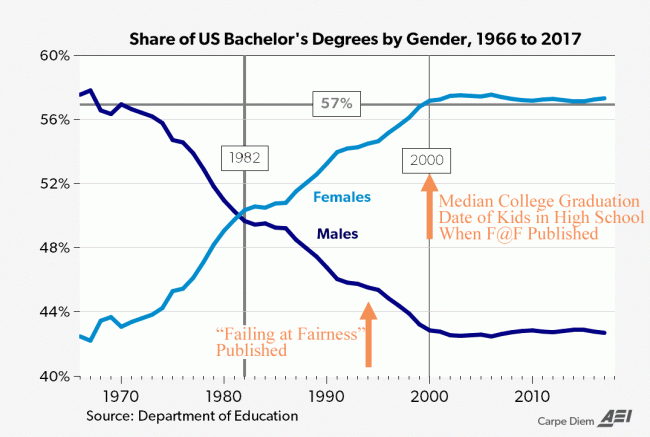
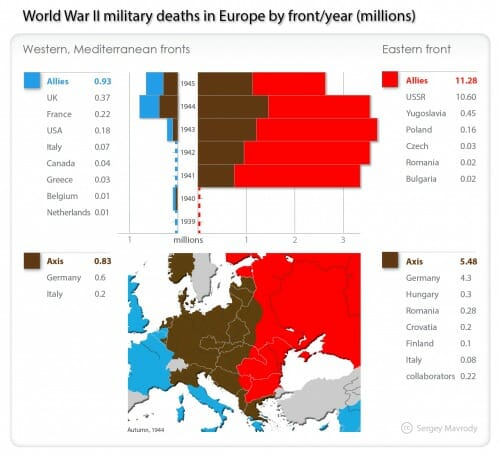
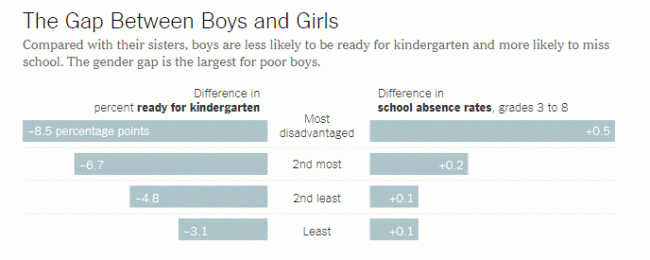After hammering various members of the G7 with new tariffs and threats of even more tariffs, Trump proposed that everyone eliminate all their tariff's and subsidies:
Q Mr. President, you said that this was a positive meeting, but from the outside, it seemed quite contentious. Did you get any indication from your interlocutors that they were going to make any concessions to you? And I believe that you raised the idea of a tariff-free G7. Is that —
THE PRESIDENT: I did. Oh, I did. That’s the way it should be. No tariffs, no barriers. That’s the way it should be.
Q How did it go down?
THE PRESIDENT: And no subsidies. I even said no tariffs. In other words, let’s say Canada — where we have tremendous tariffs — the United States pays tremendous tariffs on dairy. As an example, 270 percent. Nobody knows that. We pay nothing. We don’t want to pay anything. Why should we pay?
We have to — ultimately, that’s what you want. You want a tariff-free, you want no barriers, and you want no subsidies, because you have some cases where countries are subsidizing industries, and that’s not fair. So you go tariff-free, you go barrier-free, you go subsidy-free.
Awesome, sign me up. But is this serious? I want to get to that in a minute but first let me offer two practical observations
- Trump belabored the 270 percent Canadian dairy tariffs on US products, but at the same time the US tariff rate on Canadian dairy products is effectively infinite, because we simply don't let any in. This is the kind of complexity he is glossing over. Forget Canada, his proposal for no tariffs or subsidies would cause a major freakout among US dairy farmers, a business absolutely chock-full of crazy quilt of progressive state regulation on prices and subsidies and quotas. (and by the way, congrats to Trump for getting progressives like Drum into the free trade, anti-price-control camp).
- Simple statements like "no subsidies" are easy to make, but is a lower corporate tax rate a subsidy? How about lower minimum wages? What about really long copyright lives? What about when a governor or mayor gives out relocation incentives and tax abatements? What about the whole Amazon HQ2 deal that is coming? The list of complexities are endless. That is why long and complicated negotiations are necessary to reduce tariffs and subsidies. Fortunately we have actually done this, in deals like NAFTA and the TPP. Unfortunately, Trump has given both of these the boot. So is he really serious?
I have a love for history and like to make comparisons of modern events to history, and in this case I believe there is a very parallel case we can learn from. Here is the problem: It involves Hitler's Germany. Hitler is obviously the third rail of Internet discourse, but the example is so parallel I am still going to go ahead, with the following proviso: I am not saying Trump is Hitler, or making any such analogy or statement. I am merely attempting to learn from a very similar international negotiation that occurred in the 1930's.
If you can put aside all the emotional baggage of Hitler being either the worst mass murderer in history or at least in the top 3, he was (at least for a while until it all blew up on him) very successful in getting wins in diplomatic face-offs of the type Trump seems to want (by this I mean gains for his own country in zero-sum or even negative-sum games made by repudiating past international settlements). Hitler's brashness essentially won out with the reoccupation of the Rhineland, Germany's remilitarization, the annexation of Austria, and even led to the western powers basically handing the Sudetenland over to him.
But the example I have in mind is with the disarmament conferences of the the early 1930's. Major western powers were looking for some sort of agreement to head off an expensive and destabilizing arms race of the type that occurred in the run-up to WWI (and which by the way was way too expensive for countries bogged down in the Great Depression). As the powers discussed incremental limits or reductions, one world leader jumped into the fray and proposed that all the powers agree to total disarmament -- no more militaries at all. Can you guess who made this radical proposal that would be the envy of any 1960's hippie?**
Hitler had [President Roosevelt's] message before him when he prepared the final draft of his speech to the Reichstag. Contrary to expectation, his speech, when delivered, made no threat of immediate rearmament. Germany was ready at any time, Hitler said, to renounce the aggressive weapons forbidden to her by the Treaty of Versailles “if the whole world also bans them.” Without further ado, Germany would dissolve her whole military establishment “if neighboring nations unreservedly did the same.” For President Roosevelt's proposal the German government was “indebted with warm thanks.” Germany was ready to join in “any solemn non-aggression pact because she thinks not of attack but of her security.”
In making this speech, Hitler said that he above everyone else wanted peace. He was a soldier, he had been in the trenches, and no soldier wanted war.
Given his past actions, we suspect Hitler was not a total peacenik, so what was going on here? The Treaty of Versailles had essentially disarmed Germany, reduced its army to 100,000 men and banned it from having an air force and submarines, among other things. Germany chaffed at these limits, considering them grossly unfair, and wanted limits at parity with those on, say, France.
Hitler always liked to turn other nations' values against them in his international statements. Later, when he justified potential annexations in Austria, Czechoslovakia, and Poland, he would say that he was just interested in "self-determination of peoples" and that other powers were inconsistent and unfair when they refused to allow this principle they themselves had established to be applied to ethnic Germans in these countries. Hitler clearly didn't care one bit about free self-determination of peoples, but he was happy to throw US and British and French rhetoric back in their faces.
So in this case Hitler grabbed at the other major powers' pious pronouncements about their commitment to disarmament and again threw it back in their faces. You want disarmament? OK, let's do it -- total disarmament. Hitler knew that they would never do it -- France in particular did not trust Germany at all. Hitler waited until it was clear the other countries were not going to go for this proposal and said something like, "see, those other countries were never serious, they never wanted peace. All they want to do is keep Germany down." He proceeded to resign from the conference, renounce the military limits of the Versailles treaty, and started building Germany's army and air force. Which was what he had intended to do all along.
I know from the comments that there are folks reading my blog who honestly don't seem to understand trade and the trade deficit, and I am at my limit in explaining any more clearly. I know there are also folks who honestly think Trump is following a brinksmanship path to get to a net better set of trade rules in the future. I wrote the other day that I doubted this, but folks have emailed me the quotes about Trump proposing full free trade as proof of his intentions. Sorry, while I would love to believe this is true, and will happily admit my error later if needed, I don't believe it for a minute. It just looks too much like Germany's actions at the disarmament conference. People who truly want and understand free trade do not say things like "there are too many German cars in the United States."***
** This link is squirrelly and sometimes is gated and sometimes not. The full citation is Boeckel, R. M. (1933). The Disarmament Conference, 1933. Editorial research reports 1933 (Vol. II). Washington, DC: CQ Press. Retrieved from http://library.cqpress.com/cqresearcher/cqresrre1933100900
*** Anyone older than about 45 can tell you how badly US cars sucked before foreign competition, and how much better they are today only because we allowed this competition. Even if you don't own a German car (and I do), your American car is better and less expensive than it would be without German and Japanese and Korean competition.