the process back down.
Positive feedback is a boulder balanced on the top of a mountain, where one
push will cause it to roll down the mountain faster and faster; Negative
feedback is a boulder in a valley, where despite lots of effort, the rock will
keep coming to rest back where it started.
In global warming models, water vapor plays a key role as both a positive and a negative feedback loop to climate change. Water vapor
is a far more powerful greenhouse gas than CO2. It comes into play because CO2 driven warming will
put more water vapor in the atmosphere, because greater heat will vaporize more
water. If this extra vapor shows up as more humid clear air, then this in
turn will cause more warming as the extra water vapor absorbs more energy and
accelerates warming. However, if this extra water vapor shows up as
clouds, the cloud cover will tend to reflect energy back into space and retard
temperature growth.
Which will happen? Well, nobody knows. And this is just one
example of the many, many feedback loops that scientists are able to posit but
not prove. And climate scientists are coming up
with numerous other positive feedback looks. As one skeptic put it:
Regardless, climate models are made
interesting by the inclusion of "positive feedbacks" (multiplier
effects) so that a small temperature increment expected from increasing
atmospheric carbon dioxide invokes large increases in water vapor, which seem
to produce exponential rather than logarithmic temperature response in the
models. It appears to have become something of a game to see who can add in the
most creative feedback mechanisms to produce the scariest warming scenarios
from their models but there remains no evidence the planet includes any such
effects or behaves in a similar manner.
So, is it reasonable to assume these feedback loops? First, none have
really been proven empirically, which does not of course necessarily make them
wrong. More damning is the fact that models using mostly positive feedback
loops do a terrible job of modeling the last 100 years. It is a perfectly
reasonable back check on any model to see if it predicts history. Most of the aggressive climate models (ie the ones that tend to get quoted in the press) turn out to predict a warming for the
last 50 years far above what we have actually observed, which of course might make one
suspicious of their ability to predict the future. A while back, I said
that climate scientists had a strong incentive to "claim" as much of
the 20th century warming as possible and attribute it to man. This is
why: The need to validate models that predict a lot of manmade warming
over the last 50 years that hasn't shown up. Scientists will tell you
that they have fixed these problems, but we skeptics are fairly certain they have done it by adding artificial
fudge factors of dubious scientific merit (I will confess to my embarassment that I have done exactly this when I have created industry models for a consulting client).
But one can also answer these questions about positive feedback loops from a
broader perspective. Positive feedback loops are not unknown in nature
but are much rarer than negative feedback loops. The reason is that
positive feedback loops lead to runaway processes that we seldom see in
nature. Atomic fission is one of these thankfully rare process, and one can see that it is
probably lucky our universe is not populated with many such positive feedback
processes. In our daily lives, we generally deal with negative
feedback: inertia, wind resistance, friction are all negative feedback
processes. If one knew nothing else, and had to guess if a natural
process was governed by negative or positive feedback, Occam's razor would say
bet on negative. So, what about climate? The evidence is equivocal,
but to be fair there is an example in our near universe of a runaway global
warming event - on Venus - though it occurred for reasons very different than
we are discussing with man-made climate change.
Negatives (and Positives) of Warming: While I have some trouble with
the science employed by global warming activists up to this point, it is on the
topic of the effects of global warming that the science really gets
flaky. Now, certain effects are fairly likely. For example,
hurricane activity will likely increase with warmer ocean temperatures.
Warmer ocean temperatures will also cause sea levels to rise, even without ice
melting, due to thermal expansion of the water. And ice will melt, though
there is a really broad range of forecasts.
One reason that the ice
melting forecasts are hard is because while me may talk about the world
warming a degree, the world does not warm evenly. Most climate models
show the most warming on dry winter nights (Siberian winters, for
example, get a disproportionate share of the warming). An extra summer
degree in Arizona would suck; an
extra winter degree in Siberia would probably be
welcomed, and would likely extend growing seasons.
And it is here that you get the greatest silence from warming
fanatics. Because
it should be self-evident that warming can be good and bad. Warming
can raise ocean levels and lead to droughts. It can also extend growing
seasons and increase rain. It all depends on where you are and what
forecast you are using. The only common denominator is that most official
warming reports, such as those from the UN, spend an inordinate amount of time
discussing the negatives and very little time, if any, mentioning positive
offsets. One of the reasons for this is that there is a culture in which
every environmental activist has been steeped in for years -- that man always
ruins nature. That everything man does is bad. Growth is bad.
Technology is bad. To be fair, its not that many environmental scientists
are hiding the positive offsets, it's that they have been programmed for years to be
unable to recognize or acknowledge them.
Shouldn't We Fix it, Just to Be Safe: If you get beyond the
hard core of near religious believers in the massive warming scenarios, the
average global warming supporter would answer this post by saying:
"Yes there is a lot of uncertainty, but you said it yourself:
Though the doomsday warming scenarios via positive feedback in the climate
can't be proven, they are so bad that we need to cut back on CO2 production
just to be safe."
This would be a perfectly reasonable approach if cutting back on CO2
production was nearly cost-free. But it is not. The burning of
hydrocarbons that create CO2 is an entrenched part of our lives and our economies.
Forty years ago we might have had an easier time of it, as we were on a path to dramatically cut back on CO2 production
via what is still the only viable technology to massively replace fossil fuel
consumption -- nuclear power. Ironically, it was environmentalists that
shut down this effort, and power industries around the world replaced capacity
that would have gone nuclear mostly with coal, the worst fossil fuel in terms
of CO2 production (per btu of power, Nuclear and hydrogen produce no CO2,
natural gas produces some, gasoline produces more, and coal produces the most).
Just halting CO2 production at current levels (not even rolling it back)
would knock several points off of world economic growth. Every point of
economic growth you knock off guarantees you that you will get more poverty,
more disease, more early death. If you could, politically, even
make such a freeze stick, you would lock China and India,
nearly 2 billion people, into continued poverty just when they were about to
escape it. You would in the process make the world less secure, because
growing wealth is always the best way to maintain peace. Right now, China can become wealthier from peaceful internal growth than it can from trying to loot
its neighbors. But in a zero sum world created by a CO2 freeze, countries
like China would have much more incentive to create trouble outside its borders. This
tradeoff is often referred to as a cooler but poorer world vs. a richer but
warmer world. Its not at all clear which is better.
One final statement: I have lost trust in the scientific
community on this. There are just too many statements floating around like
this one that make it clear that getting people converted to the global
warming cause is more important than getting the science right. Mann's
refusal to share his data so that his results can be validated (or invalidated,
as seems more likely now), the refusal
to consider any dissenting views in its "scientific" conferences,
the sloppy
science uncovered, the willingness to absurdly blame
every natural event on global warming -- all these create the
impression that global warming is a religion with doctrines that can't be
questioned, rather than what it actually is -- a really, really chaotic and complex area
of science we have only just begun to understand.
For other reading, probably the first place to look is the Skeptical Environmentalist by Bjorn
Lomborg. Lomborg in this book has probably the best counter-case to the
enviro-disaster stories filling the media. He has become an object of absolute
hatred among the anti-growth anti globalization fanatics who have latched onto climate
change as the key to advancing their anti-technology and anti-capitalist
political agenda. The attacks on him have become nearly as edifying about what
drives the environmental movement as his book itself. The Economist has
a nice article about his book and about the wild-eyed furious reaction of
environmental activists to it. The Economist also editorializes
here, and you can follow all the criticism and response here on Lomborg's site.
The site junkscience.com is
invaluable, in fact with a better compendium of data on climate than most
climate sites. A good
place to start is this article.
Other sources: This paper is
a good roundup of all the issues I have addressed. Cato has a lot of other
material here
as does the Heartland
Institute and at The
Commons. A great post from Silflay Hraka that is much more eloquent
(and concise) than I am is linked here.
Update: I have published a (free) more comprehensive guide to the skeptics
arguments concerning man-made global warming. You can find the HTML version here and a free pdf download here.