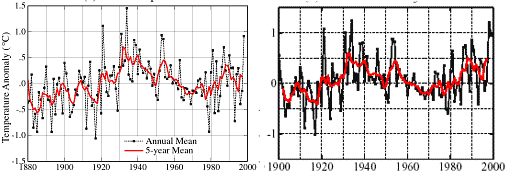
This is really big news, and a fabulous example of why two-way scientific discourse is still valuable, in the same week that both Newsweek and Al Gore tried to make the case that climate skeptics were counter-productive and evil.
Climate scientist Michael Mann (famous for the hockey stick chart) once made the statement that the 1990's were the
warmest decade in a millennia and that "there is a 95 to 99% certainty
that 1998 was the hottest year in the last one thousand years." (By
the way, Mann now denies he ever made this claim, though you can watch him say
these exact words in the CBC documentary Global
Warming: Doomsday Called Off).
Well, it turns out, according to the NASA GISS database, that 1998 was not even the hottest year of the last century. This is because many temperatures from recent decades that appeared to show substantial warming have been revised downwards. Here is how that happened (if you want to skip the story, make sure to look at the numbers at the bottom).
One of the most cited and used historical surface temperature databases is that of NASA/Goddard's GISS. This is not some weird skeptics site. It is considered one of the premier world temperature data bases, and it is maintained by anthropogenic global warming true believers. It has consistently shown more warming than any other data base, and is thus a favorite source for folks like Al Gore. These GISS readings in the US rely mainly on the US Historical Climate Network (USHCN) which is a network of about 1000 weather stations taking temperatures, a number of which have been in place for over 100 years.
Frequent readers will know that I have been a participant in an effort led by Anthony Watts at SurfaceStations.org to photo-document these temperature stations as an aid to scientists in evaluating the measurement quality of each station. The effort has been eye-opening, as it has uncovered many very poor instrument sitings that would bias temperature measurements upwards, as I found in Tucson and Watts has documented numerous times on his blog.
One photo on Watt's blog got people talking - a station in MN with a huge jump in temperature about the same time some air conditioning units were installed nearby. Others disagreed, and argued that such a jump could not be from the air conditioners, since a lot of the jump happened with winter temperatures when the AC was dormant. Steve McIntyre, the Canadian statistician who helped to expose massive holes in Michael Mann's hockey stick methodology, looked into it. After some poking around, he began to suspect that the GISS data base had a year 2000 bug in one of their data adjustments.
One of the interesting aspects of these temperature data bases is that they do not just use the raw temperature measurements from each station. Both the NOAA (which maintains the USHCN stations) and the GISS apply many layers of adjustments, which I discussed here. One of the purposes of Watt's project is to help educate climate scientists that many of the adjustments they make to the data back in the office does not necessarily represent the true condition of the temperature stations. In particular, GISS adjustments imply instrument sitings are in more natural settings than they were in say 1905, an outrageous assumption on its face that is totally in conflict to the condition of the stations in Watt's data base. Basically, surface temperature measurements have a low signal to noise ratio, and climate scientists have been overly casual about how they try to tease out the signal.
Anyway, McIntyre suspected that one of these adjustments had a bug, and had had this bug for years. Unfortunately, it was hard to prove. Why? Well, that highlights one of the great travesties of climate science. Government scientists using taxpayer money to develop the GISS temperature data base at taxpayer expense refuse to publicly release their temperature adjustment algorithms or software (In much the same way Michael Mann refused to release the details for scrutiny of his methodology behind the hockey stick). Using the data, though, McIntyre made a compelling case that the GISS data base had systematic discontinuities that bore all the hallmarks of a software bug.
Today, the GISS admitted that McIntyre was correct, and has started to republish its data with the bug fixed. And the numbers are changing a lot. Before today, GISS would have said 1998 was the hottest year on record (Mann, remember, said with up to 99% certainty it was the hottest year in 1000 years) and that 2006 was the second hottest. Well, no more. Here are the new rankings for the 10 hottest years in the US, starting with #1:
1934, 1998, 1921, 2006, 1931, 1999, 1953, 1990, 1938, 1939
Three of the top 10 are in the last decade. Four of the top ten are in the 1930's, before either the IPCC or the GISS really think man had any discernible impact on temperatures. Here is the chart for all the years in the data base:

There are a number of things we need to remember:
- This is not the end but the beginning of the total reexamination that needs to occur of the USHCN and GISS data bases. The poor correction for site location and urbanization are still huge issues that bias recent numbers upwards. The GISS also has issues with how it aggregates multiple stations, apparently averaging known good stations with bad stations a process that by no means eliminates biases. As a first step, we must demand that NOAA and GISS release their methodology and computer algorithms to the general public for detailed scrutiny by other scientists.
- The GISS today makes it clear that these adjustments only affect US data and do not change any of their conclusions about worldwide data. But consider this: For all of its faults, the US has the most robust historical climate network in the world. If we have these problems, what would we find in the data from, say, China? And the US and parts of Europe are the only major parts of the world that actually have 100 years of data at rural locations. No one was measuring temperature reliably in rural China or Paraguay or the Congo in 1900. That means much of the world is relying on urban temperature measurement points that have substantial biases from urban heat.
- All of these necessary revisions to surface temperatures will likely not make warming trends go away completely. What it may do is bring the warming down to match the much lower satellite measured warming numbers we have, and will make current warming look more like past natural warming trends (e.g. early in this century) rather than a catastrophe created by man. In my global warming book, I argue that future man-made warming probably will exist, but will be more like a half to one degree over the coming decades than the media-hyped numbers that are ten times higher.
So how is this possible? How can the global warming numbers used in critical policy decisions and scientific models be so wrong with so basic of an error? And how can this error have gone undetected for the better part of a decade? The answer to the latter question is because the global warming and climate community resist scrutiny. This weeks Newsweek article and statements by Al Gore are basically aimed at suppressing any scientific criticism or challenge to global warming research. That is why NASA can keep its temperature algorithms secret, with no outside complaint, something that would cause howls of protest in any other area of scientific inquiry.
As to the first question, I will leave the explanation to Mr. McIntyre:
While acolytes may call these guys "professionals", the process of
data adjustment is really a matter of statistics and even accounting.
In these fields, Hansen and Mann are not "professionals" - Mann
admitted this to the NAS panel explaining that he was "not a
statistician". As someone who has read their works closely, I do not
regard any of these people as "professional". Much of their reluctance
to provide source code for their methodology arises, in my opinion,
because the methods are essentially trivial and they derive a certain
satisfaction out of making things appear more complicated than they
are, a little like the Wizard of Oz. And like the Wizard of Oz, they
are not necessarily bad men, just not very good wizards.
For more, please see my Guide to Anthropogenic Global Warming or, if you have less time, my 60-second argument for why one should be skeptical of catastrophic man-made global warming theory.
Update: Nothing new, just thinking about this more, I cannot get over the irony that in the same week Newsweek makes the case that climate science is settled and there is no room for skepticism, skeptics discover a gaping hole and error in the global warming numbers.
Update #2: I know people get upset when we criticize scientists. I get a lot of "they are not biased, they just made a mistake." Fine. But I have zero sympathy for a group of scientists who refuse to let other scientists review their methodology, and then find that they have been making a dumb methodology mistake for years that has corrupted the data of nearly every climate study in the last decade.
Update #3: I labeled this "breaking news," but don't expect to see it in the NY Times anytime soon. We all know this is one of those asymmetric story lines, where if the opposite had occurred (ie things found to be even worse/warmer than thought) it would be on the front page immediately, but a lowered threat will never make the news.
Oh, and by he way. This is GOOD news. Though many won't treat it that way. I understand this point fairly well because, in a somewhat parallel situation, I seem to be the last anti-war guy who treats progress in Iraq as good news.
Update #4: I should have mentioned that the hero of the Newsweek story is catastrophic man-made global warming cheerleader James Hansen, who runs the GISS and is most responsible for the database in question as well as the GISS policy not to release its temperature aggregation and adjustment methodologies. From IBD, via CNN Money:
Newsweek portrays James Hansen, director of NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies, as untainted by corporate bribery.
Hansen
was once profiled on CBS' "60 Minutes" as the "world's leading
researcher on global warming." Not mentioned by Newsweek was that
Hansen had acted as a consultant to Al Gore's slide-show presentations
on global warming, that he had endorsed John Kerry for president, and
had received a $250,000 grant from the foundation headed by Teresa
Heinz Kerry.
Update #5: My letter to the editor at Newsweek. For those worried that this is some weird skeptic's fevered dream, Hansen and company kind of sort of recognize the error in the first paragraph under background here. Their US temperature chart with what appears is the revised data is here.
Update #6: Several posts are calling this a "scandal." It is not a scandal. It is a mistake from which we should draw two lessons:
- We always need to have people of opposing opinions looking at a problem. Man-made global warming hawks expected to see a lot of warming after the year 2000, so they never questioned the numbers. It took folks with different hypotheses about climate to see the jump in the numbers for what it was - a programming error.
- Climate scientists are going to have to get over their need to hold their adjustments, formulas, algorithms and software secret. It's just not how science is done. James Hansen saying "trust me, the numbers are right, I don't need to tell you how I got them" reminds me of the mathematician Fermat saying he had a proof of his last theorem, but it wouldn't fit in the margin. How many man-hours of genius mathematicians was wasted because Fermat refused to show his proof (which was most likely wrong, given how the theorem was eventually proved).
Final Update: Some parting thoughts, and recommendations, here.