Peoples Republic of Hawaii
Well, our most socialist state is attempting to repeal the laws of supply and demand:
Hawaii issued a list of wholesale price caps for gasoline, the
state Public Utilities Commission said, amid this month's
record-breaking run up in retail gas that saw island residents paying
some of the highest prices in the nation.
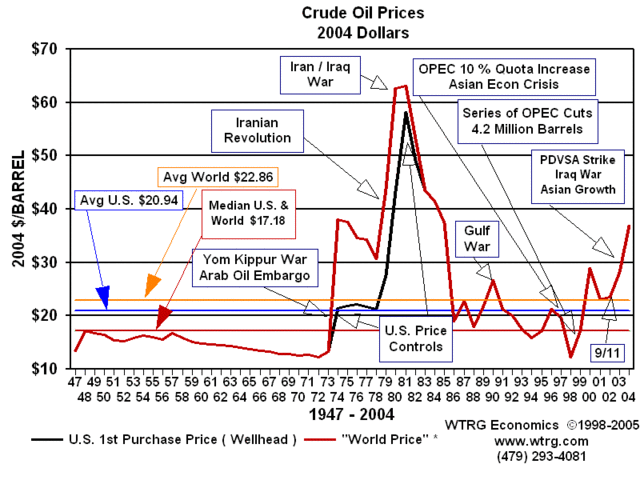
This marks the first state cap on gasoline prices since the 1970s
energy crisis, when the average inflation-adjusted price of a gallon of
regular unleaded hit $3.Hawaii's recently enacted gas cap law goes into effect on September 1, with the pre-tax wholesale cap in Honolulu set at $2.1578
Gee, I bet this will work out really well. Either the price cap will be set high, such that it is meaningless, or it will be set low, such that Hawaii will likely get this:

update: given the structure of the price caps, the result could actually be higher rather than lower prices at the pump -- see update #2 below.
It's good to know that Hawaii is looking to China for economics ideas.
The Chinese government and its state-owned oil companies are locked
in battle over artificially low gasoline prices at the pump that has
caused a massive shortage in the southern manufacturing province of
Guangdong....The crisis
highlights the persistent problems Beijing faces as the economy is
transformed to a more market-based system but that is often retarded by
authorities who fear loosing political control in the face of
full-fledged capitalist rules.
Beyond the obvious run-up in world-wide oil prices and Hawaii's logistical isolation that raises all of the prices on the island, the article on CNN identified one other possible culprit for high prices: the state government
Higher-than-average taxes on gasoline in Hawaii contribute to those
high prices. The state levies a 16 cent per gallon tax, and various
local authorities add on other taxes.In Honolulu, for example, total state, federal and local gas taxes
amount to about 53 cents per gallon, one of the highest rates in the
United States. The national average, according to the American
Petroleum Institute, is about 42 cents per gallon
It seems like only a few days ago I was pointing how governments have a hard time resisting meddling in oil markets, and that this meddling never works out well.
Even in the US, which is typically more comfortable with the operation
of the laws of supply and demand than other nations, the government has
been loathe to actually allow these laws to operate on oil. During the
70's, the government maintained price controls that limited demand side
incentives to conserve, thus creating gas lines like the ones we are
seeing in China today for the same reason. When these controls were
finally removed, a "windfall profits tax" was put in place to make sure
that producers would get none of the benefit of the price increases,
and therefore would have no financial incentive to seek out new oil
supplies or substitutes. Within a few years of the repeal of these
dumb laws, oil prices fell back to historical levels and stayed there
for 20 years.
Like the gas rationing and price controls in the 1970's, this occurs in a Republican administration (Hawaiian Governor Lingle). It continue to be difficult to take the Republican Party's professed support for free markets seriously.
Hawaii's Star Bulletin reported that Governor Linda
Lingle (R) is an opponent of the caps. The newspaper said Lingle
believes it would be better to force oil companies to open their books
and show consumers how much money they make at each stage of business.
If she is so opposed to it, why didn't she veto the bill? And is having government officials marching into private offices to confiscate accounting data really her preferred "free market" alternative?
Update: Apparently the cap in Hawaii was passed pre-Lingle, and she fought to reverse it, so I will cut her some slack. Lynne Kiesling has more details on the plan, which includes how the cap will be calculated week to week. Politicians there are calling it a "market-based price cap". LOL. Next we will see freedom-based speech limitations and privacy-based telephone taps. Note that how the cap is calculated does not change the statement I made before: Either the price cap will be set high, such that it is meaningless, or
it will be set low, such that Hawaii gets gas lines.
PS- Lynn is the economic goddess of energy markets, so if energy and power markets and regulation interest you, I recommend her blog.
Update #2: Jane Galt makes the good point that the Hawaiian price caps are on wholesale gasoline prices, so while there may be gas shortages at the wholesale level, retail prices may be able to float higher to close the supply gap. This would ironically lead to higher, not lower prices at the pump, and large profits for gasoline retailers. Since wholesale sources of gas tend to be out-of-state corporations, and gasoline retailers tend to be smaller, locally owned businesses, I wonder if this is a case of rent-seeking by gas station owners.