Cool Places I Didn't Know Existed
Via Scouting NY, restored 19th century domed West Baden Springs Hotel. In southern Indiana. I am amazed I never heard of it, because I used to run campgrounds almost next door to it.
Dispatches from District 48
Posts tagged ‘NY’
Via Scouting NY, restored 19th century domed West Baden Springs Hotel. In southern Indiana. I am amazed I never heard of it, because I used to run campgrounds almost next door to it.
From JM Berstein in the NY Times, via Kevin Drum, this is about Tea Partiers, but since it addresses the Tea Party distrust and disdain for government, I suppose it applies equally well to we libertarians:
My hypothesis is that what all the events precipitating the Tea Party movement share is that they demonstrated, emphatically and unconditionally, the depths of the absolute dependence of us all on government action, and in so doing they undermined the deeply held fiction of individual autonomy and self-sufficiency that are intrinsic parts of Americans' collective self-understanding.
....This is the rage and anger I hear in the Tea Party movement; it is the sound of jilted lovers furious that the other "” the anonymous blob called simply "government" "” has suddenly let them down, suddenly made clear that they are dependent and limited beings, suddenly revealed them as vulnerable.
Do you get that - we oppose the overwhelming size of government not for any rational reason, but out of a psychological need to deny that the government is inevitably going to grow larger and increase its control over our lives. This is so absurd it is freaking hilarious. This is what Louis the XVI's sycophants were telling him to make him feel better in 1789. I mean, after 200 years of only limited government interference in health care, how is it that a law passed over majority opposition for government takeover of healthcare somehow "demonstrates the absolute dependence of us all on government action?" Why doesn't it reasonably demonstrate the depth of risk we all face from a minority who have constantly through history been bent on wielding power over us.
Kevin Drum, sort of to his credit, rejects this thesis in favor of his own
So then: why have tea partiers gone off the rails about the federal deficit? It's not because of something unique in their psyches. And it's not because they're suddenly worried that America is going to go the way of Greece. (The polls I linked to above show that tea partiers care more about cutting taxes than reducing the size of government.) It's because they're the usual reactionary crowd that goes nuts whenever there's a Democrat in the White House and they're looking for something to be outraged about
So while he rejects the goofy psychobabble, he accepts the underlying premise, that any opposition to expansion of government and its power of coercion over individuals is irrational.
So take your pick -- libertarians are either a) advocating limited government only as a psychological crutch to hide from ourselves that Obama is really our daddy or b) scheming reactionary nuts. Whichever the case, remember that there can be no principled opposition to Big Brother.
From the NY Times, I am having a hard time reconciling these statements from the same article:
First statement:
The law provides a partial exemption for certain health plans in existence on March 23, when Mr. Obama signed the legislation. Under this provision, known as a grandfather clause, plans can lose the exemption if they make significant changes in deductibles, co-payments or benefits.
About half of employer-sponsored health plans will see such changes by the end of 2013, the administration says in an economic analysis of the rules.
Second statement:
About 133 million Americans are in group health plans from employers with 100 or more employees, the administration said, and most "will not see major changes to their coverage as a result of this regulation."
My translation: Yes, you will lose your current health plan despite Obama's promises, but he doesn't want you to realize this until 2013, conveniently just after the next presidential election.
Rep. Jose Serrano is firing a brushback pitch at the state of Arizona for passing a strict new immigration law
Seeking Major League retribution, the Bronx Democrat will ask big-league baseball Commissioner Bud Selig to move the 2011 All-Star Game from Phoenix. Serrano will make his request to the commissioner in a letter to be sent later today.
I have made it pretty plain I don't like AZ's new immigration law, but this is silly. While overly authoritarian, it is no more so than any number of cash confiscation or stop and search laws on the books in other states. I am pretty sure Arizona could remain standing in a head-to-head fight between AZ and NY on whose laws are the most authoritarian. A Representative of a city that bans trans fats, zones to exclude certain fast food restaurants, has proposed a salt ban and initiated a campaign against soft drinks needs to get his own authoritarian house in order.
Over five years ago, I wrote this article about retirees in RV's who have become the new American nomads. Many of these folks work for my company each season, getting wages and a camping site in exchange for taking care of campgrounds. This is often called work camping.
A reader sent me this video from the NY Times discussing the same phenomenon (here is the print article). The only difference is these folks work for the government, which means that unlike at private companies, they don't get paid. I find it kind of fascinating that the NY Times thinks it's a wonderful innovation that "cash-strapped state governments" help balance the budget on the backs of free labor from older people. Can you imagine what the headlines would be if all the facts were changed, but the entity was a manufacturing company rather than a state park? It would have been torches and pitchforks (it is illegal except in narrow cases for private companies to accept free labor -- the government of course exempts itself from this requirement, as it does from much of labor law).
I actually think my article was better. The way work campers tend to disperse over the summer and then congregate over the winter in a couple of gathering spots (Colorado River in AZ, South Texas, Florida) reminds me a lot of the plains Indian tribes. And the challenges of a nomadic lifestyle when the world wants you to have a permanent address are interesting, and there are whole business models being crafted to solve these problems.
Anyway, our company hires nearly 500 of these folks every year, and are huge supporters of this lifestyle (and we pay!) If you are interested, check out our websites above and sign up for our job newsletter.
Paul Krugman in the NY Times, Via Todd Zwycki
The truth is that given the state of American politics, the way the Senate works is no longer consistent with a functioning government. Senators themselves should recognize this fact and push through changes in those rules, including eliminating or at least limiting the filibuster. This is something they could and should do, by majority vote, on the first day of the next Senate session.
Don't hold your breath. As it is, Democrats don't even seem able to score political points by highlighting their opponents' obstructionism.
It should be a simple message (and it should have been the central message in Massachusetts): a vote for a Republican, no matter what you think of him as a person, is a vote for paralysis.
OK, sign me up.
From the NY Times, June 23, 2005
Mr. Bush has reacted by railing against Democrats for obstruction -- as if Democrats are duty-bound to breathe life into his agenda and, even sillier, as if opposing a plan that the people do not want is an illegitimate tactic for an opposition party.
Kevin Drum writes a post that I would interpret as saying "I really can't dispute the Supreme Court speech decision on principles but I am going to anyway because I don't like the result. He ends by saying
In the end, I guess I think the court missed the obvious "” and right "” decision: recognizing that while nonprofit corporations created for the purpose of political advocacy can be fairly described as "organized groups of people" and treated as such, that doesn't require us to be willfully oblivious to the fact that big public companies are far more than that and can be treated differently. Exxon is not the Audubon Society and Google is not the NRA. There's no reason we have to pretend otherwise.
This is silly. Just because people are not organized primarily as an influence group does not mean that those folks, once they are pursuing their goals, don't find the need to try to have influence, or have somehow given up their right to try to have influence. And whose fault is this anyway if Exxon shareholders feel the need to influence the political process? If the Left hadn't targeted commerce with a never-ending proliferation of restrictions and wealth-confiscations, commercial enterprises probably would not see much reason to waste money on advocacy. I can tell you that the last possible thing I want to spend money on in my company is kissing some Senator's ass or buffing up the NY Times ad budget, and would spend money to do so only under a pretty existential threat.
But why is there some mythology that members of Audubon or the NRA somehow have more control of the organization's advocacy than Exxon's shareholders? Sure, when you join the NRA you probably have a good idea what their positions are going to be, but are you really any less able to predict Exxon's positions on most issues? As I wrote in his comment section:
When you say "Exxon is not the Audubon society," I am not sure how? I am a stockholder of the first and a member of and contributor to the second. I have bought products from both. I have written both (well, actually I wrote Mobil once but it is the same now as Exxon) about their issue advocacy, each time with equally small effect. It is as difficult as a stockholder of Exxon to even get a disclosure of their issue advocacy and lobbying efforts as it is for Audubon (though I am smart enough to take a pretty good guess at both). Neither allows me, as a shareholder/member/contributor to vote on their advocacy/lobbying, either in terms of amount spent or direction. Each carry substantial influence in particular government realms.
So I am confused how they are different, except perhaps that you are personally sympathetic to one and not the other.
Just to remind you the existential threat that causes corporations to want to speak out in public, I will take an example from Drum himself, when he said:
It means the health insurance industry is scared that we might actually do something in 2009 and they want to be seen as something other than completely obstructionist. That means only one thing: they've shown fear, and now it's time to bore in for the kill and gut them like trouts. Let's get to it.
So I guess Exxon is indeed different from the Audubon Society - no one is trying to gut the Audubon Society like trouts.
One aspect of the recent debate about the Supreme Court's Citizen's United decision that really irritates me is the notion, propounded by the NY Times among others, that corporations and the individuals assembled in them do not have free speech rights because corporations are "state-created entities."
This is wildly untrue, or alternatively, if you accept the logic, then nearly every aspect of our lives is state-created. Take your pick. Basically, the argument is that because the government has set the rules for corporate incorporation, and that these incorporations require state approval, that makes corporate entities "state-created." But corporations are nothing more than a structure by which people can assemble and aggregate their capital and share ownership of an enterprise that employs that capital. If government incorporation law did not exist, individuals still would have the incentive to assemble in some sort of entity.
I don't know of anything in the corporate structure that could not be duplicated with contract terms. People point to the liability limitation as some sort of government gift to the corporate world, but that could easily be written in to every contract of, say, a partnership (certain torts are an exception I would have to think about). Vendors might choose not to accept such contracts, preferring to be able to pierce the partnership to go after individual owners to settle debts, but that choice exists today. I have many, many vendor contracts in my corporation, and nearly all of my bank loans, that require the personal guarantee of all the owners, effectively waiving the liability limitation for those transactions.
My point, though, is that corporate forms have evolved as they are because that is what the sum of investors and business people were working towards on their own, and government merely enshrined these forms into law. In fact, this basic rules-setting of the contracts playing field is one of the few arguably useful things government has done. If we allow government rules-setting over certain activities to be the test of whether it can further restrict our Constitutional rights, then nearly every aspect of our lives would be subject to such restrictions.
At its heart, this is the classic "heads I win, tails you lose" argument of statists. They claim that individuals must petition the state to register their corporation and license their business, and then use the fact of these required registrations to argue that the business is a "state-created entity" and that individuals give up their ability to exercise their rights when assembled into these entities. By the same logic, the fact that every commercial transaction is subject to license and taxation by the state would make our every transaction a "government-created exchange." Think I am exaggerating? Just look at this from our Arizona state web site:
The Arizona transaction privilege tax is commonly referred to as a sales tax; however, the tax is on the privilege of doing business in Arizona and is not a true sales tax. Although the transaction privilege tax is usually passed on to the consumer, it is actually a tax on the vendor.
Rights, like the ability of free exchange between individuals, supposedly can't be revoked, but privileges can. Thus the name. For folks who treasure individual liberty, we have already lost the battle when we allow the state this kind of language.
Anyway, I feel like I am having a failure of eloquence over this issue. Ilya Somin got me started thinking about these issues, so I will turn it over to him here.
Third, it's important to consider what is meant by "state-created entity." If the term refers only to institutions that literally would not exist absent state authorization, it does not accurately characterize many, perhaps most corporations. If the federal government passed a statute abolishing corporate status tomorrow, most actual corporations would still exist and still continue to engage in the same business or nonprofit activities. They just would do so under different and perhaps less efficient legal rules (maybe as LLCs, partnerships, or sole proprietorships). But they wouldn't all just collapse or go away. There would still be a demand for most of the products produced by corporations.
If "state-created entity" doesn't refer to the mere existence of organizations currently defined as corporations but to the particular bundle of legal rights currently attached to the corporate form, then it turns out that virtually all other organizations are state-created entities as well. Universities, schools, charities, churches, political parties, partnerships, sole proprietorships, and many other private organizations all have official definitions under state and federal law. And all have special government-created privileges and obligations that don't apply to other types of organizations.
Even individual citizens might be considered "state-created" entities under this logic. After all, the status of "citizen" is a government-created legal entitlement that carries various rights and privileges, many of which the government could alter by legislation, just as it can with those of corporations (e.g. "” the right to receive Social Security benefits, which the Supreme Court has ruled can be altered by legislation any time Congress wants). In that sense, "citizens" are no less "state-created" entities than corporations are.
By the way, in case I was not careful with my language, I offer the same proviso as does Somin:
I should clarify that in this post, as before, I'm not arguing that corporations themselves are "persons" with constitutional rights. Rather, I'm asserting that their owners and employees are such persons and that that status enables them to use corporations to exercise their constitutional rights. Similarly, partnerships, universities, schools, and sole proprietorships aren't people either. But people can use them to exercise their constitutional rights, and the government can't forbid it on the sole ground that they are using assets assets assigned to "state-created entities." This distinction was unfortunately obscured in the current post by my shorthand references to "corporations'" rights. I only used that terminology because it's cumbersome to always write something like "people exercising their constitutional rights through corporations."
It is not often that the NY Times will question the long-term consequences of any Democratic program ostensibly aimed at mitigating a short-term need. So I don't want to fail to highlight this:
The Obama administration's $75 billion program to protect homeowners from foreclosure has been widely pronounced a disappointment, and some economists and real estate experts now contend it has done more harm than good.
Since President Obama announced the program in February, it has lowered mortgage payments on a trial basis for hundreds of thousands of people but has largely failed to provide permanent relief. Critics increasingly argue that the program, Making Home Affordable, has raised false hopes among people who simply cannot afford their homes.As a result, desperate homeowners have sent payments to banks in often-futile efforts to keep their homes, which some see as wasting dollars they could have saved in preparation for moving to cheaper rental residences. Some borrowers have seen their credit tarnished while falsely assuming that loan modifications involved no negative reports to credit agencies.
Some experts argue the program has impeded economic recovery by delaying a wrenching yet cleansing process through which borrowers give up unaffordable homes and banks fully reckon with their disastrous bets on real estate, enabling money to flow more freely through the financial system.
"The choice we appear to be making is trying to modify our way out of this, which has the effect of lengthening the crisis," said Kevin Katari, managing member of Watershed Asset Management, a San Francisco-based hedge fund. "We have simply slowed the foreclosure pipeline, with people staying in houses they are ultimately not going to be able to afford anyway."
Every one of these members of the House Subcommittee on Commerce, Trade, and Consumer Protection voted to pass this absurd law out of committee except Rep. John Barrow, D-Ga.
Bobby L. Rush, Illinois, Chairman
Jan Schakowsky, IL, Vice Chair George Radanovich, CA, Ranking Member John P. Sarbanes, MD Cliff Stearns, FL Betty Sutton, OH Ed Whitfield, KY Frank Pallone, Jr., NJ Joseph R. Pitts, PA Bart Gordon, TN Mary Bono Mack, CA Bart Stupak, MI Lee Terry, NE Gene Green, TX Sue Wilkins Myrick, NC Charles A. Gonzalez, TX John Sullivan, OK Anthony D. Weiner, NY Tim Murphy, PA Jim Matheson, UT Phil Gingrey, GA G. K. Butterfield, NC Steve Scalise, LA John Barrow, GA (voted NO!)
Doris O. Matsui, CA Kathy Castor, FL Zachary T. Space, OH Bruce L. Braley, IA Diana DeGette, CO
Hat tip: Don Boudreaux
Via Flowing Data, a cool chart in the NY Times with every batter faced by Rivera in the playoffs.
We can't just say everybody can go everyplace and do anything they want.
To his final query, I do work in a building without security and I am fine, thank you.
I couldn't really get up enough energy to post about the whole Van Jones kerfuffle. Apparently, as one of Obama's 129 czars, this guy whose job it is to redistribute billions of dollars from one group of individuals to another and issue diktats to be followed by private citizens and businesses, is *gasp* a communist. Well, no sh*t. All of these various czars have communist roles so why is it surprising Obama might have picked a communist to hold one of them. The only surprise was that Van Jones was dumb enough to admit it in print rather than hiding it in leftish double-speak like most of the rest of the administration.
Anyway, all that aside, you gotta love the NY Post, which has no problem dropping any pretense of statesmanship and is perfectly willing to skewer its cross town rival. This editorial is pretty dang funny. An excerpt:
Newspaper of record? The Times isn't so much a newspaper as a clique of high school girls sending IMs to like-minded friends about their feuds and faves and raves and rants. OMFG you guys! It's no more objective than Beck is....
The Times continues to treat communism as a cute campus peccadillo like pot smoking or nude streaking. A Times think piece (Sept. 9) worried that Jones' fall was "swift and personal." Being a communist is personal but being the pregnant teen daughter of a vice presidential candidate is public business?
In a quasi-related post, Virginia Postrel says the Washington Post lost $1.10 per copy of their newspaper last quarter. Wow!
I have to disagree with Ed Driscoll, though. He like many conservatives argues that this economic problem of newspapers is somehow because the Times has dropped its objectivity. I am not sure anyone has evidence that is true. One could make, I think, an equally strong case that the Times should be less objective and go openly partisan. After all, this notion of politically neutral newspapers is a pretty recent phenomenon in the US.
I actually think the problem with newspapers like the Washington Post is the "Washington" part. Local business models dominated for decades in fields where technology made national distribution difficult or where technology did not allow for anything but a very local economy of scale. Newspapers, delivery of television programming, auto sales, beverage bottling and distribution, book selling, etc. were all mainly local businesses. But you can see with this list that technology is changing everything. TV can now be delivered via sattelite and does not require local re-distribution via line of sight broadcast towers or cable systems. Amazon dominated book selling via the Internet. Many of these businesses (e.g. liquor, auto dealers, TV broadcasting) would have de-localized faster if it had not been for politicians in the pocket of a few powerful companies passing laws to lock in outdated business or technological models.
Newspapers are ripe for a restructuring. How can one support a great Science page or Book Review section or International Bureau on local circulation? How much effort do the NY Times, Washington Post, LA Times, SF Chronicle, etc. duplicate every day? People tell me, "that's what the wire services are for." Bah. The AP is 160 years old! It is a pre-Civil War solution to this problem. Can it really be that technology and changing markets have not facilitated a better solution?
The future is almost certainly a number of national papers (ala the WSJ and USA Today) printed locally with perhaps local offices to provide some local customization or special local section. Paradoxically, such a massive consolidation from hundreds of local papers to a few national papers would actually increase competition. While we might get a few less stories about cats being saved from trees in the local paper, we could well end up not with one paper selection (as we have today in most cities) but five or six different papers to choose from (just look at Britain). Some of these papers might choose to sell political neutrality while some might compete on political affiliation.
If I were running the Washington Post, I would think very seriously about creating a national news offering, a USA Today with substance. If you offered me a Washington Post re-branded as a national paper, with some strong side offerings like the NY Times Science section and a good local sports section and a local news section, I'd toss my Arizona Republic in a second. Its going to take some good thought as to how to weave together the national offering with locally customized content and to manage local vs. national advertising accounts, but with technology this is doable -- Clear Channel does something similar in radio.
I wonder, in fact, why no one has done this yet -- when you look at the circulation numbers, only the USA Today and WSJ, the two papers pursuing this path, are seeing growth. My only thought is that news is one of those businesses dominated by passionate people who are tied deeply, emotionally into the industry in a way that makes it impossible to envision or consider new models (aviation is another such business, in my opinion, and the US auto business is probably another). What we need is for the Post and a few other major papers to fail and then let some really bright, right people from outside the business come and shake it up. This is, by the way, one of the unsung benefits of bankruptcy, is that it takes assets out of the hands of the people who got the company in the mess to begin with -- a benefit we short-circuited when we spent billions of taxpayer dollars in the auto industry to keep GM and Chrysler assets out of new and potentially more innovative hands.
I am always amazed at the lengths to which some folks will try to put lipstick on the light rail pig. One example I found today. Michael Graham Richard wrote on treehugger in June:
The sprawling city of Phoenix, of all places, is showing us how light rail should be done. They just opened a 20 mile line with 28 stops last December, and ridership statistics are beating all forecasts (evidence that the same might be true in other cities where they are afraid to invest because their forecasts are too low) with 40,000 daily riders instead of the 25,000 expected.
But here are the ridership figures from Valley Metro, who runs Phoenix Light Rail. This is weekday ridership (actually number of daily boardings) -- weekend ridership is much less:
It is hard to see where one gets a 40,000 figure, especially since a true daily rider/boarding figure would have to average in the lower Saturday/Sunday numbers.
And who cares if it meets some sandbagged forecast or not? Is 40,000 even a reasonable number? Note that even at the higher 40,000 figure this implies just 20,000 round trip customers. This higher ridership number would still make the capital cost of the $1.4 billion line to be $70,000 per round trip rider, and ABSURD subsidy.
Update: The ridership numbers will likely pick up when Arizona State is back in school. ASU and the baseball stadium are about the only major destinations on the line through dispersed, low-density Phoenix (it goes through our "downtown" but that is not saying much -- it is not a big center of employment). Did we really build light rail as another subsidy for ASU students?
Update #2: Let's say there are 50,000,000 big city commuters in the US in cities outside of Boston/NY/Chicago with large transit systems. Serving these commuters at $70,000 each would create a capital cost of $3.5 trillion for light rail. Who on the planet really thinks this is reasonable? Sure, you would get some network effects as you built out lines that increased ridership, but these would be offset by diminishing returns (presumably the first Phoenix line was built on the most promising corridor, and all future corridors will be less promising).
To some extent, there are signs Obama may be willing to walk back health care "reform" to just insurance "reform," though the two are highly related. As a minimum, insurance "reform" is likely to include rules that no one can be denied coverage, community rating, and minimum covered service requirements.
These are really, really expensive. Megan McArdle on the NY experience:
John Cole takes me to task for not knowing that health insurance premia have tripled in New York State. Indeed, he's right--I should have checked.
But this is not the "gotcha" the left believes. I erred so low because I was trying to be charitable to the cause of national health care. You see, the reason that insurance premia are so high in New York State is that New York State enjoys community rating, guaranteed issue, and a very generous bevy of mandatory services. The result is that the cost of insurance is very, very high. What I failed to realize was just how radically out of line New York's rules had pushed its health care costs. The average premium across the United States has increased about 25% since 2004. In New York, the rate of inflation has apparently been about 16 times that. I wasn't "aware" that insurance premiums have doubled and tripled over the last seven years, because for the country as a whole, this isn't true.
McArdle is sometimes irritating in bending over backwards to be fair to folks whose views don't deserve such charity and who would not ever extend the same favor back at her. So it is kind of fun to see her going a bit postal over the last few days.
The NY Post has a very good editorial on the health care bills (HT: Q&O). Too much good stuff to excerpt, it includes even more crazy provisions in the House and Senate bills I had not seen yet (its like a scavenger hunt as people go through the 1000 pages, or maybe more like searching for landmines).
But since the bill doesn't even start taking effect until 2013 (except for the higher taxes, which come earlier, of course), we have to really really rush and make sure its approved before the August recess (and before critics are able to actually read the thing - no chance those in Congress will read it, ever). Also, its such a burning problem, it just must be solved now, as evidenced by...
The most recent ABC News/Washington Post poll (June 21) finds that 83 percent of Americans are very satisfied or somewhat satisfied with the quality of their health care, and 81 percent are similarly satisfied with their health insurance.
They have good reason to be. If you're diagnosed with cancer, you have a better chance of surviving it in the United States than anywhere else, according to the Concord Five Continent Study. And the World Health Organization ranked the United States No. 1 out of 191 countries for being responsive to patients' needs, including providing timely treatments and a choice of doctors.
I have written a number of times, the fact that we spend more on health care is not a bug, its a feature. We are the wealthiest nation on earth, and there is only so much we can spend on food, clothing, shelter, plasma TV's and other necessities. We choose to spend a lot of that extra money on our health and longevity. Why is that a bad decision?
I thought this Kenneth Chang column in the NY Times was pretty interesting. Much like we can sometimes spot plagiarism by spotting where spelling errors have been reproduced, apparently errors in our DNA give clear pointers to our evolution from other species.
All my complaints about the NY Times not-withstanding, I think if the Times were to disappear, I would miss their science reporting the most.
Krispy Kreme in the Harrod's food court.

What's next? Page 3 girls at the NY Times? Well, it couldn't hurt...
A reader sent me this, and I found it pretty funny:
Minnesota Public Radio and two neighboring churches in downtown St. Paul are escalating their opposition to the proposed line.
MPR said noise and vibrations from the train, connecting Minneapolis and St. Paul, could harm their ability to record and broadcast. The churches say those very same effects could rattle their aging buildings and disrupt their worship services.
In the latest salvo, MPR has asked the project planners to study alternative routes through downtown St. Paul.
MPR and the churches say they support light-rail, but not the proposed route along Cedar Street. The tracks would be laid about 14 feet from the front door of the broadcast center.
"As far as we know, this is the closest a light-rail line will run to federally designated noise- and vibration-sensitive facilities anywhere in the country," said Jeff Nelson, public-affairs director for MPR.
I am not sure a comment is even necessary. MPR has published any number of light rail stories about budget and approval battles that were thinly disguised cheerleading for light rail. Take this article for example, which discusses how light rail might be saved from trouble, but because it only quotes light rail supporters, a reader can't even figure out why the trouble exists.
Basically, MPR is saying "please put the rail line, which we support, near someone else who may hate it being nearby as much as we but don't have the access to the media and the political process to make a big stink about it." Already, the line has apparently made an expensive accommodation for just one organization -- the University of Minnesota, a state agency. The arrogance of this is staggering. It reminds me of the NY Times and Columbia University, both of whom claim to be advocates for the underdog, except when the underdog gets in the way of their real estate deal and eminent domain grab.
By the way, am I the only one who has never heard of a federal designation for "noise- and vibration-sensitive facilities?" If such a designation really exists (and I sure can't find it with any similar search terms on Google), what percentage of the list would you guess is politically connected organizations using the designation to get privileged treatment vs. those without power?
Update: The "federally designated" thing is a bit of an exaggeration. The PR department of MPR was kind enough to send me a link. They are referring to the category 1 designation in this report, which merely says that amphitheaters and recording studios should be in the quietest category when assessing impacts of transit nearby (neither MPR or any other facility is mentioned by name). This same report essentially comes to the conclusion that it is perfectly possible for light rail to be near to recording studios and amphitheaters, just that some care needs to be taken in design.
By the way, the "As far as we know, this is the closes a light-rail line will run to" such a facility is just nuts. I guess the "as far as we know" covers them from outright fraud, but I have to look no further than my own town of Phoenix to find light rail in proximity to such venues. I know of a few radio stations and TV stations right on the rail line, but a quick Google maps search found at least 9 radio stations and TV stations and recording studios right on just the Central Avenue portion of the route. In addition, I know of at least 5 ampitheaters on the route, not to mention our main public library. (In fact, the library is right near the intersection of the rail line and Interstate-10, and I find it perfectly quiet there). In fact, I would challenge MPR to identify one urban passenger rail line where there is NOT a radio station, TV station, recording studio, or ampitheater in close proximity.
Activists are always making exaggerated statements on current problems and extrapolate these into forecasts of doom. One thing activists really, really hate is when people come back later and hold them accountable for these forecasts. You can see it as NASA officials squirm and fire off condescension at skeptics who have the temerity to actually check their global warming forecasts against actual temperatures.
If I had a newspaper, I'd have a special regular feature where I dig back 10-20 years in my archives to find such forecasts of doom and check them against reality (actually, if I had a paper, I would not allow activist's press releases to show up virtually unedited as "news" stories, but that is another matter). Heck, I could have a regular feature just reality-checking old Paul Ehrlich forecasts.
Well, I don't have a newspaper, but I do have a blog, and this is a new feature I am working on. I am still trying to play with various search engines and news libraries (such as the NY Times) to see if I can come up with some kind of query format that efficiently digs up such predictions that are at least 10 years old. I am still a little stumped on this, but I am working on it.
But, as a sort of beta-test of the feature, one such comparison fell into my lap today. I remember my feminist wife reading a book published in 1994 called "Failing at Fairness." This work was a big, big deal at the time. Media such as the NY Times fawned on it. I will let a 1994 review on the Society for Women Engineers' site summarize the book:
Failing at Fairness: How American Schools Cheat Girls eloquently describes the results of years of research into sexism in schools. The study began as an examination of gender bias in textbooks, and evolved into a decade of painstaking classroom observation uncovering a "hidden curriculum" in classroom interaction. Authors Myra and David Sadker present a compelling tale of gender bias in education at all levels.
Taken at face value, the book more than proves the point of the subtitle: our schools cheat girls out of an education equal to that received by boys. The authors do an excellent job of pointing out some of the more subtle ways of favoring boys over girls. However, so many descriptions of incidents of sexism -- blatant, subtle, by old teachers, young teachers, male teachers, female teachers, and even by one of the Sadkers' own "trained" researchers -- are included that it can seem like overkill at
times. In addition, the wealth of statistics can be overwhelming, and yes, even slightly depressing.One of the more horrifying aspects of Failing at Fairness is the discussion about standardized tests, their historical deliberate design as culturally biased for exclusionary purposes, and the dive in the scores received by girls as they progress through their education.
Current standardized test administrators claim to be more sensitive to cultural prejudices in today's tests, although minority students still score less than white students (at least on the SAT). Also, the book states quite plainly, "Regardless of ethnic or racial background, all American girls share a common bond: a gender gap in test performance that leaves them behind the boys." The prevailing opinion of the discussion group is that the tests are still exclusionary; they are not measuring achievement, but are rather reflecting the way students are taught.
I don't doubt that they found their share of anecdotal issues. I am sure I could find them today. But their overall premise that girls were getting hosed by primary education and that standardized tests were structured to exclude girls from college education made no sense even at the time the book was published:
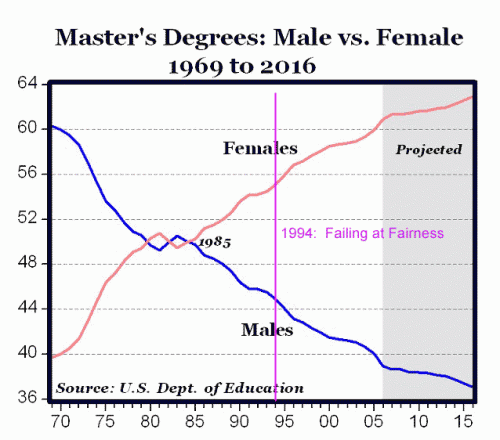
The chart is from Mark Perry, and he shows a similar picture for bachelor's degrees, where women blew past men in 1981, and in PHDs, where women passed men in 2006. People would laugh at this book today, as most discussion is about under-performance of boys.
I don't know the authors, but I would interpret this as the classic inability of activists to declare victory. I am fairly certain that their hypothesis was far more correct in 1969 than in 1994. But society really went through a step-change in the 1970s vis a vis attitudes about females. The previous generation of women's activists did great work to make these issues plain and help lead change in societal attitudes.
But activists have a really hard time declaring victory. From a quite personal standpoint, declaring victory as an activist is exactly the same as walking into your boss and telling him that the company really doesn't need your job position. Money, prestige, academic advancement, and attention, and (self-esteem, for certain types of people) are all tied to there being a major problem. If there is no longer a big problem, then all this stuff goes away.
Recent circulation numbers showing continued, substantial declines of traditional newspapers give me an excuse to make a point I have wanted to make for some time.
I am a frequent critic of newspapers. I think they have lost focus on the hard-hitting investigative journalism which used to be their highest and best calling, instead considering reiteration of an activist's press release sufficient to check the journalism box on some particular issue. When investigative reporting does occur, it almost always is focused to support the dominant or politically correct outcome, rather than to really challenge conventional wisdom. Media coverage of any technical issue involving science or statistics or economics is often awful, in large part because journalism is too often the default educational path of folks who want to avoid numbers. Any time I have been on the inside of some issue receiving coverage, I have generally been astounded by how little the print descriptions matched reality. Now that I am interviewed more as a source for articles, I never think my views are well-quoted (though that may be my fault for not talking in sound bites). And, like many, I get irritated that the media's arrogance and self-referential reporting seems to increase in direct proportion to their drop in circulation.
All that being said, the world without healthy newspapers is a bad thing.
First, we bloggers can blather on all day about being the new media, but with the exception of a few folks like Radley Balko, we're all editorial writers, not reporters (I consider my role at Climate-Skeptic.com to be more like journalism, but only because there is such a glaring hole on that topic in traditional media). I couldn't do what I do here, at least on this particular blog, without the New York Times and the Washington Post. I'm a remora feeding on their scraps. I can't bring down the big fish by myself, I can only feed on the bits they miss.
Second, and perhaps more important in this world of proposed reinstatement of the Fairness Doctrine, print media is the mode of speech best protected by the First Ammendment. This isn't the way it should be -- all speech should be equal -- but in reality goofy regulatory regimes for radio, TV, and even the Internet all offer the government leverage points for speech control they don't have with the print media. It's why half the dystopic sci fi novels out there have a world dominated by TV -- because that is where government has the most control of speech.
So here's hoping you guys at the NY Times get your act together.
Yeah, I think the title is worded awkwardly, but I am trying to curb my enthusiasm for ending sentences with prepositions (I will continue to boldly split infinitives that no man has split before).
Anyway, in the spirit of this post and this one, I try from time to time to reinforce my support for free speech as an absolute right by publicly supporting the speech rights of those with whom I disagree. Today's case is the public University of Nebraska-Lincoln deciding to un-invite former terrorist William Ayers to speak on campus. The reason given was the current weak-ass excuse often used to reverse the invitation of controversial speakers, "we can't gaurantee security."
Though I would never have hired the guy, Ayers is a professor at a real public university, and what he has to say is particularly relevant given his ties to Barack Obama. I find the behavior of Nebraska's conservative politicians to be especially absurd here -- after months of calling for more discussion and disclusore of Ayers and his ties to Obama, they want to prevent Ayers from speaking publicly?
Update: In an odd coincidence, at about the same time I was writing this post, the NY Times blog was posting on split infinitives.
The media is really bending over backwards to find ways to twist earnings data for average Americans to try to make the point that real income for many folks has stagnated or dropped. They are doing this to support a two-pronged legislative strategy in the next Obama administration:
They are firing on all cylinders behind this strategy. They are even mobilizing the neo-Keynesians to make the pitch that the Great Depression and the current financial crisis were caused by a shift in wealth from laborers to the capital classes, and that the only way to prevent future crises and depressions is to, wait for it, increase the power of unions and institute more wealth redistribution (Example here, via Kevin Drum).
I was going to do a post fisking the James Livingston article linked above on Kevin Drum's site, but Livingston's hypothesis was such a mess that it was just going to take too much of my day. But in doing some research, I found this chart from a couple of years ago in the NY Times that really caught my attention:
Talk about chutzpuh -- look at the lede on the chart and then look at the chart itself. Yes, the lede is correct, but only if you choose the totally meaningless number of "cash wages" rather than total compensation. If one looks at total compensation (or what they call "overall" compensation), the entire argument falls apart. Workers have maintained about their same "share" of the economy.
Sure, a large percentage of that is now in health care benefits, but that's a choice workers have made (and the government has encouraged through tax policy). In fact, this compensation mix has been driven in large part by the Left's beloved unions, so on what basis can folks say that these other benefits somehow "don't count?" Certainly, they cost their employers equally, whether it is cash or health care. Corporate profits are up a bit, but in line with their normal historical levels in the 1950s and 1960s, the golden age of the US economy, according to the Left. (By the way, the pattern of falling wage shares and rising profit shares after recessions is a well-documented one. Wage-earners do best at the end of an economic cycle, employers more towards the beginning. The chart cut off after 1997 would look about the same as the last several years).
I will tell you right now that every time you hear someone bemoaning the stagnation of wages, they will never, ever, ever be talking about total compensation per individual. Having, through government policy and union activity pushed the compensation mix to non-cash elements, they then play a heads-I-win-tails-you-lose game of not giving any credit for those compensation elements.
Other games that are played to try to make the case that real earnings have stagnated include:
Saul Hansell at the NY Times has an interesting article about why risk assessment programs in investment banks were not sounding the alarm coming into the recent turmoil. The article contains this gem:
Ms. Rahl said that it was now clear that the computers needed to
assume extra risk in owning a newfangled security that had never been
seen before."New products, by definition, carry more risk," she said. The models
should penalize investments that are complex, hard to understand and
infrequently traded, she said. They didn't.
I continue to see parallels between recent problems and the meltdown at Enron. In fact, in many ways events in the natural gas trading market were a dry run for events in the mortgage market. One filmmaker coined the phrase "Smartest Guys in the Room" to describe the hubris of the guys who ran Enron. To some extent the phrase was absolutely true - I knew Jeff Skilling at McKinsey and he was indeed the smartest guy in the room. But everyone can be wrong, and sometimes the smartest guys can be spectacularly wrong as they overestimate their ability to predict and control complex events. I think this is a fair description of what went on in Wall Street over the past several years.