Denying the Climate Catastrophe: 5a. Arguments For Attributing Past Warming to Man
This is part A of Chapter 5 of an ongoing series. Other parts of the series are here:
- Introduction
- Greenhouse Gas Theory
- Feedbacks
- A) Actual Temperature Data; B) Problems with the Surface Temperature Record
- Attribution of Past Warming: A) Arguments for it being Man-Made (this article); B) Natural Attribution
- Climate Models vs. Actual Temperatures
- Are We Already Seeing Climate Change
- The Lukewarmer Middle Ground
- A Low-Cost Insurance Policy
Having established that the Earth has warmed over the past century or so (though with some dispute over how much), we turn to the more interesting -- and certainly more difficult -- question of finding causes for past warming. Specifically, for the global warming debate, we would like to know how much of the warming was due to natural variations and how much was man-made. Obviously this is hard to do, because no one has two thermometers that show the temperature with and without man's influence.
I like to begin each chapter with the IPCC's official position, but this is a bit hard in this case because they use a lot of soft words rather than exact numbers. They don't say 0.5 of the 0.8C is due to man, or anything so specific. They use phrases like "much of the warming" to describe man's affect. However, it is safe to say that most advocates of catastrophic man-made global warming theory will claim that most or all of the last century's warming is due to man, and that is how we have put it in our framework below:
By the way, the "and more" is not a typo -- there are a number of folks who will argue that the world would have actually cooled without manmade CO2 and thus manmade CO2 has contributed more than the total measured warming. This actually turns out to be an important argument, since the totality of past warming is not enough to be consistent with high sensitivity, high feedback warming forecasts. But we will return to this in part C of this chapter.
Past, Mostly Abandoned Arguments for Attribution to Man
There have been and still are many different approaches to the attributions problem. In a moment, we will discuss the current preferred approach. However, it is worth reviewing two other approaches that have mostly been abandoned but which had a lot of currency in the media for some time, in part because both were in Al Gore's film An Inconvenient Truth.
Before we get into them, I want to take a step back and briefly discuss what is called paleo-climatology, which is essentially the study of past climate before the time when we had measurement instruments and systematic record-keeping for weather. Because we don't have direct measurements, say, of the temperature in the year 1352, scientists must look for some alternate measure, called a "proxy," that might be correlated with a certain climate variable and thus useful in estimating past climate metrics. For example, one might look at the width of tree rings, and hypothesize that varying widths in different years might correlate to temperature or precipitation in those years. Most proxies take advantage of such annual layering, as we have in tree rings.
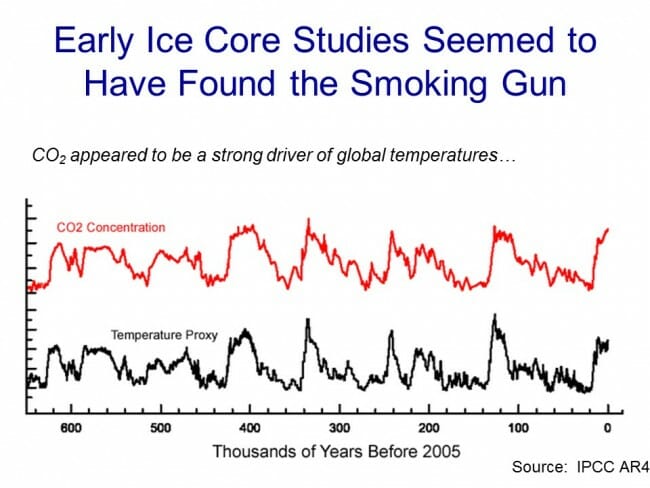
One such methodology uses ice cores. Ice in certain places like Antarctica and Greenland is laid down in annual layers. By taking a core sample, characteristics of the ice can be measured at different layers and matched to approximate years. CO2 concentrations can actually be measured in air bubbles in the ice, and atmospheric temperatures at the time the ice was laid down can be estimated from certain oxygen isotope ratios in the ice. The result is that one can plot a chart going back hundreds of thousands of years that estimates atmospheric CO2 and temperature. Al Gore showed this chart in his movie, in a really cool presentation where the chart wrapped around three screens:
As Gore points out, this looks to be a smoking gun for attribution of temperature changes to CO2. From this chart, temperature and CO2 concentrations appear to be moving in lockstep. From this, CO2 doesn't seem to be a driver of temperatures, it seems to be THE driver, which is why Gore often called it the global thermostat.
But there turned out to be a problem, which is why this analysis no longer is treated as a smoking gun, at least for the attribution issue. Over time, scientists got better at taking finer and finer cuts of the ice cores, and what they found is that when they looked on a tighter scale, the temperature was rising (in the black spikes of the chart) on average 800 years before the CO2 levels (in red) rose.
This obviously throws a monkey wrench in the causality argument. Rising CO2 can hardly be the cause of rising temperatures if the CO2 levels are rising after temperatures.
It is now mostly thought that what this chart represents is the liberation of dissolved CO2 from oceans as temperatures rise. Oceans have a lot of dissolved CO2, and as the oceans get hotter, they will give up some of this CO2 to the atmosphere.
The second outdated attribution analysis we will discuss is perhaps the most famous: The Hockey Stick. Based on a research paper by Michael Mann when he was still a grad student, it was made famous in Al Gore's movie as well as numerous other press articles. It became the poster child, for a few years, of the global warming movement.
So what is it? Like the ice core chart, it is a proxy analysis attempting to reconstruct temperature history, in this case over the last 1000 years or so. Mann originally used tree rings, though in later versions he has added other proxies, such as from organic matter laid down in sediment layers.
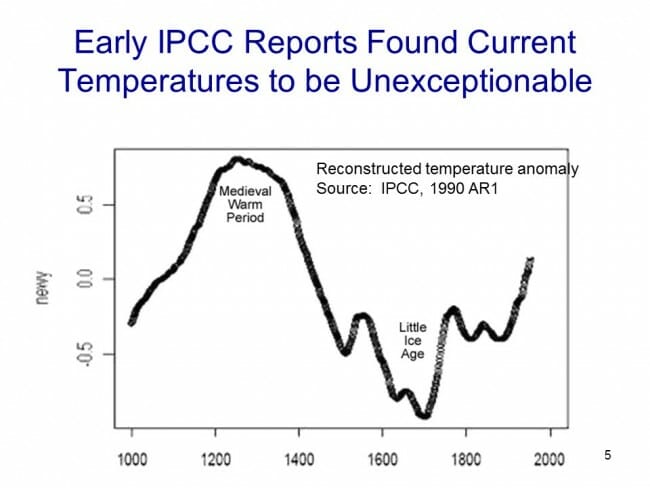
Before the Mann hockey stick, scientists (and the IPCC) believed the temperature history of the last 1000 years looked something like this:
Generally accepted history had a warm period from about 1100-1300 called the Medieval Warm Period which was warmer than it is today, with a cold period in the 17th and 18th centuries called the "Little Ice Age". Temperature increases since the little ice age could in part be thought of as a recovery from this colder period. Strong anecdotal evidence existed from European sources supporting the existence of both the Medieval Warm Period and the Little Ice Age. For example, I have taken several history courses on the high Middle Ages and every single professor has described the warm period from 1100-1300 as creating a demographic boom which defined the era (yes, warmth was a good thing back then). In fact, many will point to the famines in the early 14th century that resulted from the end of this warm period as having weakened the population and set the stage for the Black Death.
However, this sort of natural variation before the age where man burned substantial amounts of fossil fuels created something of a problem for catastrophic man-made global warming theory. How does one convince the population of catastrophe if current warming is within the limits of natural variation? Doesn't this push the default attribution of warming towards natural factors and away from man?
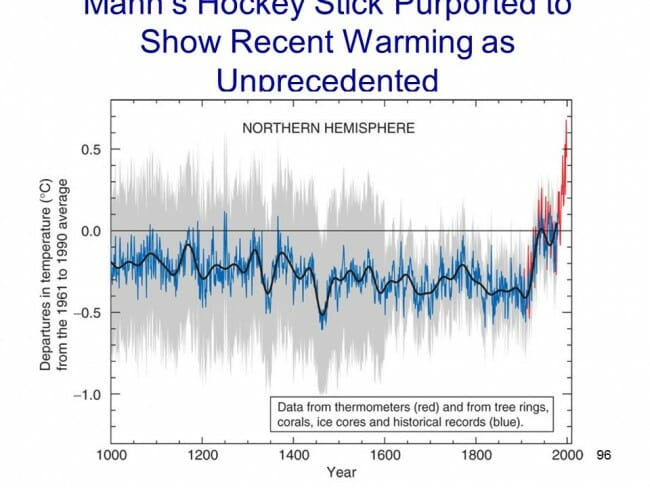
The answer came from Michael Mann (now Dr. Mann but actually produced originally before he finished grad school). It has been dubbed the hockey stick for its shape:
The reconstructed temperatures are shown in blue, and gone are the Medieval Warm Period and the Little Ice Age, which Mann argued were local to Europe and not global phenomena. The story that emerged from this chart is that before industrialization, global temperatures were virtually flat, oscillating within a very narrow band of a few tenths of a degree. However, since 1900, something entirely new seems to be happening, breaking the historical pattern. From this chart, it looks like modern man has perhaps changed the climate. This shape, with the long flat historical trend and the sharp uptick at the end, is why it gets the name "hockey stick."
Oceans of ink and electrons have been spilled over the last 10+ years around the hockey stick, including a myriad of published books. In general, except for a few hard core paleoclimatologists and perhaps Dr. Mann himself, most folks have moved on from the hockey stick as a useful argument in the attribution debate. After all, even if the chart is correct, it provides only indirect evidence of the effect of man-made CO2.
Here are a few of the critiques:
- Note that the real visual impact of the hockey stick comes from the orange data on the far right -- the blue data alone doesn't form much of a hockey stick. But the orange data is from an entirely different source, in fact an entirely different measurement technology -- the blue data is from tree rings, and the orange is form thermometers. Dr. Mann bristles at the accusation that he "grafted" one data set onto the other, but by drawing the chart this way, that is exactly what he did, at least visually. Why does this matter? Well, we have to be very careful with inflections in data that occur exactly at the point that where we change measurement technologies -- we are left with the suspicion that the change in slope is due to differences in the measurement technology, rather than in the underlying phenomenon being measured.
- In fact, well after this chart was published, we discovered that Mann and other like Keith Briffa actually truncated the tree ring temperature reconstructions (the blue line) early. Note that the blue data ends around 1950. Why? Well, it turns out that many tree ring reconstructions showed temperatures declining after 1950. Does this mean that thermometers were wrong? No, but it does provide good evidence that the trees are not accurately following current temperature increases, and so probably did not accurately portray temperatures in the past.
- If one looks at the graphs of all of Mann's individual proxy series that are averaged into this chart, astonishingly few actually look like hockey sticks. So how do they average into one? McIntyre and McKitrick in 2005 showed that Mann used some highly unusual and unprecedented-to-all-but-himself statistical methods that could create hockey sticks out of thin air. The duo fed random data into Mann's algorithm and got hockey sticks.
- At the end of the day, most of the hockey stick (again due to Mann's averaging methods) was due to samples from just a handful of bristle-cone pine trees in one spot in California, trees whose growth is likely driven by a number of non-temperature factors like precipitation levels and atmospheric CO2 fertilization. Without these few trees, most of the hockey stick disappears. In later years he added in non-tree-ring series, but the results still often relied on just a few series, including the Tiljander sediments where Mann essentially flipped the data upside down to get the results he wanted. Taking out the bristlecone pines and the abused Tiljander series made the hockey stick go away again.
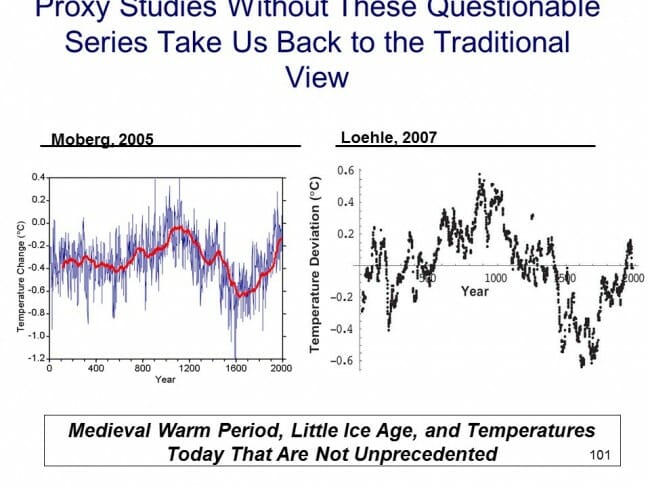
There have been plenty of other efforts at proxy series that continue to show the Medieval Warm Period and Little Ice Age as we know them from the historical record
As an aside, Mann's hockey stick was always problematic for supporters of catastrophic man-made global warming theory for another reason. The hockey stick implies that the world's temperatures are, in absence of man, almost dead-flat stable. But this is hardly consistent with the basic hypothesis, discussed earlier, that the climate is dominated by strong positive feedbacks that take small temperature variations and multiply them many times. If Mann's hockey stick is correct, it could also be taken as evidence against high climate sensitivities that are demanded by the catastrophe theory.
The Current Lead Argument for Attribution of Past Warming to Man
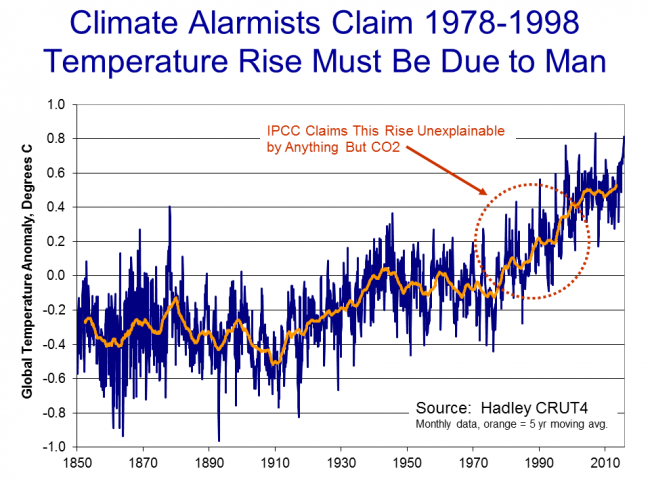
So we are still left wondering, how do climate scientists attribute past warming to man? Well, to begin, in doing so they tend to focus on the period after 1940, when large-scale fossil fuel combustion really began in earnest. Temperatures have risen since 1940, but in fact nearly all of this rise occurred in the 20 year period from 1978 to 1998:
To be fair, and better understand the thinking at the time, let's put ourselves in the shoes of scientists around the turn of the century and throw out what we know happened after that date. Scientists then would have been looking at this picture:
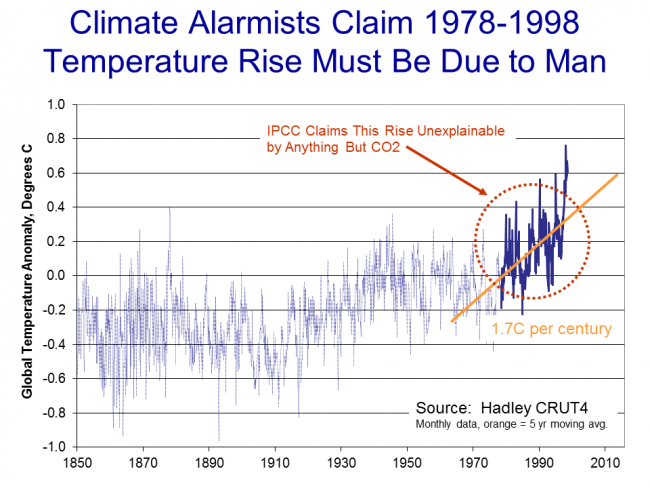
Sitting in the year 2000, the recent warming rate might have looked dire .. nearly 2C per century...
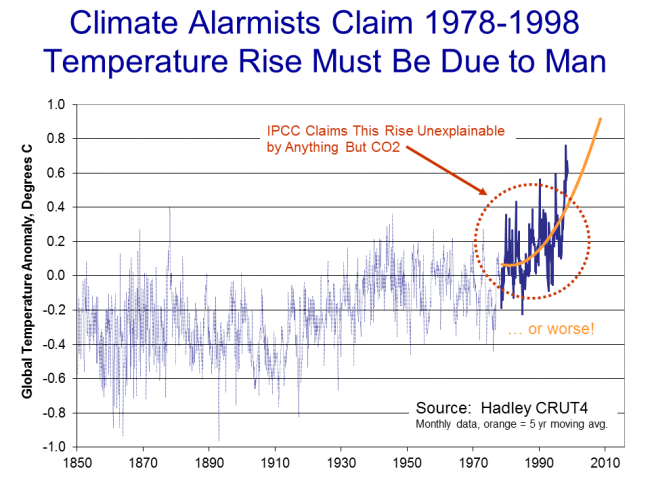
Or possibly worse if we were on an accelerating course...
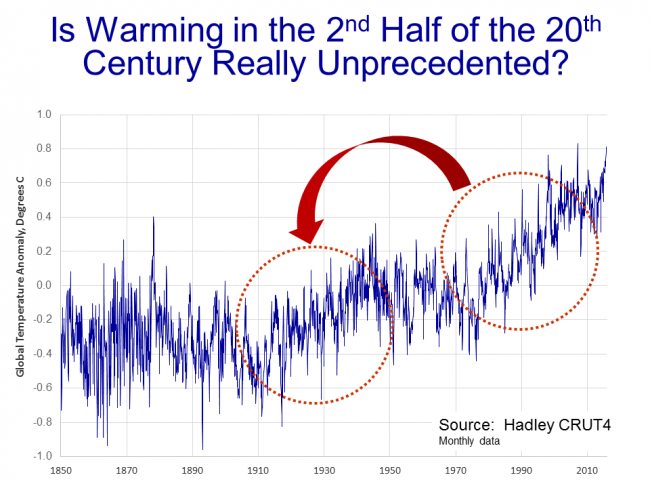
Scientists began to develop a hypothesis that this temperature rise was occurring too rapidly to be natural, that it had to be at least partially man-made. I have always thought this a slightly odd conclusion, since the slope from this 20-year period looks almost identical to the slope centered around the 1930's, which was very unlikely to have much human influence.
But never-the-less, the hypothesis that the 1978-1998 temperature rise was too fast to be natural gained great currency. But how does one prove it?
What scientists did was to build computer models to simulate the climate. They then ran the computer models twice. The first time they ran them with only natural factors, or at least only the natural factors they knew about or were able to model (they left a lot out, but we will get to that in time). These models were not able to produce the 1978-1998 warming rates. Then, they re-ran the models with manmade CO2, and particularly with a high climate sensitivity to CO2 based on the high feedback assumptions we discussed in an earlier chapter. With these models, they were able to recreate the 1978-1998 temperature rise. As Dr. Richard Lindzen of MIT described the process:
What was done, was to take a large number of models that could not reasonably simulate known patterns of natural behavior (such as ENSO, the Pacific Decadal Oscillation, the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation), claim that such models nonetheless accurately depicted natural internal climate variability, and use the fact that these models could not replicate the warming episode from the mid seventies through the mid nineties, to argue that forcing was necessary and that the forcing must have been due to man.
Another way to put this argument is "we can't think of anything natural that could be causing this warming, so by default it must be man-made. With various increases in sophistication, this remains the lead argument in favor of attribution of past warming to man.
In part B of this chapter, we will discuss what natural factors were left out of these models, and I will take my own shot at a simple attribution analysis.
The next section, Chapter 6 Part B, on natural attribution is here