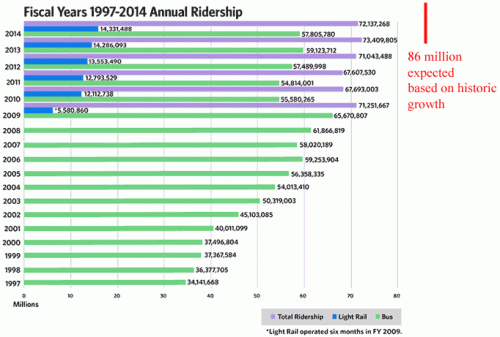
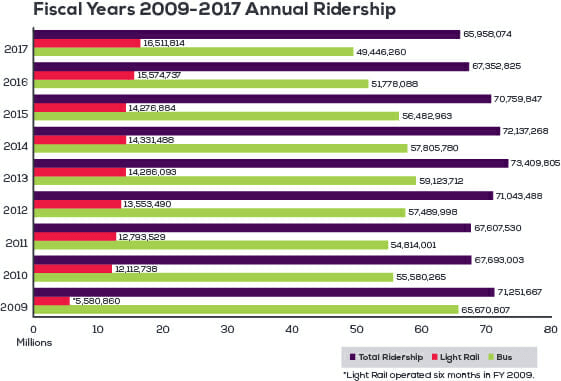
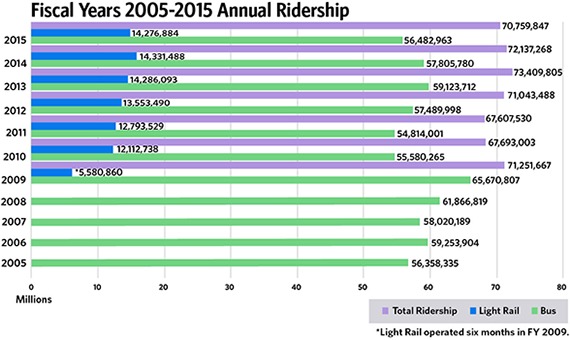
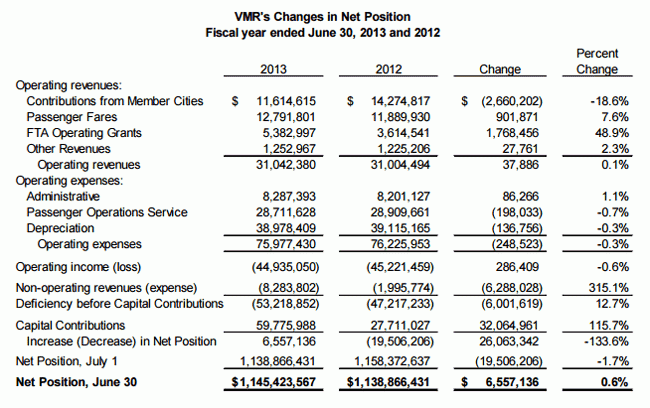
I am mostly going to leave highways out of this post. Most evidence I have seen is that the numbers do not actually show highway infrastructure to be getting worse. To the extent highways are underfunded, in my mind it is because gasoline taxes paid by drivers and meant for highway repair and construction have been shifted to grand projects like light rail that get politicians excited but carry at least an order of magnitude fewer passengers per dollar spent than do highways.
But in worlds I am more familiar with - government transit agencies and parks agencies - there has been a real deterioration of infrastructure. Systems like the Washington Metro clearly are falling apart and most public parks and recreation areas have huge deferred maintenance accounts that are growing every year. California State Parks and the National Parks Service alone have deferred maintenance tallied well into the tens of billions of dollars.
Most of these agencies will argue the problem is -- wait for it -- that they are underfunded by their legislatures. But this is not the case in my experience. My company routinely takes over public parks that some government agency said were too expensive to remain open and profitably reopens them to the public -- not only keeping up with the maintenance but paying to catch up on all the maintenance the agency let slide when it was operating the park.
The problem is that most agencies, whatever their stated public purpose and mission, tend to be run for the benefit of their employees. I understand some but not all the reasons for this, but it is simply an observable fact that this happens time and time again. This means that the priority is to build up large staffs with good pay and large benefits and retirement packages. Worse, the preference is usually to build up headquarters and administrative staff, rather than staff that actually does stuff like serve the public or fix things. When cutbacks need to occur, the priority order always is: cut maintenance first; cut field staff actually doing useful things second; cut administrative staff only in case of the apocalypse; cut benefits packages never.
Deferred maintenance is the way that agency's can borrow without transparency and without any outside authorization to do things like maintain staff in the face of cutbacks. In effect, the agency is borrowing against the infrastructure the public has built to help fund staffing levels and benefits. What is deferred maintenance? It is all kind of things. It is having one out of three toilets in a bathroom break and just roping it off rather than fixing it. It is allowing potholes to multiply in the road without repair. It is constantly chasing more and more leaks in an underground water line and not just replacing it. It is an acknowledgement that all manmade things have a fixed life. Take picnic tables. Let's say a type of picnic table in a campground, of which there might be hundreds, lasts about 10 years. That means a responsible person should budget to replace 10% every year. But what if we skip a year? No one will probably notice if some old tables slide from 10 to 11 years old, and we save some money. But really we are only borrowing that money, because we will need to do twice as many next year. But then we do it again the next year, to borrow more, and the bill just increases for the future. Before you know it, the NPS has $12 billion in deferred maintenance, a $12 billion debt for which there is little transparency and no legislative approval -- and the interest on which all of us in the public pay when we have to live with these deteriorating public facilities.
I have written about this many times, but here is what I wrote about Arizona State Parks several years ago:
At every turn, [Former Arizona State Parks Director Ken] Travous made decisions that increased the agency's costs. For example, park rangers were all given law enforcement certifications, substantially increasing their pay and putting them all into the much more expensive law enforcement pension fund. There is little evidence this was necessary -- Arizona parks generally are not hotbeds of crime -- but it did infuriate many customers as some rangers focused more on citation-writing than customer service. There is a reason McDonald's doesn't write citations in their own parking lot.
What Mr. Travous fails to mention is that the parks were falling apart on his watch - even with these huge budgets - because he tended to spend money on just about anything other than maintaining current infrastructure. Infrastructure maintenance is not sexy, and sexy projects like the Kartchner Caverns development (it is a gorgeous park) always seem to win out in government budgeting. You can see why in this editorial -- Kartcher is his legacy, whereas bathroom maintenance is next to invisible. I know deferred maintenance was accumulating during his tenure because Arizona State Parks itself used to say so. Way back in 2009 I saw a book Arizona State Parks used with legislators. It showed pictures of deteriorating parks, with notes that many of these locations had not been properly maintained for a decade. The current management inherited this problem from previous leaders like Travous, it did not create it.
So where were those huge budgets going, if not to maintenance? Well, for one, Travous oversaw a crazy expansion of the state parks headquarters staff. When he left, there were about 150 people (possibly more, it is hard to count) on the parks headquarters staff. This is almost the same number of full-time employees that were actually in the field maintaining parks. As a comparison, our company runs public parks and campgrounds very similar to those in Arizona State Parks and we serve about the same number of visitors -- but we have only 1.5 people in headquarters, allowing us to put our resources on the ground in parks serving customers and performing maintenance. None of the 100+ parks we operate have the same deferred maintenance problems that Arizona State Parks have, despite operating with less than a third of the budget that Travous had in his heyday.
Arizona State Parks has a new Director, but its the same old story. They have complained about deferred maintenance in the parks for years, but when times are good (and I can tell you all of us in public recreation are having visitation records the last few years) they use the extra money to add headquarters staff and pay headquarters staff more.
State Parks, which receives no state general-fund money, saw a record 2.78 million visitors come to its parks for the fiscal year that ended June 30. The agency generated nearly $17.9 million largely from park fees, another record.
The result: Black has been generous with pay for people she has brought on staff. Some salaries are up to 32 percent higher than what her predecessor paid for the same positions. And she has approved raises of up to 25 percent for some carry-over staff as more money rolls into the agency's coffers....
Meanwhlile, records show [former director Bryan] Martyn's top two deputies were paid $110,250, while Black pays her top assistant $142,000 — 29 percent more. Black brought in a new development chief at nearly $105,000, a 32 percent bump over what the position paid under Martyn.
Black also boosted the pay of the natural-resources chief, who also worked for Martyn, by 25 percent, to $84,000 a year.
State Parks payroll records show Martyn, around the time he left, had 41 staffers making more than $50,000 [incredibly this is apparently personal staff, not the total headquarters staff]. Black had 58 staff members in March making more than $50,000. Black also brought in staff at higher salaries than what Martyn paid, giving some holdovers significant raises.
An agency spokeswoman said Parks is increasingpay to recruit and retain talent, and staffers are dealing with more visitors.
Black said she also has increased the pay of those in the field.
So, as we see some really good years in public recreation, Arizona State Parks is using the extra money to pay staff rather than address fundamental infrastructure issues. Anyone want to guess what will happen when the next downturn comes? Will administrative pay be cut? Will headquarters staff be cut? Or will maintenance be cancelled and parks closed? Place your bets.
When companies or other entities get into debt holes they cannot climb out of, their debt is restructured and perhaps partially forgiven or even bailed out, but rules are put in place to ensure more responsible financial behavior in the future. The same needs to be true of infrastructure spending. These agencies got themselves into the deferred maintenance holes they are in. They cannot get out without a bailout, but we should understand that it is a bailout of these agencies and there need to be conditions attached to the funding tied responsible maintenance spending by the agency itself.