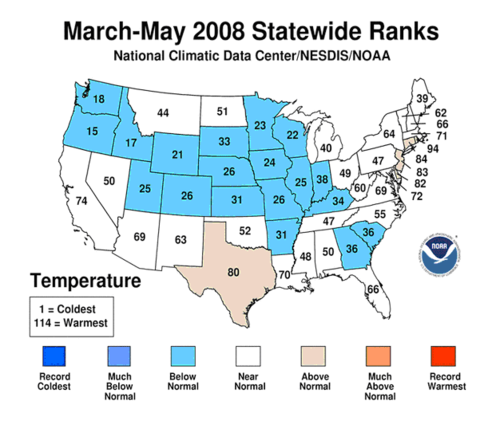
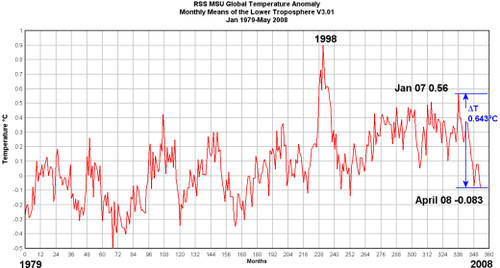
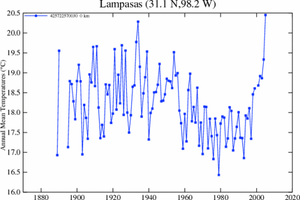
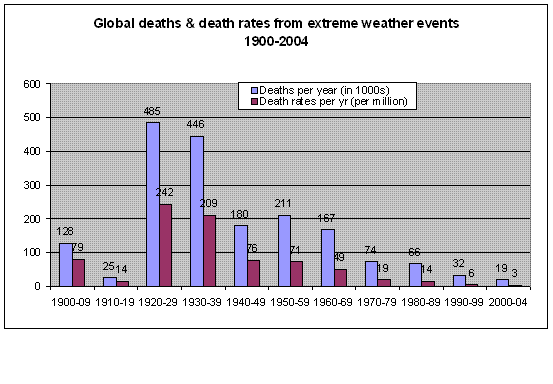
Cross-posted from Climate Skeptic. I believe this to be an extremely important issue. Catastrophic global warming forecasts are driven not by greenhouse gas theory, but by the theory that the Earth's climate is dominated by positive feedback. This post discusses these issues:
It is silly to argue whether CO2 in the atmosphere can cause global warming: It clearly does. The issue is not "if" but "how much". The warming from man's CO2 might be 8 degrees in a century, as Al Gore might argue, in which case man's CO2 would be incredibly disruptive. Or it might cause just a few tenths of a degree of warming, which might be unnoticeable within the noise of natural climate variation.
Interestingly, the key to understanding this issue of the amount of warming does not actually lie in greenhouse gas theory. Most scientists, skeptics and alarmists alike, peg the warming directly from CO2 at between 0.3 and 1.0 degrees Celsius for a doubling in CO2 levels (this notion of how much temperatures would increase for a doubling of CO2 levels is called climate sensitivity). If this greenhouse gas warming was the only phenomenon at work, we would expect man-made warming over the next century even using the most dire assumptions to be less than 1C, or about the same amount we have seen (non-catastrophically) over the last century. Warming forecasts of this magnitude would not in any way, shape, or form justify the draconian economic impacts of many current government carbon reduction proposals.
The key, as I have written before (and here), lies not in greenhouse gas theory itself but in the theory that the earth's climate is dominated by positive feedback. This theory hypothesizes that small changes in temperature from greenhouse gas increases would be multiplied 3,4,5 times or more by positive feedback effects, from changes in atmospheric water vapor to changing surface albedo.
Let me emphasize again: The catastrophe results not from greenhouse gas theory, but from the theory of extreme climactic positive feedback. In a large sense, all the debate in the media is about the wrong thing! When was the last time you saw the words "positive feedback" in a media article about climate?
Christopher Monckton has an absolutely dead-on post at Roger Pielke's blog about this feedback theory that I want to excerpt in depth.
This chart is a good place to start. It shows the changes in the IPCC's estimate for climate sensitivity to CO2 and how it has changed over the course of the reports. More importantly, he splits the forecast between the amount due directly to Co2, and the amount due to the multiplicative effect of positive feedback. The green bar is the direct contribution of Co2, and the pink is the feedback.

We can observe a couple of things. First, the IPCC's estimate of the amount of warming due to CO2 directly via the greenhouse gas effect has actually been going down over time. (Note that there are those, like Richard Lindzen, who suggest these numbers are still three times too high given that we have not observed a difference in surface and lower troposphere warming that greenhouse gas theory seems to predict).
Second, you will see that the IPCC's overall forecasts of climate sensitivity have been going up only because their estimates of positive feedback effects have gone way up. The IPCC assumes that feedback effects multiply warming from CO2 by three. And note that the IPCC's forecasts of feedback effects trail those of folks like James Hansen and Al Gore.
So how confident are we in these feedback effects? Well, it turns out we are not even sure of the sign! As Monckton writes:
The feedback factor f accounts for at least two-thirds of all radiative forcing in IPCC (2007); yet it is not expressly quantified, and no "Level Of Scientific Understanding" is assigned either to f or to the two variables b and κ upon which it is dependent....
Indeed, in IPCC (2007) the stated values for the feedbacks that account for more than two-thirds of humankind's imagined effect on global temperatures are taken from a single paper. The value of the coefficient z in the CO2 forcing equation likewise depends on only one paper. The implicit value of the crucial parameter κ depends upon only two papers, one of which had been written by a lead author of the chapter in question, and neither of which provides any theoretical or empirical justification for the IPCC's chosen value. The notion that the IPCC has drawn on thousands of published, peer-reviewed papers to support its central estimates for the variables from which climate sensitivity is calculated is not supported by the evidence.
Given the importance of feedback to their forecasts, the treatment in the latest IPCC report of feedback borders on the criminal. I have read the relevant sections and it is nearly impossible to find any kind of discussion of these issues. A cynical mind might describe the thousands of pages of the IPCC report as the magician grabbing your attention with his left hand to hide what is in his right hand. And what is being hidden is that ... there is nothing there! Feedback is the pivotal point on which the whole discussion of drastic carbon abatement should turn and there is nothing there.
Monckton goes further, to point out that hidden in the IPCC numbers lies an absurdity:
if the upper estimates of each of the climate-relevant feedbacks listed in IPCC (2007) are summed, an instability arises. The maxima are -
Water vapor 1.98, lapse rate -0.58, surface albedo 0.34, cloud albedo 1.07, CO2 0.57, total 3.38 W m-2 K-1.
The equation f = (1 - bκ)-1 becomes unstable as b → κ-1 = 3.2 W m-2 K-1. Yet, if each of the individual feedbacks imagined by the IPCC is increased to less than the IPCC's maximum, an instability or "runaway greenhouse effect" is reached.
Yet it is reliably inferred from palaeoclimatological data that no "runaway greenhouse effect" has occurred in the half billion years since the Cambrian era, when atmospheric CO2 concentration peaked at almost 20 times today's value
Positive feedback can be weird and unstable. If there is enough of it, processes tend to run away (e.g. nuclear fission), which is what Monckton is arguing that some of the IPCC assumptions lead to. Even when feedback is less positive, it still can cause processes to fluctuate wildly. In fact, it is fairly unusual for long-term stable processes like climate to be dominated by positive feedback. Most scientists, when then meet a new process, would probably assume negative feedback until proven otherwise. This is a particular issue in climate, where folks like Michael Mann have gone out of their way to argue that the world temperature history over the last 1000 years before man began burning fossil fuels is incredibly stable and unchanging. If so, how can this be consistent with strong positive feedback?
Anyway, there is a lot more numerical detail in Monckton's post if you want to dig into the equations.
I would add one thing to his analysis: If you look at the last 100 years of history, the change in temperature given the observed change in CO2 levels comes no where close to a climate sensitivity of 3 or more, even when you assign all historical warming to CO2 rather than other effects like the sun. In fact, as I showed in this analysis, climate sensitivity appears to be 1.2 when one assigns all past warming to CO2, and something well less than that if one accepts the sun and other effects also play a role. These historical analyses would point to feedback that is either zero or negative rather than positive, more in line with what one would expect from complex natural systems.
You can see a discussion of many of these topics in the video below:



 Wall Street Journal
Wall Street Journal