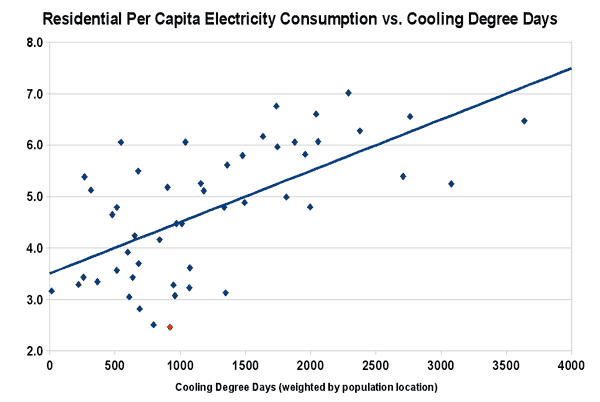
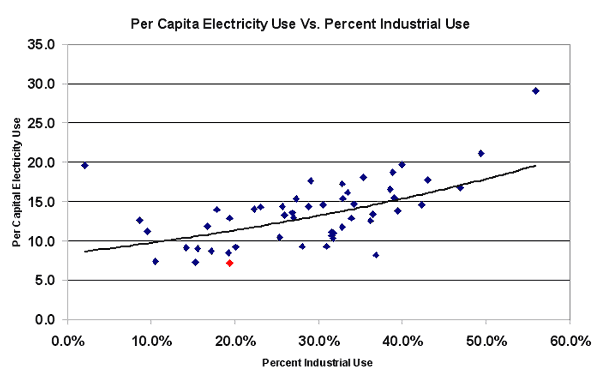
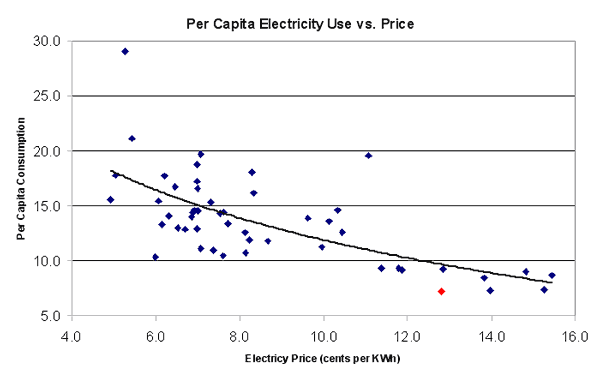
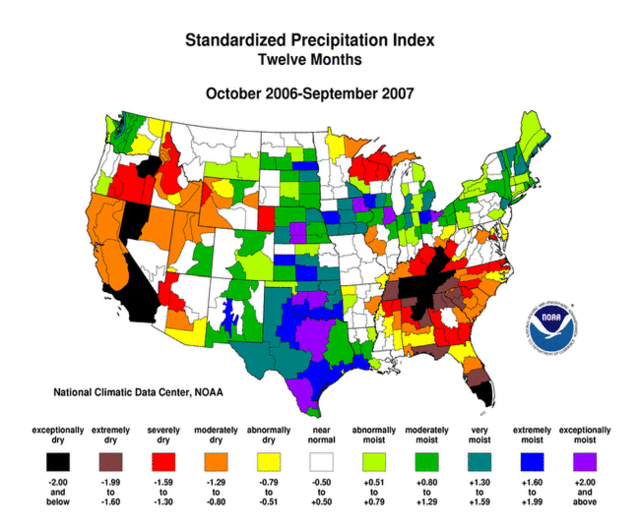
I'm Sure This Is Not In Any Way Relevant To Recent Events
Via Carpe Diem, comes this September 30, 1999 NY Times story:
In a move that could help increase home ownership rates among
minorities and low-income consumers, the Fannie Mae Corporation is
easing the credit requirements on loans that it will purchase from
banks and other lenders.The action, which will begin as a
pilot program involving 24 banks in 15 markets -- including the New
York metropolitan region -- will encourage those banks to extend home
mortgages to individuals whose credit is generally not good enough to
qualify for conventional loans. Fannie Mae officials say they hope to
make it a nationwide program by next spring.Fannie Mae, the
nation's biggest underwriter of home mortgages, has been under
increasing pressure from the Clinton Administration to expand mortgage
loans among low and moderate income people and felt pressure from stock
holders to maintain its phenomenal growth in profits.In
addition, banks, thrift institutions and mortgage companies have been
pressing Fannie Mae to help them make more loans to so-called subprime
borrowers. These borrowers whose incomes, credit ratings and savings
are not good enough to qualify for conventional loans, can only get
loans from finance companies that charge much higher interest rates --
anywhere from three to four percentage points higher than conventional
loans.''Fannie Mae has expanded home ownership for millions of
families in the 1990's by reducing down payment requirements,'' said
Franklin D. Raines, Fannie Mae's chairman and chief executive officer.
''Yet there remain too many borrowers whose credit is just a notch
below what our underwriting has required who have been relegated to
paying significantly higher mortgage rates in the so-called subprime
market.''Demographic information on these borrowers is
sketchy. But at least one study indicates that 18 percent of the loans
in the subprime market went to black borrowers, compared to 5 per cent
of loans in the conventional loan market.In moving, even
tentatively, into this new area of lending, Fannie Mae is taking on
significantly more risk, which may not pose any difficulties during
flush economic times. But the government-subsidized corporation may run
into trouble in an economic downturn, prompting a government rescue
similar to that of the savings and loan industry in the 1980's.''From
the perspective of many people, including me, this is another thrift
industry growing up around us,'' said Peter Wallison a resident fellow
at the American Enterprise Institute. ''If they fail, the government
will have to step up and bail them out the way it stepped up and bailed
out the thrift industry.''
Those heartless free marketing guys at the AEI -- always predicting doom every time we open our hearts to poor people. Bailout? What ridiculous scare-mongering.