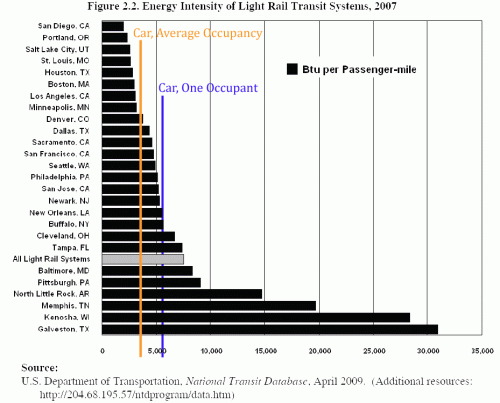
When Phoenix was building its light rail system, I made the following two-part bet:
- I could take all the money spent on construction and easily buy a Prius for every single daily rider, with money to spare
- I could take the operating deficits for light rail and buy everyone gas to run their Prius 10,000 miles per year and still have money left over.
This bet has been tested in a number of cities, including LA and Albuquerque, and I have not lost yet. Now the numbers are in for Phoenix initial ridership, and I am winning the first half of my bet in a landslide.
The other day, Phoenix trumpeted that its daily ridership had reached 37,000 boardings per weekday. Since most of those people have two boardings per day (one each direction) we can think of this as 18,500 people making a round trip each day.
Well, if we bought each of these folks a brand new Prius III for $23,000 it would cost us just over $425 million. This is WAY less than the $1.4 billion we pay to move them by rail instead. We could have bought every regular rider a Prius and still have a billion dollars left over! And, having a Prius, they would be able to commute and get good gas mileage anywhere they wanted to go in Phoenix, rather than just a maximum of 20 miles on just one line. Sure, I suppose one could argue that light rail is still relatively new and will grow, but even if ridership triples, I still win the fist half of my bet. And as the system expands, my bet just looks better, as every single expansion proposal has been at a cost of $100 million a mile or more, more expensive than the first 20 miles.
So now, all we have to do is wait to see the operating results to settle the second half of my bet. If common practice is followed from other metro areas, this will be extremely difficult to prove because the authority will do everything it can to hide the huge operating dollar hole light rail is creating.
But Coyote, what about congestion?
I am glad you asked. Folks will argue that rail reduces congestion. Normally, I would agree but argue that it reduces congestion at way too high of a price. But for Phoenix light rail, it may even be that rail makes congestion worse.
Here is why: In building Phoenix light rail, the city along most of the line had to remove two lanes of traffic (one each way) to build the line. So here is the comparison:
- Light rail carries 37,000 trips per day or about 2,000 per hour (1,000 each way) through its 18-hour operating day, though certainly there are peaks and valleys around this average
- A typical lane of road has a capacity of 2000 cars per hour, so light rail removed 4,000 cars per hour of road capacity (2,000 each way). Its unclear how many riders this equates to, but the average car in the city has 1.5 passengers, so we will call this a road capacity of 6,000 trips per hour (3,000 each way).
So, we have replaced roads that can carry 6,000 trips per hour with train tracks carrying 2,000 trips per hour. Sure, the train carries more than 2,000 in some peak periods, but probably not more than the road it replaced was capable of carrying. Further, I can attest from personal experience that the complexity of trains on the road and passing through intersections screws up the timing of lights and results in lost capacity on the roads in the area that remain.
A Thought on Sports Team Subsidies
I would love to see the ridership of the light rail on days with and without a baseball game or basketball game downtown. My sense is that a significant portion of the ridership is from game attendees (its the only time I have found it useful to ride the train). If this is the case, then this massive overspending for light rail represents yet another subsidy for professional sports teams.
By the way, I just realized that I am underestimating the financial cost to the city of the train. Most sports fans ride it not as a transit substitute per se but as a parking substitute -- the train allows one to park cheaply away from downtown and ride the the game without traffic hassles. I wonder how much the lost $15 a pop parking in city lots by the stadium due to the train is costing the city?
Light Rail Hurts the Working Poor
I think it is always important to reiterate why light rail is such a threat to the working poor who depend on transit. As I wrote the other day:
"¦light rail is simply not transit for the working poor. It is transit for yuppies that happens to be used by some working poor. They are built for white collar workers commuting to town who are too high and mighty to be caught dead in a "grubby" bus. But since light rail is orders of magnitude more expensive than buses, two things happen in every city that ever builds light rail.
1) Light rail fares skyrocket to cover their immense operating deficits and capital costs, giving the lie to politicians that sold these systems as helping working poor.
2) Bus service, the form of transit that serves most of the working poor even today in the Bay Area, is cut back to help pay for rail.
Light rail is the worst enemy of providing transit services to the working poor ever devised in this country.