After having time to think more about the current crisis, I think the reason it is confusing is that it is the result of two parallel but largely independent causes that worked together to create this mess. I told my mother-in-law in an email last week that the financial crisis would likely be a Rorschach test where everyone sees the crisis caused by all the things they opposed before the crisis. Conservatives will see government intervention, liberals will see greed and deregulation.
What makes this situation particularly confusing is that of the two causes I believe led to the crisis, each has been embraced by one of the two parties as the only cause. It's a case where everyone is half right, but the other half is important too. It's a two part recipe, with neither active ingredient causing much of an explosion until mixed with the other. (special thanks to the folks at Q&O who have had a lot of good posts on these issues).
Cause 1: Creating the Asset Bubble
The first thing that had to happen for the crisis was the creation of an asset bubble. We need some type of over-valued asset whose prices crash to earth to spark the crisis. So we begin with housing.
Home prices have gone through boom-bust cycles for years, just as have many commodities. There is a whole body of literature on such cycles, so we will leave that aside and accept their existence as a feature of markets and human behavior.
But this housing bubble had a strong accelerant, in the form of the Federal government. For years, this nation has made increasing home ownership a national goal and many laws and tax policies have been aimed at this goal. The mortgage interest deduction on personal income taxes is just one example.
Starting in 1992, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, which were strange quasi-public / quasi-private entities, came under pressure from the Congress (e.g. Barney Frank) and the Clinton administration to add increasing home ownership to poorer people part of their missions.
Fannie Mae, the
nation's biggest underwriter of home mortgages, has been under
increasing pressure from the Clinton Administration to expand mortgage
loans among low and moderate income people and felt pressure from stock
holders to maintain its phenomenal growth in profits.
In
addition, banks, thrift institutions and mortgage companies have been
pressing Fannie Mae to help them make more loans to so-called subprime
borrowers. These borrowers whose incomes, credit ratings and savings
are not good enough to qualify for conventional loans, can only get
loans from finance companies that charge much higher interest rates --
anywhere from three to four percentage points higher than conventional
loans.
''Fannie Mae has expanded home ownership for millions of
families in the 1990's by reducing down payment requirements,'' said
Franklin D. Raines, Fannie Mae's chairman and chief executive officer.
''Yet there remain too many borrowers whose credit is just a notch
below what our underwriting has
The results were astonishing:
Beginning in 1992, Congress pushed Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac to
increase their purchases of mortgages going to low and moderate income
borrowers. For 1996, the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) gave Fannie and Freddie an explicit target "” 42% of their mortgage financing had to go to borrowers with income below the median in their area. The target increased to 50% in 2000 and 52% in 2005.
For 1996, HUD required that 12% of all mortgage purchases by Fannie and Freddie be "special affordable" loans, typically to borrowers with income less than 60% of their area's median income. That number was increased to 20% in 2000 and 22% in 2005. The 2008 goal was to be 28%. Between 2000 and 2005,
Fannie and Freddie met those goals every year, funding hundreds of
billions of dollars worth of loans, many of them subprime and
adjustable-rate loans, and made to borrowers who bought houses with
less than 10% down.
Fannie and Freddie also purchased hundreds
of billions of subprime securities for their own portfolios to make
money and to help satisfy HUD affordable housing goals. Fannie and
Freddie were important contributors to the demand for subprime
securities.
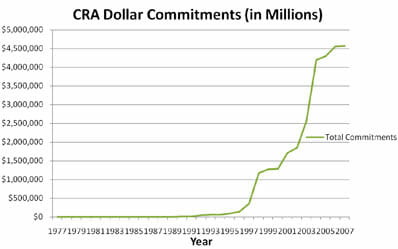
Simultaneously, the 1977 Community Reinvestment Act was pushing private banks to make more loans to less qualified borrowers:
The Community Reinvestment Act (CRA) did the same thing with
traditional banks. It encouraged banks to serve two masters "” their
bottom line and the so-called common good. First passed in 1977, the
CRA was "strengthened" in 1995, causing an increase of 80% in the
number of bank loans going to low- and moderate-income families.
These actions had a double whammy on the current crisis. First, by pushing up housing demand, they inflated the housing pricing bubble. Second, it meant that these inflated-price homes were being bought with lower and lower down payments. In effect, individuals were taking on much more leverage (leverage is a term that I will use to mean the percentage of debt used to finance a set of assets -- more leverage means more debt and less equity. The term comes from the physics of a mechanical lever, in that more debt, like a lever, can magnify force. Profits from assets are multiplied by leverage, but, alas, so are losses.)
When the economy softened and the housing bubble started to burst, these new mortgage customers the government went out of its way to bring into the system did not have any resources to handle the changes -- they did not have the down payment to cushion them (or the banks) against falls in asset value and did not have the cash flow to cushion them against falling income in the recession and/or rising interest rates.
The result: Huge portfolios of failing loans with rapidly falling collateral values.
Cause 2: Over-leverage of Risky Assets and Related De-regulation of Capital Requirements
I think the word "greed" was used about a zillion times last night in the Vice-Presidential debate. But what does it mean in this context? After all, we are all greedy in one way or another, if one equates greed with looking after one's self-interest.
So I will translate "greed" for you: When you hear "greed on Wall Street", think leverage. Remember, we said above that as long as the underlying asset values are going up, leverage (ie more debt) multiplies profitability. [Quick example: Assume a stock that goes from $100 to $110 in a year. Assume you pay 5% interest on money. No leverage, you make $10 on a $100 investment. With 95% leverage -- ie buying $2000 worth of the stock with $100 equity and $1900 debt -- you would make $105 on the same $100 equity investment. Leverage multiplied your returns by more than a factor of 10]
Remember that around the year 2000 we had the Internet bubble burst in a big way. A lot of companies not only dropped, but went to $0 in value. This was painful, but we did not have a cascading problem. Why? In part because most of the folks who invested in Internet companies did not do so in a highly leveraged way. The loss was the loss, time to move on. Similarly in this case, if these mortgage packages had been held as a piece of a un-leveraged portfolio, like a pension fund our an annuity, the loss would not have been fun to write off but it would not have cascaded as it has. The government would have had to bail out Fannie and Freddie, a few banks would have failed, but the disaster would have been limited.
One reason this problem has cascaded (leaving aside blame for Henry Paulson's almost criminal chicken-little proclamations of doom to the world) is that many of these mortgage packages or securities got stuck in to highly leveraged portfolios. The insurance contracts that brought down AIG were structured differently but in the end were also highly leveraged bets on the values of mortgage securities in that small changes in values could result in huge losses or gains for the contracts. (Some folks have pointed to actual securitization of the loans as a problem. I don't see that. Securitization is a fabulous tool. Without it, we would be seeing a ton more main street bank failures, as they would have had to keep many more of these on their books.)
If this all sounds a bit like cause #1 above, ie buying inflated assets with more and more debt, then you are right. There is an interesting parallel that no one wants to delve into between the incentives of home buyers trying to jump into hot housing markets with interest-only loans and Wall Street bankers putting risky securities into highly leveraged portfolios. Leverage is really the key theme here. In a sense, houses were double-leveraged, bought the first time around with smaller and smaller down payments, and then leveraged again as these mortgages were tossed into highly-leveraged portfolios. Sometimes they were leveraged even further via oddball derivatives and insurance contracts whose exact operation are still opaque to many.
Those who have read me for a while know that I am in the "let them die" camp. These Wall Street guys have been living high on the extra profits from this leverage in the good times. They knew perfectly well that leverage is a two-edged sword, and that it would magnify their losses in a bad time. But their hubris pushed them into doing crazy things for more profit, and I am all for a Greek-tragedy-like downfall for their hubris. The sub-prime, first-time home buyer can claim ignorance or unsophistication, but not these guys.
During the Bush Administration, these bankers came to the SEC trumpeting their own brilliance, and begged to be allowed to leverage themselves even more via a relaxation of capital requirement rules. And, in 2004, without too much discussion or scrutiny, the SEC gave them what they wanted:
Many events in Washington, on Wall Street and elsewhere around the country have led to what has been called the most serious financial crisis
since the 1930s. But decisions made at a brief meeting on April 28,
2004, explain why the problems could spin out of control. The agency's
failure to follow through on those decisions also explains why
Washington regulators did not see what was coming.
On that
bright spring afternoon, the five members of the Securities and
Exchange Commission met in a basement hearing room to consider an
urgent plea by the big investment banks.
They wanted an
exemption for their brokerage units from an old regulation that limited
the amount of debt they could take on. The exemption would unshackle
billions of dollars held in reserve as a cushion against losses on
their investments. Those funds could then flow up to the parent
company, enabling it to invest in the fast-growing but opaque world of
mortgage-backed securities; credit derivatives, a form of insurance for
bond holders; and other exotic instruments.
In part they traded capital requirements for computer models, a very dubious decision in the first place, made worse by the fact that most of the banks were gaming the models to reduce the apparent risk. The crazy thing is that, in gaming the models, they really weren't trying to fool regulators, who pretty much were not watching anyway, but they were fooling themselves! Certainly I would not expect government regulators to do a better job of risk assessment in this environment, which argues for a return to the old bright-line capital requirements that are fairly simple to monitor. Investment banks played a game of Russian Roulette, and eventually blew their own brains out. Which begs the question of whether the government's job is to protect consumers at large or to protect financial institutions from themselves.
"We foolishly believed that the firms had a strong culture of
self-preservation and responsibility and would have the discipline not
to be excessively borrowing," said Professor James D. Cox, an expert on
securities law and accounting at Duke School of Law (and no
relationship to Christopher Cox).
The Dog that Didn't Bark: Ratings Agencies
Clearly, ratings agencies have really failed in their mission during this fiasco. Right up to the last minute, they were giving top ratings to highly risky securities. But I think folks who want to lay primary blame on the rating agencies go to far. Ratings agencies are for individuals and state pension funds and the like -- I have a hard time imagining Goldman or Lehman depending on them for risk assessment. Its a nice excuse, and we may well have very different companies rating securities five years form now, but its just a small contributor.
The Fix
So you see what is going on. Republicans are running around saying "the government caused it with the CRA" and Democrats are saying "it was greed and deregulation." Incredibly, both parties seem to come to the conclusion that sickly mortgage securities need to be pulled out of the hands of the folks who created and bought them and put in ... my hands. I had smugly thought that I had avoided buying a home with zero-down at the peak of the market, but I was wrong. Via the federal government, I have bought a lot of them!
I personally would let the whole thing sort itself out, and live with the consequences. My hypothesis is that much of the current credit squeeze in the money markets is due to Henry Paulson's clumsy public statements and the Fed's busting open the door to overnight borrowing. Everyone is frozen not by the crisis, but by the prospect of some sort of government action. Short term borrowers and lenders are doing their business with the Fed, as the government crowds out the private short term markets and causes the very problem it is trying to prevent.
Without the government bending over backwards to take in short term money from lenders, private firms would be forced to find private options. Lenders have to lend to stay alive financially, just as much as borrowers have to borrow. Money may go into the mattresses for a week or two or three, but it can't stay there forever.
I do know that the fix is NOT.
Fixing these financial problems listed above does not include:
Sec. 101. Renewable energy credit.
Sec. 102. Production credit for electricity produced from marine renewables.
Sec. 103. Energy credit.
Sec. 104. Energy credit for small wind property.
Sec. 105. Energy credit for geothermal heat pump systems.
Sec. 106. Credit for residential energy efficient property.
Sec. 107. New clean renewable energy bonds.
Sec. 108. Credit for steel industry fuel.
Sec. 109. Special rule to implement FERC and State electric restructuring policy.
Sec. 111. Expansion and modification of advanced coal project investment credit.
Sec. 112. Expansion and modification of coal gasification investment credit.
Sec. 113. Temporary increase in coal excise tax; funding of Black Lung Disability
Trust Fund.
Sec. 114. Special rules for refund of the coal excise tax to certain coal producers
and exporters.
Sec. 115. Tax credit for carbon dioxide sequestration.
Sec. 116. Certain income and gains relating to industrial source carbon
dioxide treated as qualifying income for publicly traded partnerships.
Sec. 117. Carbon audit of the tax code. Sec. 111. Expansion and modification of advanced coal project investment credit. Sec. 113. Temporary increase in coal excise tax; funding of Black Lung Disability Trust Fund. Sec. 115. Tax credit for carbon dioxide sequestration. Sec. 205. Credit for new qualified plug-in electric drive motor vehicles. Sec. 405. Increase and extension of Oil Spill Liability Trust Fund tax.Sec. 306. Accelerated recovery period for depreciation of smart meters and
smart grid systems. Sec. 309. Extension of economic development credit for American Samoa. Sec. 317. Seven-year cost recovery period for motorsports racing track facility. Sec. 501. $8,500 income threshold used to calculate refundable portion of child tax credit.
And, of course, the big one:
Sec. 503 Exemption from excise tax for certain wooden arrows designed for use by children.
All of these, however, are part of the bailout bill approved by the Senate. Sources here and here.