I know I have deluged you with a lot of climate change posts of late. I think this particular post is important, as it is the clearest single argument I can make as to why I am skeptical that man-made global warming will rise to catastrophic levels. It is not comprehensive, it took me 80 pages to do that, but it should get anyone thinking.
It turns out to be quite easy to do a simple but fairly robust reality check of global warming forecasts, even without knowing what a "Watt" or a "forcing" is. Our approach will be entirely empirical, based on the last 100 years of climate history. I am sensitive that we skeptics not fall into the
9/11 Truther syndrome of arguing against a coherent theory from
isolated anomalies. To this end, my approach here is holistic and not
anomaly driven. What we will find is that, extrapolating from history, it is almost impossible to get warming numbers as high as those quoted by global warming alarmists.
Climate Sensitivity
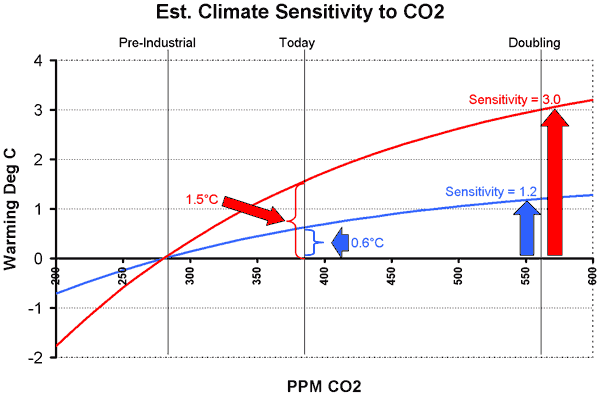
The one simple concept you need to understand is "climate sensitivity." As used in most global warming literature, climate sensitivity is the amount of global warming that results from a doubling in atmospheric CO2 concentrations. Usually, when this number is presented, it refers to the warming from a doubling of CO2 concentrations since the beginning of the industrial revolution. The pre-industrial concentration is generally accepted as 280ppm (0.028% of the atmosphere) and the number today is about 380ppm, so a doubling would be to 560ppm.
As a useful, though not required, first step before we begin, I encourage you to read the RealClimate simple "proof" for laymen that the climate sensitivity is 3ºC, meaning the world will warm 3 degrees C with a doubling of CO2 concentrations from their pre-industrial level. Don't worry if you don't understand the whole description, we are going to do it a different, and I think more compelling, way (climate scientists are a bit like the Wizard of Oz -- they are afraid if they make things too simple someone might doubt they are a real wizard). 3ºC is a common number for sensitivity used by global warming hawks, though it is actually at the low end of the range that the UN IPCC arrived at in their fourth report. The IPCC (4th report, page 798) said that the expected value is between 3ºC and 4ºC and that there was a greater chance the sensitivity was larger than 6ºC than that it was 1.5ºC or less. I will show you why I think it is extraordinarily unlikely that the number is greater even than 1.5ºC.
Our Approach
We are going to derive the sensitivity (actually a reasonable range for sensitivity) for ourselves in three steps. First, we will do it a simple way. Then, we will do it a slightly harder but more accurate way. And third, we will see what we would have to assume to get a number anywhere near 3ºC. Our approach will be entirely empirical, using past changes in CO2 and temperature to estimate sensitivity. After all, we have measured CO2 going up by about 100 ppm. That is about 36% of the way towards a doubling from 280 to 560. And, we have measured temperatures -- and though there are a lot of biases in these temperature measurements, these measurements certainly are better than our guesses, say, of temperatures in the last ice age. Did you notice something odd, by the way, in the RealClimate derivation? They never mentioned measured sensitivities in the last 100 years -- they jumped all the way back to the last ice age. I wonder if there is a reason for that?
A First Approximation
OK, let's do the obvious. If we have experienced 36% of a doubling, then we should be able to take the historic temperature rise from CO2 for the same period and multiply it by 2.8 (that's just reciprocal of 36%) and derive the temperature increase we would expect for a full doubling.
The problem is that we don't know the historic temperature rise solely form CO2. But we do know how to bound it. The IPCC and most global warming hawks place the warming since 1900 at about 0.6ºC. Since no one attributes warming before 1900 to man-made CO2 (it did warm, but this is attributed to natural cyclical recovery from the little ice age) then the maximum historic man-made warming is 0.6ºC. In fact, all of that warming is probably not from CO2. Some probably is from continued cyclical warming out of the little ice age. Some, I believe strongly, is due to still uncorrected biases, particularly of urban heat islands, in surface temperature data.
But let's for a moment attribute, unrealistically, all of this 0.6ºC to man-made CO2 (this is in fact what the IPCC does in their report). This should place an upper bound on the sensitivity number. Taking 0.6ºC times 2.8 yields an estimated climate sensitivity of 1.7ºC. Oops. This is about half of the RealClimate number or the IPCC number! And if we take a more realistic number for man-made historic warming as 0.4ºC, then we get a sensitivity of 1.1ºC. Wow, that's a lot lower! We must be missing something important! It turns out that we are, in this simple analysis, missing something important. But taking it into account is going to push our sensitivity number even lower.
A Better Approximation
What we are missing is that the relation between CO2 concentration and warming is not linear, as implied in our first approximation. It is a diminishing return. This means that the first 50 ppm rise in CO2 concentrations causes more warming than the next 50 ppm, etc. This effect has often been compared to painting a window. The first coat of paint blocks out a lot of light, but the window is still translucent. The next coat blocks out more light, but not as much as the first. Eventually, subsequent coats have no effect because all the light is already blocked. CO2 has a similar effect on warming. It only absorbs certain wavelengths of radiation returning to space from earth. Once the absorption of those wavelengths is saturated, extra CO2 will do almost nothing. (update: By the way, this is not some skeptic's fantasy -- everyone in climate accepts this fact).
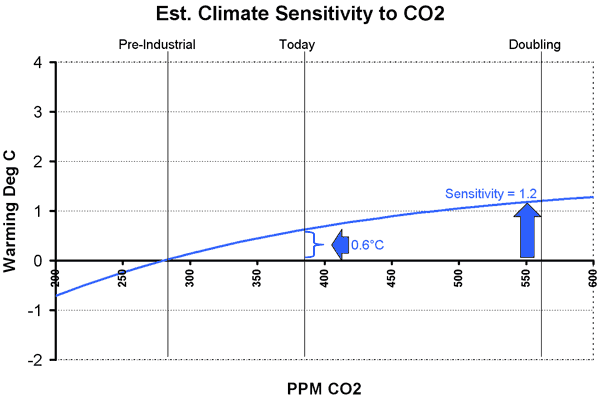
So what does this mean in English? Well, in our first approximation, we assumed that 36% of a CO2 doubling would yield 36% of the temperature we would get in a doubling. But in reality, since the relationship is a diminishing return, the first 36% of a CO2 doubling will yield MORE than 36% of the temperature increase you get for a doubling. The temperature increase is front-loaded, and diminishes going forward. An illustration is below, with the linear extrapolation in red and the more realistic decreasing exponential extrapolation in blue.
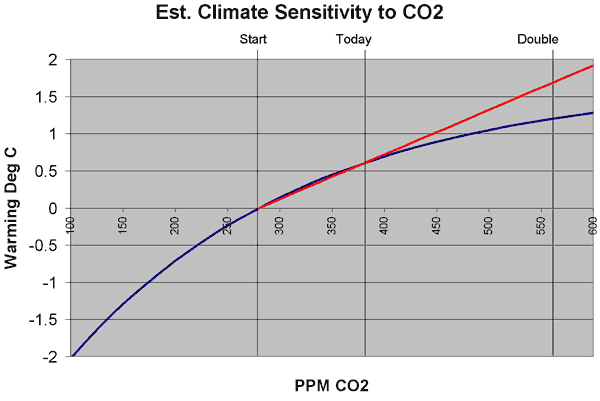
The exact shape and equation of this curve is not really known, but we can establish a reasonable range of potential values. For any reasonable shapes of this curve, 36% of a CO2 doubling (where we are today) equates to from 43% to 63% of the final temperature increase over a doubling. This would imply that a multiplier between 2.3 and 1.6 for temperature extrapolation (vs. 2.8 derived above for the straight linear extrapolation above) or a climate sensitivity of 1.4ºC to 1.0ºC if man-made historic warming was 0.6ºC and a range of 0.9ºC to 0.6ºC for a man-made historic warming of 0.4ºC. I tend to use the middle of this range, with a multiplier of about 1.9 and a man-made historic warming of 0.5ºC to give a expected sensitivity of 0.95ºC, which we can round to 1ºC.
This is why you will often hear skeptics cite numbers closer to 1ºC rather than 3ºC for the climate sensitivity. Any reasonable analysis of actual climate experience over the last 100 years yields a sensitivity much closer to 1ºC than 3ºC. Most studies conducted before the current infatuation with showing cataclysmic warming forecasts came up with this same 1ºC, and peer-reviewed work is still coming up with this same number.
So what does this mean for the future? Well, to predict actual temperature increases from this sensitivity, we would have to first create a CO2 production forecast and, you guessed it, global warming hawks have exaggerated that as well. The IPCC says we will hit the full doubling to 560ppm around 2065 (Al Gore, incredibly, says we will hit it in the next two decades). This means that with about 0.5C behind us, and a 3 sensitivity, we can expect 2.5C more warming in the next 60 years. Multiply that times exaggerated negative effects of warming, and you get instant crisis.
However, since actual CO2 production is already below IPCC forecasts, we might take a more reasonable date of 2080-2100 for a doubling to 560. And, combining this with our derived sensitivity of 1ºC (rather than RealClimate's 3ºC) we will get 0.5C more warming in the next 75-100 years. This is about the magnitude of warming we experienced in the last century, and most of us did not even notice.
I know you are scratching you head and wondering what trick I pulled to get numbers so much less than the scientific "consensus." But there is no trick, all my numbers are empirical and right out of the IPCC reports. In fact, due to measurement biases and other climate effects that drive warming, I actually think the historic warming from CO2 and thus the sensitivity is even lower, but I didn't want to confuse the message.
So what are climate change hawks assuming that I have not included? Well, it turns out they add on two things, neither of which has much empirical evidence behind it. It is in fact the climate hawks, not the skeptics, that need to argue for a couple of anomalies to try to make their case.
Is Climate Dominated by Positive Feedback?
Many climate scientists argue that there are positive feedbacks in the climate system that tend to magnify and amplify the warming from CO2. For example, a positive feedback might be that hotter climate melts sea ice and glaciers, which reduces the reflectiveness of the earth's surface, which causes more sunlight to be absorbed, which warms things further. A negative feedback might be that warmer climate vaporizes more water which forms more clouds which blocks sunlight and cools the earth.
Climate scientists who are strong proponents of catastrophic man-made warming theory assume that the climate is dominated by positive feedbacks. In fact, my reading of the IPCC report says that the climate "consensus" is that net feedback in the climate system is positive and tends to add 2 more degrees of temperature for every one added from CO2. You might be thinking - aha - I see how they got a sensitivity of 3ºC: Your 1ºC plus 2ºC in feedback equals 3ºC.
But there is a problem with that. In fact, there are three problems with this. Here they are:
- We came up with our 1ºC sensitivity empirically. In other words, we observed a 100ppm past CO2 increase leading to 0.5ºC measured temperature increase which implies 1ºC sensitivity. But since this is empirical, rather than developed from some set of forcings and computer models, then it should already be net of all feedbacks. If there are positive feedbacks in the system, then they have been operating and should be part of that 1ºC.
- There is no good scientific evidence that there is a large net positive feedback loop in climate, or even that the feedback is net positive at all. There are various studies, hypotheses, models, etc., but no proof at all. In fact, you can guess this from our empirical data. History implies that there can't be any large positive feedbacks in the system or else we would have observed higher temperatures historically. In fact, we can go back in to the distant historical record (in fact, Al Gore showed the chart I am thinking of in An Inconvenient Truth) and find that temperatures have never run away or exhibited any sort of tipping point effect.
- The notion that a system like climate, which has been reasonably stable for millions of years, is dominated by positive feedback should offend the intuition of any scientist. Nature is dominated in large part by negative feedback processes. Positive feedback processes are highly unstable, and tend to run away to a distant endpoint. Nuclear fission, for example, is a positive feedback process
Do aerosols and dimming imply a higher sensitivity?
Finally, the last argument that climate hawks would employ is that anthropogenic effects, specifically emission of SO2 aerosols and carbon black, have been reflecting sunlight and offsetting the global warming effect. But, they caution, once we eliminate these pollutants, which we have done in the West (only to be offset in China and Asia) temperatures will no longer be suppressed and we will see the full extent of warming.
First, again, no one really has any clue the magnitude of this effect, or even if it is an effect at all. Second, its reach will tend to be localized over industrial areas (since their presence in the atmosphere is relatively short-lived), whereas CO2 acts worldwide. If these aerosols and carbon black are concentrated say over 20% of the land surface of the world, this means they are only affecting the temperature over 5% of the total earth' s surface. So its hard to argue they are that significant.
However, let's say for a moment this effect does exist. How large would it have to be to argue that a 3.0ºC climate sensitivity is justified by historical data? Well, taking 3.0ºC and dividing by our derived extrapolation multiplier of 1.9, we get required historic warming due to man's efforts of 1.6ºC. This means that even if all past 0.6ºC of warming is due to man (a stretch), then aerosols must be suppressing a full 1ºC of warming. I can't say this is impossible, but it is highly unlikely and certainly absolutely no empirical evidence exists to support any number like this. Particularly since dimming effects probably are localized, you would need as much as 20ºC suppression in these local areas to get a 1ºC global effect. Not very likely.
Why the number might even be less
Remember that when we calculated sensitivity, we needed the historical warming due to man's CO2. A simple equation for arriving at this number is:
Warming due to Man's CO2 = Total Historic Measured Warming - Measurement Biases - Warming from other Sources + Warming suppressed by Aerosols
This is why most skeptics care if surface temperature measurements are biased upwards or if the sun is increasing in intensity. Global warming advocates scoff and say that these effects don't undermine greenhouse gas theory. And they don't. I accept greenhouse gases cause some warming. BUT, the more surface temperature measurements are biased upwards and the more warming is being driven by non-anthropogenic sources, the less that is being caused by man. And, as you have seen in this post, the less warming caused by man historically means less that we will see in the future. And while global warming hawks want to paint skeptics as "deniers", we skeptics want to argue the much more interesting question "Yes, but how much is the world warming, and does this amount of warming really justify the costs of abatement, which are enormous."
As always, you can find my Layman's Guide to Skepticism about Man-made Global Warming here. It is available for free in HTML or pdf download, or you can order the printed book that I sell at cost. My other recent posts about climate are here.