I generally have a bet I make for new light (and heavy) commuter rail systems. I bet that for the amount the system cost to build, every single daily rider could have instead been given a Prius to drive for the same money; and, with the operating losses and/or subsidy the system requires each year, every one of those Prius drivers could be given enough gas to make their daily commute. And still have money left over. I have tested this bet for the systems in Los Angeles and Albuquerque.
Well, it turns out I left something out. Many people are interested in commuter rail because it is perceived to be greener, which nowadays generally means narrowly that it uses less energy and thus produces less CO2. But in fact, it may not. Blogger John Moore sent me a link to this article by Brad Templeton analyzing energy usage in various transportation modes. While a full train can be fairly efficient (just as a full SUV could be if 7 passengers were in it), cars and trains and busses are seldom full. When you look at their average load factors, trains are seldom better than cars:
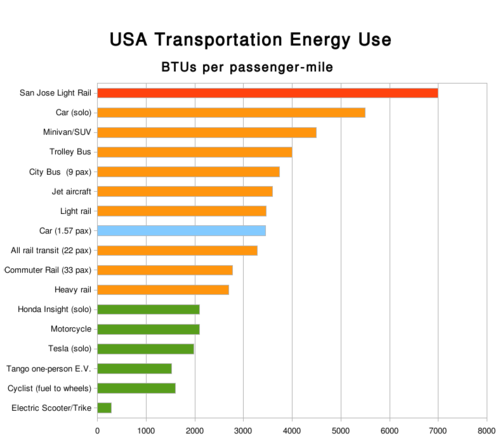
In fact, a car at its average load factor (1.57 pax) has about the same energy use as busses or light rail per passenger mile. The analysis is difficult to do well, but even with errors, its clear that rail projects do not dominate over car travel in terms of energy use (One must be careful to differentiate rail project construction decisions from individual choice of mode decisions -- an individual at the margin shifting from car to train saves a lot of energy; a city choosing to invest in a large new rail system to entice drivers off the road does not).
In fact, relevent to my bet, Mr. Templeton says this:
My first conclusion is that we would get more efficient by pushing
small, fuel efficient vehicles instead of pushing transit, and at
a lower cost.
He explains his results, which are counter-intuitive to many
A full bus or trainload of people is more efficient than private cars,
sometimes quite a bit more so. But transit systems never consist
of nothing but full vehicles. They run most of their day with light
loads. The above calculations came from figures citing the
average city bus holding 9 passengers, and the average train (light
or heavy) holds 22. If that seems low, remember that every packed
train at rush hour tends to mean a near empty train returning down
the track.
Transit vehicles also tend to stop and start a lot, which eats
a lot of energy, even with regenerative braking. And most
transit vehicles are just plain heavy, and not very aerodynamic.
Indeed, you'll see tables in the DoE reports that show that over the past 30 years,
private cars have gotten 30% more efficient, while buses have
gotten 60% less efficient and trains about 25% worse. The
market and government regulations have driven efforts to make cars
more efficient, while transit vehicles have actually worsened.
In order to get people to ride transit, you must offer frequent
service, all day long. They want to know they have the freedom to leave at
different times. But that means emptier vehicles outside of
rush hour. You've all seen those huge empty vehicles go by, you just
haven't thought of how anti-green they were. It would be better
if off-hours transit was done by much smaller vehicles, but that
implies too much capital cost -- no transit agency will buy enough
equipment for peak times and then buy a second set of equipment for
light demand periods.
A lot of his data can be checked at the US Department of Energy data book here. In particular, you can see the key numbers in table 2.12. After perusing this data for a bit, I had a few other reactions:
- Commercial air travel gets a bad rap. On a passenger mile basis, it is really not worse than driving and only about 20% worse than Amtrack (and probably the same as Amtrak or better if you leave out the Northeast Corridor). (table 2.14)
- Busses have really gotten way more inefficient over the years, at the same time cars have become substantially more efficient. While the government criticizes its citizens for not practicing enough energy conservation, in fact its citizens have been buying more and more fuel efficient vehicles while the government has been buying less efficient vehicles. (table 2.13)
- While passenger cars have increased substantially in efficiency, over the road trucks have seen no progress, and have actually gotten less efficient over the last 10 years (table 2-18)
Make sure to read the whole article. I think the author is pretty fair at achnowleging where the uncertainties are in the analysis. He also has comparisons of mass transit energy numbers between cities. A few individual cities seem to beat even the most efficient cars -- most, including places like New York, do not.
Postscript: I don't think numbers for New York include taxis. If they did, New York would likely look terrible. From an energy standpoint, taxis are a horrible transportation option, perhaps the worst possible. It would be interesting to know how many New Yorkers who look down on SUV's routinely get around town using taxis.