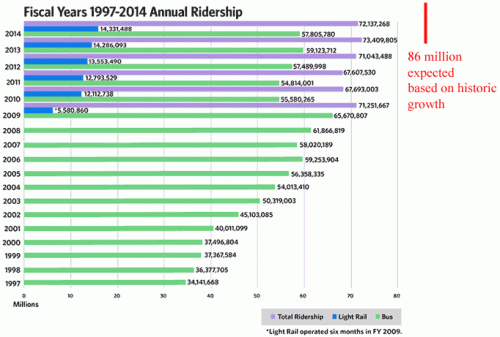
Please, Please. Please Do Not Rely on Your Tesla Autopilot
You folks can disagree with me about the prospects for the Tesla stock price. You may hero worship Elon Musk and think he's a genius where I think he is a charlatan with PT Barnum promotion skills. You may really, really love our Tesla car (I thought the Model S was a fine car when it first came out -- the Model 3, not so much). But PLEASE do not rely on your Tesla autopilot. Or at least read this Ars Technica article first.
A while back I went to a party in the suburbs of New York and needed a ride back to my hotel in the city. A friend of a friend offered to give me a ride. It turned out he was driving a Tesla Model X (SUV). In the same way that you can't go 3 minutes with a Vegan without getting a diatribe on the virtues of veganism, for some distance in the ride we heard a paean to Elon Musk and Tesla. This guy had really drunk the Kool-Aid. Before my wife started kicking my ankle, I expressed a few of the reservations I had about the company and Musk, and the driver got really defensive. So much so he set out to prove Tesla's superiority. So he drove us the rest of the way home (mostly) with his hands off the wheel through the freeways around Manhattan. It scared the cr*p out of me, because I knew that while the AP could drive impressive distances and navigate on its own, it was only 99% reliable. And since it makes hundreds of decisions every trip, those are not great odds.
What worried me is that he insisted on using the AP almost as a test of religious faith. There is this weird dichotomy where all the Tesla literature that is actually reviewed by their lawyers and the DOT tell you never to take your hands off the wheel, but Musk goes on 60 Minutes bragging and doing exactly that (almost hitting another car) and verbally the company constantly brags on its AP capability.
This is crazy. You only have to look at Boeing and the 737MAX experience to understand that even a very careful and experienced company like Boeing can screw up the software-hardware interaction The 737MAX worked most of the time, just like the Tesla AP, but in Boeing's case you don't see consumers arguing that this makes it OK -- you see the DOJ initiating criminal investigations. Tesla is a much less experienced and far less careful and organized company than is Boeing. Despite Musk's bluster, third parties rank them close to dead last in self-driving technology development, but they are the only major self-driving provider who are actively encouraging their customers to use it outside of a carefully controlled test environment. Everyone who actually understands AI believes Musk is totally full of sh*t when he talks about AI, particularly the much-hyped "shadow mode."
Interestingly, that latter reaction is the same one I hear from nearly everyone who hears Musk discuss something they actually know about. My moment came listening to Musk talk about the hyperloop, which is truly a crazy, unfeasible, uneconomic joke. As I wrote before:
Elon Musk is not the smartest guy in the world. He is clearly a genius at marketing and brand building. He has a creative mind -- I have said before he would have been fabulous at coming up with each issue's cover story for Popular Mechanics. A mile-long freight blimp! Trains that run in underground vacuum tubes! A colony on Mars! But he suffers, I think, from the same lack of self-awareness many people develop when they are expert or successful in one thing -- they assume they will automatically be equally as brilliant and successful in other things. Musk creates fanciful ideas that are exciting and might work technically, but will never ever pencil out as profitable business (e.g. Boring company, Hyperloop).
I watched the Ant-man and the Wasp the other night and listening to Musk is a lot like Marvel movie physics -- both use recognizable terms (if you had a drinking game in this last Ant-man movie that took a shot when they said "quantum" you would be dead now) that sound good to laymen but make no sense to people who actually understand the topic. There may have been some excuse to lionize Musk's brilliance a year or five years ago, but how can anyone think this guy is anything but a knucklehead with an overcharged ego after the Boring Company fiasco?
Anyway, don't rely on this guy's reputation. If you like what you see in the Tesla showroom (if there are any left), then by all means by the car. But do not turn on the auto-pilot. Please. A loss of even one of you readers could... reduce my blog visitation by whole number percentage points.