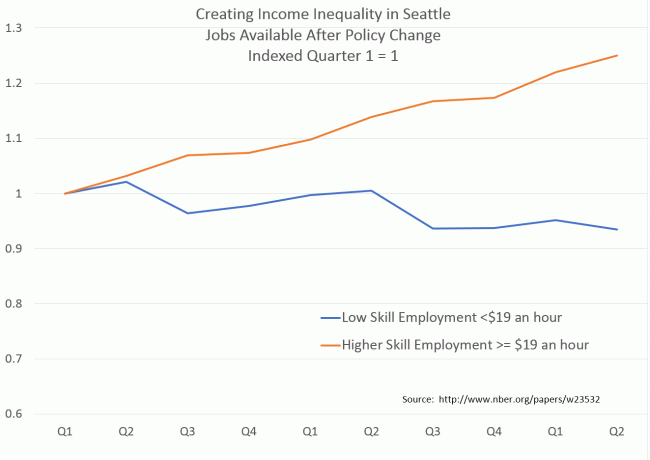I am not sure I am able to continue blogging in the current environment. When I began blogging over 12 years ago, it was to report on my various adventures in trying to run a small business. It soon morphed into a platform for me to think out loud about various policy issues. For example, while I didn't really understand this when I started, it became a platform for me to think through mistakes I made in my initial enthusiasm for the Iraq War. You can see me in the early years evolve from a kind of knee-jerk global warming absolute denier to a lukewarmer with much more understanding of the underlying science. I think of myself as an intellectual (though one who cannot spell or proof-read) who likes to discuss policy.
But I am not sure this is the time for that. The world seems to be moving away from intellectualism. I say this not because Trump voters were somehow rejecting intellectualism, but because intellectuals themselves seem to be rejecting it. They act like children, they are turning universities into totalitarian monoculters, and they compete with each other to craft mindless 140-character "gotchas" on Twitter. I challenge you to even find a forum today for intellectual exchange between people who disagree with one another. In politics, Trump clearly rejects intellectualism but for whatever reasons, the Democratic opposition has as well.
We have a tribal war going on in this country that has officially gone beyond any real policy issues. While the US and the Soviet Union had real differences in philosophy and approach, most of their confrontations were in proxy wars which bore little resemblance to these values. That is what politics are now -- a series of proxy wars. We spend several days focusing attention on Jeff Sessions, but spend pretty much zero time talking about real issues like approaches to the drug war, and police accountability, and sentencing reform. Instead all we can focus on is the political proxy war of this stupid Russia hacking story. Obama's birth certificate and Hillary's servers and Russian hacking and Trump's real estate sales -- all we fight are proxy wars.
And like most tribal warfare, the two tribes are incredibly similar. I have called them the Coke and Pepsi party for years. Go talk to the the rank and file and sure, one group may like Nascar and barbecue while the other likes Phish concerts and kale, but you will see them asking for the same sorts of things out of government. Take the minimum wage, a traditional blue tribe issue. In Arizona, a heavily red state (we have a super-majority in the legislature of the red team), a $10 minimum wage referendum passed by nearly 60% of the vote last year. The members of the two tribes absolutely hate each other, but they support the same laws. I guess I should be happy they don't get together, since as a libertarian I think many of these things they want are bad ideas.
People tell me I need to just deal with the adversity. But I don't mind opposition per se. I love when I get a chance to respond to real criticism. Hell, I wrote 5000 words or so here in response to such criticism. It's fun. But more likely nowadays I will write a couple thousand words on school choice and the response will be, in total, "Your a Trump cuckservative." Several years ago I wrote a long article on rail in response to a Joel Epstein piece. Epstein had argued the US rail rail system was inferior to those in Europe and Asia because we don't have enough passenger rail. I argued with a series of charts and analysis that the US rail system was superior because it focused on freight over passengers, and that shifting freight to rail had far more environmental benefits than shifting passengers to rail. Epstein's entire response to my article was, "You should get out of the country more often." This is the classic intellectual argument of our day. It was smug. It implied my article was based on being part of the wrong tribe, the narrow-minded denizens of flyover country rather than the coastal set that have been to Gstaad but not Tulsa. At it did not even bother addressing the issues raised.
Or look at Black Lives Matter. BLM actually had what looked to me to be the outlines of a pretty good plan. To really achieve their goals, though, was going to take a lot of work jurisdiction by jurisdiction, establishing some model legislation and best practices and bringing it to various municipalities. It didn't even try. It abandoned this plan in favor of just disrupting sh*t and shaming the unwoke for saying that "all lives matter." Today, invocations of BLM consist pretty much 100% of virtue signalling for one's own tribe or shaming of the other tribe. Its the equivalent of dueling fans at a game yelling "Yankees suck!" "No, Red Sox suck!"
People also tell me to just deal with it, that if I love the policy stuff I should ignore these problems. But let me give you an analogy. Let's say you absolutely love English Premier League football, but every time you try to go to a game, you miss most of what happens on the field because hooligans are fighting around you in the stands. Do you keep going for your love of football or at some point is the mess that surrounds it just too much?
Anyway, I am highly tempted just to say "screw it" for a while and focus on something else entirely. I am trying a different approach as a change of pace, trying to write a more formal policy piece for a think tank, but I am having a surprising amount of trouble doing it well. Writing such pieces was not really my forte at McKinsey when I was a consultant and I am not sure it is now. Not disciplined enough in my writing, I think.
Anyway, on a positive front, I now have a dedicated (though very small) room for my model railroad and I installed the first bit of benchwork. This is sort of like laying the keel for a new ship. Coyoteblog readers, I know, will be hanging on the edges of their seats for further updates.

From Parks and Recreation:
Jean-Ralphio: Why don’t you use that time to go after one of your passions? Like model trains, or toy Gandalfs or something.
Ben: I don’t know why you jumped straight to model trains. I mean, it’s accurate…