Katrina Flashback
It is December, 2005. The Gulf Coast had just been pounded, in succession, by Katrina, Rita, and Wilma. Everyone was talking about how global warming seemed to be intensifying hurricanes. In a speech just after Katrina, Al Gore said
When the corpses of American citizens are floating in toxic floodwaters five days after a hurricane strikes, it is time not only to respond directly to the victims of the catastrophe but to hold the processes of our nation accountable, and the leaders of our nation accountable, for the failures that have taken place....
There are scientific warnings now of another onrushing catastrophe. We were warned of an imminent attack by Al Qaeda; we didn't respond. We were warned the levees would break in New Orleans; we didn't respond. Now, the scientific community is warning us that the average hurricane will continue to get stronger because of global warming. A scientist at MIT has published a study well before this tragedy showing that since the 1970s, hurricanes in both the Atlantic and the Pacific have increased in duration, and in intensity, by about 50 percent....
Two thousand scientists, in 100 countries, engaged in the most elaborate, well-organized scientific collaboration in the history of humankind, have produced long-since a consensus that we will face a string of terrible catastrophes unless we act to prepare ourselves and deal with the underlying causes of global warming....
At about the same time, the IPCC was in the process of preparing its fourth report, later released in 2007. It said, in part:
Several peer-reviewed studies show a clear global trend toward increased intensity of the strongest hurricanes over the past two or three decades. The strongest trends are in the North Atlantic Ocean and the Indian Ocean. According to the 2007 Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC-AR4), it is “more likely than not” (better than even odds) that there is a human contribution to the observed trend of hurricane intensification since the 1970s. In the future, “it is likely [better than 2 to 1 odds] that future tropical cyclones (typhoons and hurricanes) will become more intense, with larger peak wind speeds and more heavy precipitation associated with ongoing increases of tropical [sea surface temperatures].”
So what happened? Since Wilma in 2005, we have gone 6 full years without a category 3+ hurricane making landfall in the US, the longest span since 1900 without such an event. And the clock is still counting. When alarmists of all stripes were breathlessly predicting hurricane after hurricane in late 2005, the reality is that we wouldn't see another in the US for over six years.
Of course, US landfall is in fact a terrible indicator of hurricane activity. Its relevant to us, but it is a pretty random metric. I said this when there were a lot of landfalls and I say it again since there have been so few.
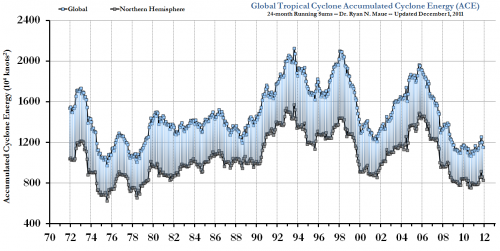
A better metric is accumulated cyclonic energy, a sort of time integral of all large cyclonic storms worldwide. Here is the most recent ACE figures:
As it turns out, the total strength of hurricane and hurricane-like storms has been falling almost since the exact day of Al Gore's speech in 2005 (another Gore effect!) In fact, of late, it has hit numbers close to all-time lows.
Of course this chart will go back up some day, and then back down, and then up ... because hurricane activity has always been cyclical over decadal time scales.
The media loves to trumpet end-of-the-world predictions from folks like Al Gore and Paul Ehrlich, but they never go back five years later and back-check their predictions. And despite their horrendous record for accuracy, the media eagerly publishes the next one. Here is a proposed editorial rule for the MSM -- no breathless publication of anyone's next prediction without first revisiting the last one.