D-Day: In Retrospect, More About Keeping the Soviets Out of Western Europe than About Defeating the Nazis
I am reposting this from several years ago, but I am doing it on June 7 because last time when I posted it on June 6 people called me disrespectful. I am not really sure I understand why, but this characterization is so wrong (I already have a trip lined up to be in Normandy next year around the 75th anniversary) that it is easier just to hold off for a day.
Over time, my understanding of the importance of the D-Day invasions has shifted. Growing up, I considered these events to be the single key event in defeating the Nazis. Listening to the radio this morning, this still seems to be the common understanding.
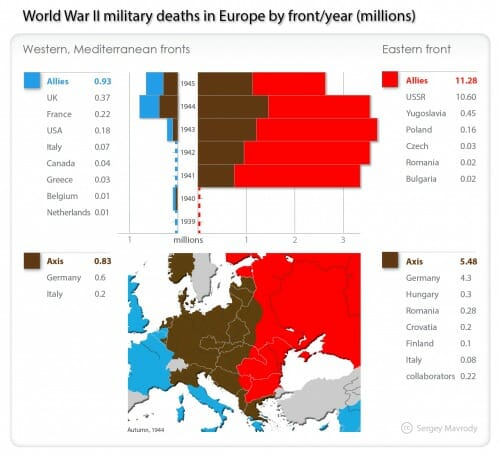
Over time, I have had to face the fact that the US (or at least the US Army) was not primarily responsible for defeating Germany -- the Russians defeated Germany, and what's more, would have defeated them whether the Allies had landed in France or not. Check out the casualties by front, from Wikipedia:
The Russians defeated Germany. Period. And I don't think the western allies would ever have had the stomach to inflict the kind of casualties on Germany that were ultimately necessary to defeat her without Russian help. To me, this is the great irony of WWII, that it was not ultimately a victory for democracy. Only totalitarian Russia could defeat totalitarian Germany. This thought often bothers me a lot. It doesn't fit with how we want to view the war.
However, D-Day did have an important effect -- it kept Western Europe out of Soviet hands. We did not know it at the time, but I would argue in retrospect that from mid-1944 on we were competing with Russia to see how Europe would get divided up after the war. D-Day allowed the western allies to overrun most of Western Europe and keep it out of Soviet hands, perhaps an even more important outcome than just speeding the defeat of the Germans. Sure, FDR gets grief for giving the farm away to Russia at Yalta, but what could he do? The Soviet occupation of Eastern Europe at that point was a fait accompli. What would have been FDR & Churchill's negotiation position at Yalta if their armies were not even on the continent (excepting Italy, where we might still be fighting in 2014 and getting nowhere)?
Postscript: There is no doubt that some German troops were pinned down in the West by the invasion, but many of these troops were already pinned down by the mere threat of invasion. Only the experienced soldiers and new equipment gathered by Hitler for the Wacht am Rhein, what we now refer to as the Battle of the Bulge, were a major diversion from the East due to the invasion, and even that was a relatively small amount of reserves compared to the immensity of the Eastern Front. Had we overrun the industrial Ruhr earlier, that would have made a real difference but we only really achieved this a few months before Berlin was taken.
There are a lots of what-ifs about the war in the West and about how the war might have been shortened. What if Montgomery really could have taken Cannes on D+1? That if the Allies had taken the larger solution to trap more Germans at Falais? What if the Allies had given limited supplies to Patton rather than Montgomery and Operation Market-Garden? What if Eisenhower had been less timid about trapping the Germans in the Bulge?
But I think the most interesting missed opportunity was a small one with huge impact -- what if the Allies had been more aggressive in taking the Scheldt Estuary? The Allies were desperately short of supplies in Northern France in the Fall of 1944. They simply could not get enough supplies over the beaches at Normandy and across France to support all the armies they had in play. They needed a real high-capacity port in the North and they actually captured one in Antwerp almost intact around September 3. Antwerp, though, is not right on the ocean -- boats had to come down an estuary which the Germans still controlled. Quick action in early September could have easily cleared the estuary and made the port almost immediately use-able. The Allies took only half measures and basically dithered for a while, failing to see the opportunity, as the Germans continued to fortify their position. In the end, it was not until nearly December before Antwerp could act as a port, long after the opportunity for a coup de grace of the Germans in the West had passed. If you are interested, here is the Wikipedia article on the Battle of the Scheldt.
Update: by the way, there were lots of good comments on the original post and you can see them here.