The Three Bubbles
If I asked you what three major American consumer products saw the largest steady price rises in the last decade (as opposed to price volatility, as we see in commodities like gasoline) one might well answer "housing, medical care, and college tuition."
Two or more of each of these share a number of features in common
- Long, sustained government programs to increase access / ownership / usage
- Substantial portion of pricing paid by third parties.
- Easy to obtain, government subsidized debt financing.
The housing bubble has of course burst. Obamacare, by further disconnecting individual use from the true costs of the services, will likely push health care costs ever higher. And then there is the college bubble. I am a bit late on this, but this is truly a remarkable chart:
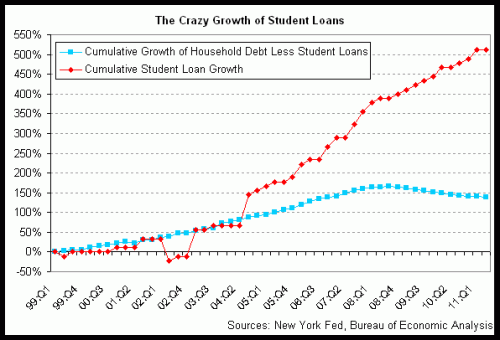
I have already heard the leftish talking point on this, which is that this increase in debt is the fault of (surprise!) private lenders and loan originators. This is a similar argument to the one made in the mortgage bubble, arguing that all the bad loans are the results of unscrupulous private originators and securities packagers.
And certainly there were many private companies originating awful mortgages and selling them to Fannie and Freddie. But what we forget in hindsight is that the government was begging for them to do so. Fannie and Freddie had active programs where they were encouraging mortgages with Loan-to-value of 97% or more. This kind of leverage is absurd, particularly for American-style no-recourse home mortgages. Sure, it was crazy to write them, but they were getting written only because the government was asking for them to be written and buying them all up.
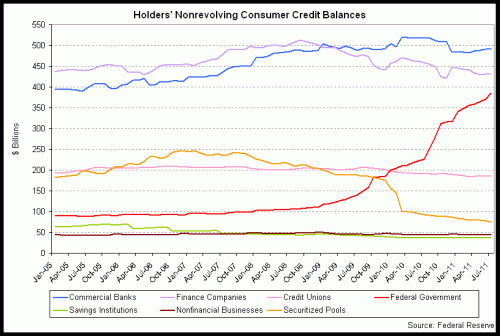
In fact, in student loans, almost all of this loan growth is eagerly being underwritten by the Feds, not by private lenders. Note the only consumer credit line really growing below is the "federal government" line (in red), which is primarily being driven by federally backed student loans.
One might argue that this is once again due to private originators going crazy. But the Feds took over origination of all federal student loans in 2010. You can see that much of the growth has occurred after the Feds took over origination. In fact, I think most of us can understand that when the origination decision is shifted from being a business decision to a political decision, student lending standards are certainly not going to get tougher. We can see that in home lending, where Fannie and Freddie have already returned to most of their worst pre-crash origination standards (here is an example of government promotion of these low down payment programs).
The other day my mother-in-law argued that the student lending business (particularly private lenders) needed reform because some students were being charged exorbitant rates. Having not been in the market for student loans lately, I wondered if this were the case. But the first thing that caught my eye was this stat: The 2-year default rate (not lifetime, but just in the first 2 years) of student loans was 8.8% last year, and 12% if one looks at the first 3 years. Compare that to credit card default rates which are around 6%. And recognized that these are apples and oranges, the student loan numbers actually understate lifetime default rates.
Based on that, the interest rate on student loans should be in the twenties. Against this backdrop, the rates I see online seem like a screaming deal. Probably too good of a deal. Which is why so many people are piling into these loans on the explicit promise society has made to them that their college degree will pay off, no matter what the cost.
Beyond the absurd price increases in both public and private education, here is the 900 pound gorilla in the room -- some majors are simply more valuable than others. A computer programming grad is going to have a lot more earning potential than the average poetry or gender studies major.
What we really need is tiered lending standards based on a student's major. Banks don't treat the earning potential of a dog-grooming business and a steel mill the same, why treat a mechanical engineering degree the same as a sociology degree? But, of course, this is never, ever going to happen.
Years ago I had these thoughts along this line, in response to a Michelle Obama rant about the cost of education
This analogy comes to mind: Let’s say Fred needs to buy a piece of earth-moving equipment. He has the choice of the $20,000 front-end loader that is more than sufficient to most every day tasks, or the $200,000 behemoth, which might be useful if one were opening a strip mine or building a new Panama Canal but is an overkill for many applications. Fred may lust after the huge monster earth mover, but if he is going to buy it, he better damn well have a big, profitable application for it or he is going to go bankrupt trying to buy it.
So Michelle Obama has a choice of the $20,000 state school undergrad and law degree, which is perfectly serviceable for most applications, or the Princeton/Harvard $200,000 combo, which I can attest will, in the right applications, move a hell of a lot of dirt. She chooses the $200,000 tool, and then later asks for sympathy because all she ever did with it was some backyard gardening and she wonders why she has trouble paying all her debt. Duh. I think the problem here is perfectly obvious to most of us, but instead Obama seeks to blame her problem on some structural flaw in the economy, rather than a poor choice on her part in matching the tool to the job. In fact, today, she spends a lot of her time going to others who have bought similar $200,000 educations and urging them not to use those tools productively, just like she did not.
Postscript: Kids who find they cannot pay their student debts and think bank home foreclosures are the worst thing in the world are in for a rude surprise -- home mortgage default consequences are positively light in this country. The worst that happens is that you lose the home and take a ding on your credit record. Student debt follows you for life, with wage garnishments and asset losses. People walk away from home debt all the time, the same is not true of student debt.