OK, so after the monks and coffins, here is the future licensing act ripe for abuse by industry incumbents to protect their position.
New state licenses required for anyone handling a mortgage application could help prevent a repeat of the bad loans that contributed to Phoenix's housing crash....
The law, passed in 2008, creates state oversight for people who take loan applications, gives consumers an avenue for reporting misconduct and establishes a fund to help repay borrowers who lose money because of unethical or illegal acts by their loan officers.
The law faces hurdles, as cash-strapped Arizona struggles to process thousands of new applications.
Still, advocates call it a success. Many of the risky - and sometimes illegal - home loans that helped lead to record foreclosures in Arizona might not have been made if the more than 10,000 unlicensed loan officers working then had been subject to more oversight.
How? If people were selling illegal home loans before, they were already breaking the law and the state obviously was unable to enforce the law. How is adding a piece of paper that must be applied for each year going to help? My company has all kinds of silly licenses - liquor licenses, guiding licenses, health licenses, tobacco sales licenses, over-the-counter drug sales licenses, even egg licenses - and in not a single case does the issuer of these licenses exercise any sort of oversight of our operations. If they get their extensive paperwork (so workers have an excuse to retain their jobs - after all someone has to process the paperwork) and their check, that is generally the sum of interactions with these organizations.
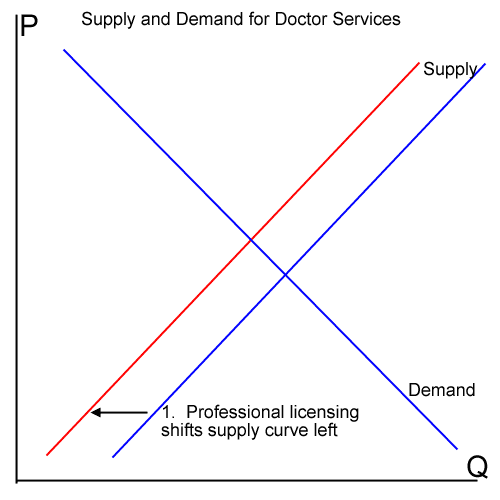
Now, some of these licenses were hard to get in the first place, but not for any reason of my character or ethics or business model. They were hard to get because their issuance has been co-opted by incumbent businesses in the state who use the process to limit competition. Liquor licenses are a great example - in places like Shasta County CA and Lake Havasu City AZ, we had a real problem getting the liquor license over opposition from existing businesses.
This is almost mindless naivete:
"Loan-officer licensing is long overdue in Arizona," said Felecia Rotellini, who for five years served as superintendent of the Department of Financial Institutions, the state agency regulating the mortgage industry. She is running for Arizona attorney general.
"A lot of bad loans wouldn't have been made if we had it before," Rotellini said. "It gives me peace of mind for consumers to know we have licensing now."
The author of the article just throws the following statement out there without any source, as if it was an axiom with which we all would agree
In Arizona, the housing boom and crash were partly fueled by loan officers, how they operated and how they were paid.
In fact, the author's incredible confidence in licensing is undermined in this adjacent statement:
Mortgage brokers, who run firms that connect borrowers with the best loans, have long been regulated by the Department of Financial Institutions.
Brokers employ loan officers, who work directly with borrowers, collecting their Social Security numbers and financial information to determine whether they qualify for a loan. Loan officers usually recommend types of mortgages and lenders.
These officers, sometimes called originators, weren't subject to state scrutiny. They worked under the licenses of their brokers, much the way an apprentice would work for a licensed contractor. Previously, that oversight was considered sufficient.
So the firms these guys worked for were licensed, but the individual employees were not. But if that licensing of firms, which after all is the level where loan practices and compensation policy are set which supposedly are at fault, how does licensing individual employees help? This is a typical political step that a) gets some state organization more money and power, b) generates one sound bite in a news cycle for some politician to tell voters that they care and c) does zero for consumers.
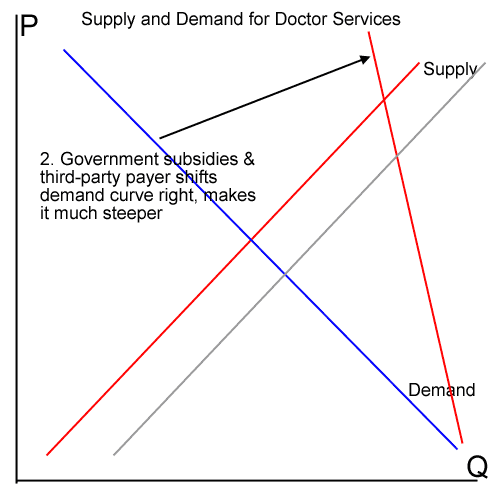
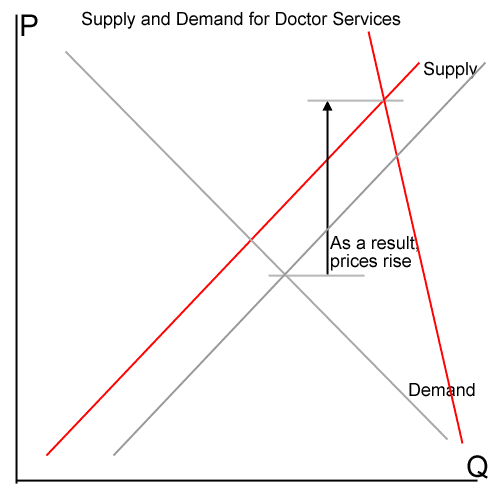
At the end of the day, the real cause of the housing boom was easy credit, and yes loan officers participated in this given that their commission-based incentives caused them to want to make every loan possible. But this incentive outcome would not have been some kind of insight to the people and system that employed the loan officers. In fact, everyone from the loan officer to the Congress wanted easy credit, and to blame one link in the chain of delivering this credit to consumers is madness. Going forward, there is absolutely no evidence that the government is going to reduce its history of promoting easy credit, as evidenced by any number of federal loan modification and lending programs over the last 2 years. So the likelihood that a government regulatory agency could have somehow headed off the bubble and its bursting is just silly. The government was a party to it.
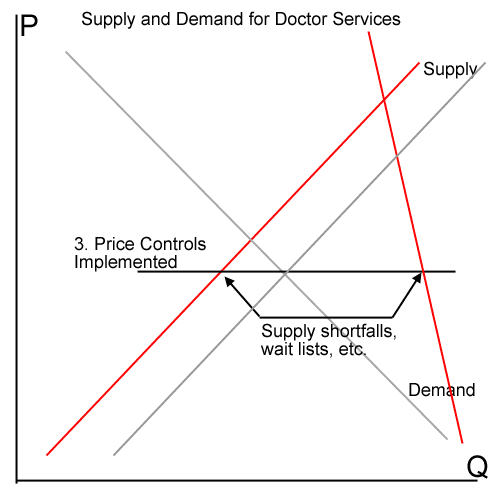
In the long run this mechanism will almost certainly be co-opted by current loan issuers as a way to limit competition, much as real estate agents and lawyers and funeral home directors already do. As a minimum, this is a way for mortgage brokers to outsource some of the cost of running background checks and such on their employment candidates onto taxpayers. In fact, I wonder who was behind this law in the first place?
Backed by mortgage brokers and real-estate regulators, the law quietly went into affect on July 1