Happy Birthday Leonhard Euler
Yesterday was apparently the 300th birthday of Leonhard Euler, one of the greatest mathematicians of all time and perhaps the greatest that the average layman has never heard of.
Euler is responsible for so much that is still important to modern mathematics it is hard to pin down his greatest achievement, but most will point to his famous equation that was sort of the unified field theory of mathematics, describing a relationship between all five of math's most important numbers:
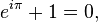
- I learned something the other day that might be interesting to you business and finance folks out there -- the constant "e" was first described by Jacob Bernoulli when he was studying compound interest rates.
-
Jacob Bernoulli discovered this constant by studying a question about compound interest.
One simple example is an account that starts with $1.00 and pays
100% interest per year. If the interest is credited once, at the end of
the year, the value is $2.00; but if the interest is computed and added
twice in the year, the $1 is multiplied by 1.5 twice, yielding $1.00×1.52 = $2.25. Compounding quarterly yields $1.00×1.254 = $2.4414"¦, and compounding monthly yields $1.00×(1.0833"¦)12 = $2.613035"¦.Bernoulli noticed that this sequence approaches a limit for more and
smaller compounding intervals. Compounding weekly yields $2.692597"¦,
while compounding daily yields $2.714567"¦, just two cents more. Using n as the number of compounding intervals, with interest of 1/n in each interval, the limit for large n is the number that came to be known as e; with continuous compounding, the account value will reach $2.7182818"¦. More generally, an account that starts at $1, and yields $(1+R) at simple interest, will yield $"‰eR with continuous compounding. - In the 20th century, we have gotten in a mind set that math is this strange discipline that lives purely out in the theoretical either. But we forget that a lot of modern math was invented to solve real-world problems. Newton invented calculus (yeah, I know, I haven't forgotten Liebnitz) to solve planetary motion problems, and it turns out "e" was invented to work with interest rates.