Update on Tesla from The Conference Call Today
Today after the market closed was Tesla's analyst conference call to review fourth quarter earnings. TL:DR It was as weird as ever, maybe weirder. Even before the call, Elon Musk said that the numbers released today would be un-audited, and the call ended by saying -- in a sort of "oh by the way" over the shoulder parting shot -- that their CFO was leaving and being replaced by a 36-year-old with only Tesla experience and no prior CFO role (not unlike the random young dude that the Arizona Cardinals just hired as their coach, but that is another story). Neither Musk statement was a big confidence boost given the myriad questions swirling around the legitimacy of Tesla's reported financials. But the REALLY weird stuff was in between.
The LA Times, which really has had some of the best Tesla coverage, has the best summary I have found so far of the call. Before I get into some things we learned that helped support my article I wrote the other day, I want to share some of the priceless other highlights of the call. All from the LAT article:
Tesla faces questions about whether enough new Model 3 sedans can be sold to generate substantial profits.
“The demand for the Model 3 is insanely high. The inhibitor is that people don’t have the money to buy one,” Tesla Chief Executive Elon Musk told analysts on the call.
This is really hilarious. The same could be said of Ferrari's, Manhattan Penthouses, and bone-in rib-eyes at most top steakhouses. Once you get past the absurdity of the statement, you realize that Musk essentially admitted the demand cliff many have suspected for the Model 3, as Tesla has burned through its entire multi-year order book for the Model 3 in just 6 months.
Yet, Musk said, the new [China] factory [which is currently a bare patch of dirt] will be building cars at an annual rate of 300,000 vehicles by the end of the year, at an expenditure of $500 million — much less than a typical auto plant normally costs.
And much faster, by the way, than any automotive company in history has ever started up a new production plant.
It turns out, by the way, the Tesla still seems to be running itself like a free-wheeling largely-unplanned software startup rather than like a capital-intensive automobile manufacturer. Imagine this from Daimler or Volkswagen or GM:
Musk said Tesla might build the Model Y at its Nevada battery factory but indicated no one should count on it. ”It’s not a for-sure thing, but it’s quite likely, and it’s our default plan,” he said.
But let's get to my thesis I have been arguing for a while. Tesla has a lot of problems, but the one I have been most focused on is that Tesla is a growth company that has stopped managing itself for growth. Both R&D and capital spending have dried up, especially in relation to revenues -- a particularly vexing problem because Tesla has chosen a strategy of owning the sales, service, and fueling networks (not just manufacturing) so growth is even more capital intensive for Tesla than it is for other automobile manufacturers (see the earlier article for details). Tesla's stock price is close to $300, but its current auto business is likely not worth more than $50 share -- the other $250 is hopes and dreams of growth, valuation that goes away if Tesla is no longer perceived as a growth story.
Beyond the fact listed above that Musk essentially admitted the demand problem in the US for Model 3, here is what else we heard:
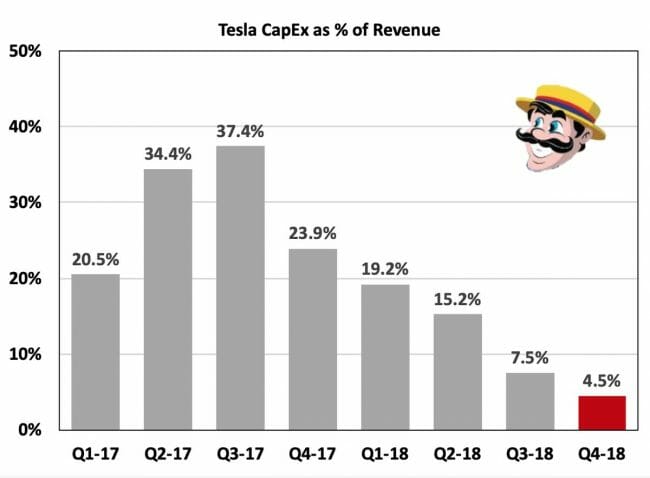
Tesla owed much of its cash-flow improvement to a drastic reduction in capital expenses — which can signal either a reduced need to buy, say, factory robots or a slowdown of investment in future growth. In the last three quarters, capital spending has shrunk from $786 million to $510 million to $324 million.
This number is insanely low. As @teslacharts showed today, this is equal to 4.5% capex as a percent of revenues!
The mature non-growing auto companies typically spend 5-5.5% or revenues on capex just to maintain their position. 4.5% is NOT a growth number.
In a conference call with analysts, Musk said he still plans to build a factory in China this year and begin building a Model Y subcompact next year. Asked where the money would come from, CFO Ahuja said cutting costs and careful spending would do the trick.
Musk was unusually subdued but his usual speculative self. The China factory site remains a bare patch of ground, and no news was offered on loans from Chinese banks that Tesla is hunting for.
Beyond the fact that Musk is almost criminally full of sh*t on his projections for his China factory production, why the hell is Tesla digging around in the couch cushions to fund their Asian expansion? Their valuation is at freaking 60-80x earnings. Why aren't they raising capital for this and a thousand other things they need to be doing?
But in fact, Tesla is actually planning to contract its capital base, announcing in the call they will likely pay the upcoming ~$1 billion bond redemption in cash.
At the same time, past announced growth projects are falling by the wayside. The semi truck, which was announced to great fanfare and helped pump up the stock price at a critical time, has essentially been dropped from the product plan (Musk did something very similar with the solar shingle at SolarCity, touting the technology and leveraging it to sell the company to Tesla, and then essentially dropping the product).
In the Model S & X, Tesla has already acknowledged that no effort has been started to update these aging products, and in fact production is being cut and much of the manufacturing workforce for these products has been laid off. These two products have always been the main source of Tesla's gross margins and its unclear how they will make up the lost margin and sales from these core products that Tesla seems to be essentially abandoning rather than investing in and refreshing. We also learned that prices are being cut on these vehicles:
On Tuesday, Tesla offered an $8,000 discount on S and X cars for customers who let Tesla limit the range of the car’s battery pack using custom software. The range for the software-limited Model S, for example, would be cut by 20 miles, to 310. That car cost $96,000 at the end of 2018. Tesla cut that price by $2,000 this month. Tuesday’s deal puts the price down to $85,000 — a reduction of $11,000 for 20 miles less range.
Note the software limitation does ZERO to cut Tesla's costs, so these are 100% hits to Tesla's margins.
Because the batteries themselves wouldn’t differ, production costs would stay the same as in the higher-range car. The gross profit margin falls by $11,000 per car. (A Tesla spokesman told The Times that improved efficiencies on the assembly line would help address that problem.)
The next milestone for Tesla will be release of fully audited 2018 numbers. I have no idea when these will appear and would not be surprised if they are delayed. There are still some real financial question marks in the numbers we have seen to date, and only the 10-K will begin to answer some of them.
In the past I have been careful to say that Tesla is a dangerous short and that you should not take my non-expert advice investing, and I repeat all that now. I understand business strategy and I am more sure than ever that Tesla's strategy is falling apart and the wheels are very likely to come completely off in the first quarter. However, I do not understand the stock market's ins and outs and whether Tesla's failings get translated now or later to the stock price is not something I can predict well. Trump could bail them out, some sucker could buy them, they could fudge their numbers for years, etc. So be careful.
One More: I forgot to mention that Tesla has reduced its SG&A expenses over the previous two quarters in absolute terms, and thus substantially on a percent of revenue basis. For a mature company this is good news. For a growth company, this is a sign that growth may not be the goal any longer. SG&A staffing represents a company's capacity to do new things and take on new projects and enter new markets and add new services. No way companies like Google or Facebook would have been trimming SG&A in the height of their growth years. Cutting SG&A is what you do when growth is over or when there is a cash crunch or both.
Postscript: Not to be too much of a pedant on myself, but I said "parting shot" which I think is OK but I believe the original term was actually "Parthian Shot" named for that army's technique of riding full on towards the enemy, then turning tail and riding away but firing backwards with a bow and arrow off their horse as they rode away. Really used to piss off the Romans.